
BNSF Railway is the largest freight railroad in the United States. One of six North American Class I railroads, BNSF has 35,000 employees, 32,500 miles (52,300 km) of track in 28 states, and nearly 8,000 locomotives. It has three transcontinental routes that provide rail connections between the western and eastern United States. BNSF trains traveled over 169 million miles in 2010, more than any other North American railroad.

The Northstar Line is a commuter rail route in the US state of Minnesota. Northstar runs 40 miles (64 km) from Big Lake to downtown Minneapolis at Target Field using existing track and right-of-way owned by the BNSF Railway. Passenger service began on November 16, 2009. The rail line serves part of the Northstar Corridor between Minneapolis and St. Cloud. Planning for the line began in 1997 when the Northstar Corridor Development Authority (NCDA) was formed. The corridor is also served by Interstate 94 and U.S. Highway 10. In 2022, the system had a ridership of 77,100, or about 300 per weekday as of the first quarter of 2023.

Milwaukee Road 261 is a class "S3" 4-8-4 "Northern" type steam locomotive built by the American Locomotive Company (ALCO) in Schenectady, New York in July 1944 for the Milwaukee Road.

Saint Paul Union Depot is a historic railroad station and intermodal transit hub in the Lowertown neighborhood of the city of Saint Paul, Minnesota, United States. It serves light rail, intercity rail, intercity bus, and local bus services.

The Soo Line Railroad is one of the primary United States railroad subsidiaries for the CPKC Railway, one of six U.S. Class I railroads, controlled through the Soo Line Corporation. Although it is named for the Minneapolis, St. Paul and Sault Ste. Marie Railroad (MStP&SSM), which was commonly known as the Soo Line after the phonetic spelling of Sault, it was formed in 1961 by the consolidation of that company with two other CPKC subsidiaries: The Duluth, South Shore and Atlantic Railway, and the Wisconsin Central Railway. It is also the successor to other Class I railroads, including the Minneapolis, Northfield and Southern Railway and the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad. On the other hand, a large amount of mileage was spun off in 1987 to Wisconsin Central Ltd., now part of the Canadian National Railway. The Soo Line Railroad and the Delaware and Hudson Railway, CPKC's other major subsidiary, presently do business as the Canadian Pacific Railway (CP). Most equipment has been repainted into the CP scheme, but the U.S. Surface Transportation Board groups all of the company's U.S. subsidiaries under the Soo Line name for reporting purposes. The Minneapolis headquarters are located in the Canadian Pacific Plaza building, having moved from the nearby Soo Line Building.

Soo Line 2719 is a 4-6-2 "Pacific" type steam locomotive built by the American Locomotive Company (ALCO) for use on passenger trains operated by the Minneapolis, St. Paul and Sault Ste. Marie Railway. No. 2719 was used to haul the Soo Line's last steam-powered train, a June 21, 1959 round-trip excursion between Minneapolis, Minnesota and Ladysmith, Wisconsin. It was then displayed in Eau Claire, Wisconsin until 1996. It was restored and operated in excursion service from 1998 until 2013 when its boiler certificate expired. Today, the locomotive remains on static display in Duluth, Minnesota.
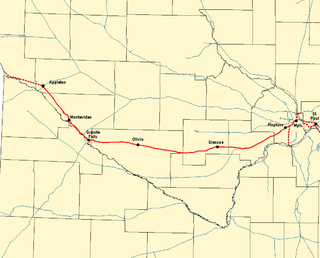
The Twin Cities and Western Railroad is a railroad operating in the U.S. state of Minnesota which started operations on July 27, 1991. Trackage includes the former Soo Line Railroad "Ortonville Line", originally built as the first part of the Pacific extension of the Milwaukee Road. This main line extends from Hopkins, Minnesota ,to Appleton, Minnesota. The line was originally built between Hopkins and Cologne, Minnesota, in 1876 by Hastings and Dakota Railroad. In 1913, the Milwaukee Road rerouted it, reducing the curves. The line was eventually extended to the Pacific.

The St. Croix Valley Railroad is a Class III short line railroad that operates over 36 miles of track in eastern Minnesota. The railroad is owned by KBN Incorporated jointly between Independent Locomotive Service of Bethel MN and Midwest Locomotive Services of Atwater MN, with the railroad headquartered in Rush City, Minnesota.
There are several passenger rail projects being discussed in Minnesota. There is one existing commuter rail service in the state, the Northstar Line, and one existing long-distance intercity rail service, the Empire Builder. Future projects include a mixture of short-distance commuter rail and medium-distance regional rail lines which would run from the Twin Cities outward to neighboring states and perhaps Canada.
The Northern Lights Express (NLX) is a planned higher-speed rail service that would run 155 miles (249 km) between Minneapolis and Duluth primarily in the U.S. state of Minnesota. A portion of the proposed line would run through neighboring Wisconsin to serve Duluth's "Twin Port" of Superior. Plans are to upgrade an existing BNSF Railway freight line to allow trains to travel at up to 90 miles per hour (145 km/h). The train service is said to provide an alternative to traveling Interstate 35 between Duluth and the Twin Cities or to other destinations along the line such as the casino in Hinckley.

The Escanaba & Lake Superior Railroad is a Class III shortline railroad that operates 347 miles (558 km) of track in Northeastern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan. Its main line runs 208 miles (335 km) from Rockland, Michigan, to Green Bay, Wisconsin, and it also owns various branch lines and out-of-service track. In 1897, the Escanaba River Company built a seven-mile (11 km) railroad from Wells, Michigan, to tap a large hardwood timber stand at LaFave’s Hill. In 1898, the company name was changed to the Escanaba & Lake Superior Railway (E&LS).

Fridley station is a commuter rail station in Fridley, Minnesota, located at Main Street NE and 61st Avenue NE. It is served by the Northstar Commuter Rail line. The station features bicycle lockers and two park and ride lots with a total capacity of 611 spaces. The commute time to downtown Minneapolis from this station is about 20 minutes. The station has a single platform on one main track, which is accessible on either side of the tracks through a tunnel.
The Aurora Subdivision or Aurora Sub is a railway line in Wisconsin and Illinois operated by BNSF Railway. It is part of BNSF's Chicago, Illinois, to Seattle, Washington, Northern Transcon. This segment runs about 262 miles (422 km) from the St. Croix Subdivision in La Crosse, Wisconsin, to the Chicago Subdivision in Aurora, Illinois.

The Staples Subdivision or Staples Sub is a railway line running about 227 miles (365 km) from Dilworth to Fridley, Minnesota. It is operated by BNSF Railway as part of their Northern Transcon and contains the busiest segment of mainline track in the state, the segment between Coon Rapids and Fridley. As of 2015, most of the route hosted an average of 60 trains per day, and there were 80 trains per day near Fridley. As of April 2022, the Staples Sub sees about 30-40 trains a day and it’s starting to rise to be more trains again on the line. The line meets the KO Subdivision in the west at East Dilworth, and runs to Interstate in Fridley, at the limits of Northtown Yard. Beyond Northtown, the rails continue as the Midway Subdivision and St. Paul Subdivision. U.S. Highway 10 closely follows the rail line for a majority of the distance between Dilworth and Fridley, Minnesota.
Coon Rapids–Foley Boulevard is a planned infill station on the Northstar commuter rail line in Coon Rapids, Minnesota, United States, at the site of a current Metro Transit park and ride facility. The station was originally included in Northstar plans, but it was cut in order to meet the Federal Transit Administration's cost-effectiveness index (CEI).
The St. Paul Subdivision or St. Paul Sub is a 30.9-mile (49.7 km) railway line running within the state of Minnesota. The line originates in Minneapolis and continues through neighboring Saint Paul, Minnesota and on into Saint Paul's southeastern suburbs along the Mississippi River. It is a segment of BNSF Railway's Northern Transcon which runs from Chicago, Illinois to Seattle, Washington. Between Minneapolis and Saint Paul themselves, this route runs on former Northern Pacific Railway trackage, and forms the northern set of BNSF tracks running through the Twin Cities. The companion route running slightly to the south is the Midway Subdivision, though the St. Paul Subdivision is the busier set of tracks, hosting about 59 trains per day as of April 2009. It is the second-busiest rail line in the state, after the segment of the Staples Subdivision between Fridley and Coon Rapids.
The Midway Subdivision or Midway Sub is a 12.4-mile (20.0 km) railway line in Minneapolis and Saint Paul, Minnesota. The line is part of BNSF Railway's Northern Transcon which runs from Chicago, Illinois to Seattle, Washington and Portland, Oregon. This is former Great Northern Railway trackage, and now forms the southern set of BNSF tracks running through the Twin Cities. The companion route running slightly to the north is the St. Paul Subdivision, former Northern Pacific Railway tracks. The Midway Subdivision hosts about 24 trains per day as of September 2015.
The Monticello Subdivision or Monticello Sub is a railway branch line that runs from the Wayzata Subdivision in Minneapolis to Monticello, Minnesota. Formerly operated by the Great Northern Railway and then Burlington Northern, it is now operated by BNSF Railway. It largely runs parallel to Broadway and Hennepin County Road 81 from Minneapolis to Rogers, and then Interstate 94 from Rogers to Monticello. Rails formerly continued on from today's Monticello Subdivision farther to the northwest along today's I-94 corridor all the way to Moorhead, Minnesota. It had been used for passenger service, such as with the Alexandrian.
The Lakes Subdivision or Lakes Sub is a railway line operated by BNSF Railway that runs about 157 miles (253 km) from the Grand Forks Subdivision at Cass Lake, Minnesota, to Superior, Wisconsin, where there are a number of lines. U.S. Highway 2 runs parallel to the line for most of its route. U.S. 2 continues across the St. Louis River east of Brookston, while the rail line stays on the southern bank of the river. Prior to the creation of BNSF, the line was operated by the Burlington Northern Railroad as part of their Lake Superior Division. Today, it is operated by BNSF's Twin Cities Division.

The Altoona Subdivision or Altoona Sub is a 90.7-mile (146.0 km) railway line owned and operated by the Union Pacific Railroad in the states of Minnesota and Wisconsin. The line originates in Saint Paul, Minnesota, crosses the St. Croix River on the Hudson Bridge into Hudson, Wisconsin, and eventually terminates in Altoona, Wisconsin where it connects to the Wyeville Subdivision. This subdivision is formerly a Chicago and North Western Railway (C&NW) mainline, on which the Twin Cities 400 operated in the mid 1900s.












