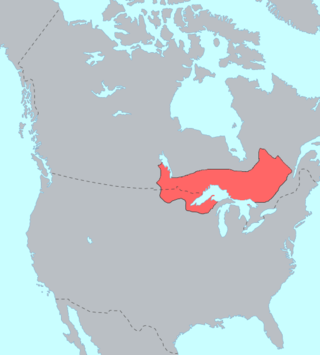
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains. They are Indigenous peoples of the Subarctic and Northeastern Woodlands.
The Wisconsin Walleye War became the name for late 20th-century events in Wisconsin in protest of Ojibwe (Chippewa) hunting and fishing rights. In a 1975 case, the tribes challenged state efforts to regulate their hunting and fishing off the reservations, based on their rights in the treaties of St. Peters (1837) and La Pointe (1842). On August 21, 1987, U.S. District Court judge Barbara Crabb ruled that six Ojibwe tribal governments had the right under these treaties for hunting and fishing throughout their former territory.

The L'Anse Indian Reservation is the land base of the federally recognized Keweenaw Bay Indian Community of the historic Lake Superior Band of Chippewa Indians.. The reservation is located primarily in two non-contiguous sections on either side of the Keweenaw Bay in Baraga County in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. The Keweenaw Bay Community also manages the separate Ontonagon Indian Reservation.


The Bad River LaPointe Band of the Lake Superior Tribe of Chippewa Indians or Bad River Tribe for short are a federally recognized tribe of Ojibwe people. The tribe had 6,945 members as of 2010. The Bad River Reservation is located on the south shore of Lake Superior and has a land area of about 193.11 square miles (500.15 km2) in northern Wisconsin, straddling Ashland and Iron counties. Odanah, the administrative and cultural center, is located five miles (8.0 km) east of the town of Ashland on U.S. Highway 2. The reservation population was 1,545 in 2020. Most of the reservation is managed as undeveloped forest and wetland, providing a habitat for wild rice and other natural resources.

The Fond du Lac Indian Reservation is an Indian reservation in northern Minnesota near Cloquet in Carlton and Saint Louis counties. Off-reservation holdings are located across the state in Douglas County, in the northwest corner of Wisconsin. The total land area of these tribal lands is 154.49 square miles (400.1 km2). It is the land-base for the Fond du Lac Band of Lake Superior Chippewa. Before the establishment of this reservation, the Fond du Lac Band of Lake Superior Chippewa were located at the head of Lake Superior, closer to the mouth of the Saint Louis River, where Duluth has developed.
The St. Croix Chippewa Indians are a historical Band of Ojibwe located along the St. Croix River, which forms the boundary between the U.S. states of Wisconsin and Minnesota. The majority of the St. Croix Band are divided into two groups: the federally recognized St. Croix Chippewa Indians of Wisconsin, and the St. Croix Chippewa Indians of Minnesota, who are one of four constituent members forming the federally recognized Mille Lacs Band of Ojibwe. The latter is one of six bands in the federally recognized Minnesota Chippewa Tribe.

The Mille Lacs Indians, also known as the Mille Lacs and Snake River Band of Chippewa, are a Band of Indians formed from the unification of the Mille Lacs Band of Mississippi Chippewa (Ojibwe) with the Mille Lacs Band of Mdewakanton Sioux (Dakota). Today, their successor apparent Mille Lacs Band of Ojibwe consider themselves as being Ojibwe, but many on their main reservation have the ma'iingan (wolf) as their chief doodem (clan), which is an indicator of Dakota origins.

The Treaty of La Pointe may refer to either of two treaties made and signed in La Pointe, Wisconsin between the United States and the Ojibwe (Chippewa) Native American peoples. In addition, the Isle Royale Agreement, an adhesion to the first Treaty of La Pointe, was made at La Pointe.
Mississippi River Band of Chippewa Indians or simply the Mississippi Chippewa, are a historical Ojibwa Band inhabiting the headwaters of the Mississippi River and its tributaries in present-day Minnesota.

Chief Buffalo was a major Ojibwa leader, born at La Pointe in Lake Superior's Apostle Islands, in what is now northern Wisconsin, USA.

The Sandy Lake Tragedy was the culmination in 1850 of a series of events centered in Big Sandy Lake, Minnesota that resulted in the deaths of several hundred Lake Superior Chippewa. Officials of the Zachary Taylor Administration and Minnesota Territory sought to relocate several bands of the tribe to areas west of the Mississippi River. By changing the location for fall annuity payments, the officials intended the Chippewa to stay at the new site for the winter, hoping to lower their resistance to relocation. Due to delayed and inadequate payments of annuities and lack of promised supplies, about 400 Ojibwe, mostly men and 12% of the tribe, died of disease, starvation and cold. The outrage increased Ojibwe resistance to removal. The bands effectively gained widespread public support to achieve permanent reservations in their traditional territories.
The Lake Superior Chippewa are a large number of Ojibwe (Anishinaabe) bands living around Lake Superior; this territory is considered part of northern Michigan, Wisconsin, and Minnesota in the United States. They migrated into the area by the seventeenth century, encroaching on the Eastern Dakota people who had historically occupied the area. The Ojibwe defeated the Eastern Dakota, who migrated west into the Great Plains after the final battle in 1745. While they share a common culture including the Anishinaabe language, this highly decentralized group of Ojibwe includes at least twelve independent bands in the region.

Lac Vieux Desert Band of Lake Superior Chippewa is a band of the Lake Superior Chippewa, many of whom reside on the Lac Vieux Desert Indian Reservation, located near Watersmeet, Michigan. It is approximately 45 miles southeast of Ironwood, Michigan in Gogebic County.
Lake Lena is an unincorporated community and Native American village in Ogema Township, Pine County, Minnesota, United States, located along the Lower Tamarack River. It currently is the administrative center for the Mille Lacs Indian Reservation, District III.
A Tribal Political Organization is a political tribal council advocating the political interests of the First Nations and Tribes of their constituency. This list focuses on the TPOs to which the various Anishinaabe nations belong.
Treaty of St. Peters may be one of two treaties conducted between the United States and Native American peoples, conducted at the confluence of the Minnesota River with the Mississippi River, in what today is Mendota, Minnesota.
The 1854 Treaty Authority is an intertribal, co-management agency committed to the implementation of off-reservation treaty rights on behalf of its two-member Ojibwa tribes.
The Harvard Project on American Indian Economic Development, also known as the Harvard Project, was founded in 1987 at Harvard Kennedy School at Harvard University. It administers tribal awards programs as well as provides support for students and conducting research. The Harvard Project aims to understand and foster the conditions under which sustained, self-determined social and economic development is achieved among American Indian nations through applied research and service.









