The Internet protocol suite, commonly known as TCP/IP, is the set of communications protocols used in the Internet and similar computer networks. The current foundational protocols in the suite are the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP).

Small Computer System Interface is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. The SCSI standard defines command sets for specific peripheral device types; the presence of "unknown" as one of these types means that in theory it can be used as an interface to almost any device, but the standard is highly pragmatic and addressed toward commercial requirements. The initial Parallel SCSI was most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and CD drives, although not all controllers can handle all devices.
In computing, iSCSI is an acronym for Internet Small Computer Systems Interface, an Internet Protocol (IP)-based storage networking standard for linking data storage facilities. iSCSI provides block-level access to storage devices by carrying SCSI commands over a TCP/IP network. iSCSI facilitates data transfers over intranets and to manage storage over long distances. It can be used to transmit data over local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), or the Internet and can enable location-independent data storage and retrieval.
Fibre Channel (FC) is a high-speed data transfer protocol providing in-order, lossless delivery of raw block data. Fibre Channel is primarily used to connect computer data storage to servers in storage area networks (SAN) in commercial data centers.

In computer networking, the transport layer is a conceptual division of methods in the layered architecture of protocols in the network stack in the Internet protocol suite and the OSI model. The protocols of this layer provide end-to-end communication services for applications. It provides services such as connection-oriented communication, reliability, flow control, and multiplexing.

In computer hardware, a host controller, host adapter, or host bus adapter (HBA), connects a computer, which acts as the host system, to other network and storage devices. The terms are primarily used to refer to devices for connecting SCSI, Fibre Channel and SATA devices. Devices for connecting to IDE, Ethernet, FireWire, USB and other systems may also be called host adapters.
In computing, the proposed Internet Storage Name Service (iSNS) protocol allows automated discovery, management and configuration of iSCSI and Fibre Channel devices on a TCP/IP network.

In computing, Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) is a point-to-point serial protocol that moves data to and from computer-storage devices such as hard disk drives and tape drives. SAS replaces the older Parallel SCSI bus technology that first appeared in the mid-1980s. SAS, like its predecessor, uses the standard SCSI command set. SAS offers optional compatibility with Serial ATA (SATA), versions 2 and later. This allows the connection of SATA drives to most SAS backplanes or controllers. The reverse, connecting SAS drives to SATA backplanes, is not possible.
ATA over Ethernet (AoE) is a network protocol developed by the Brantley Coile Company, designed for simple, high-performance access of block storage devices over Ethernet networks. It is used to build storage area networks (SANs) with low-cost, standard technologies.
Brocade is an American technology company specializing in storage networking products, now a subsidiary of Broadcom Inc. The company is known for its Fibre Channel storage networking products and technology. Prior to the acquisition, the company expanded into adjacent markets including a wide range of IP/Ethernet hardware and software products. Offerings included routers and network switches for data center, campus and carrier environments, IP storage network fabrics; Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) and software-defined networking (SDN) markets such as a commercial edition of the OpenDaylight Project controller; and network management software that spans physical and virtual devices.
IPFC stands for Internet Protocol over Fibre Channel. It governs a set of standards created in January 2006 for address resolution (ARP) and transmitting IPv4 and IPv6 network packets over a Fibre Channel (FC) network. IPFC makes up part of the FC-4 protocol-mapping layer of a Fibre Channel system.
HyperSCSI is an outdated computer network protocol for accessing storage by sending and receiving SCSI commands. It was developed by researchers at the Data Storage Institute in Singapore in 2000 to 2003. HyperSCSI is unlike iSCSI in that it bypassed the internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) and works directly over Ethernet to form its storage area network (SAN). It skipped the routing, retransmission, segmentation, reassembly, and all the other problems that the TCP/IP suite addresses. Compared to iSCSI, this was meant to give a performance benefit at the cost of IP's flexibility. An independent performance test showed that performance was unstable with network congestion. Since HyperSCSI was in direct competition with the older and well established Fibre Channel, and the standardized iSCSI, it was not adopted by commercial vendors. Some researchers at Huazhong University of Science and Technology noted the failure to provide any transport layer protocol, so implemented a reliability layer in 2007. Another version called HS/IP was developed over the Internet Protocol (IP).
Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) is the SCSI interface protocol utilising an underlying Fibre Channel connection. The Fibre Channel standards define a high-speed data transfer mechanism that can be used to connect workstations, mainframes, supercomputers, storage devices and displays. FCP addresses the need for very fast transfers of large volumes of information and could relieve system manufacturers from the burden of supporting a variety of channels and networks, as it provides one standard for networking, storage and data transfer. Some Fibre Channel characteristics are:
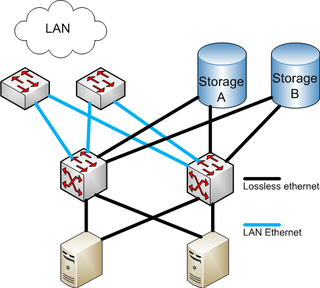
Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) is a computer network technology that encapsulates Fibre Channel frames over Ethernet networks. This allows Fibre Channel to use 10 Gigabit Ethernet networks while preserving the Fibre Channel protocol. The specification was part of the International Committee for Information Technology Standards T11 FC-BB-5 standard published in 2009.

A storage area network (SAN) or storage network is a computer network which provides access to consolidated, block-level data storage. SANs are primarily used to access data storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries from servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as direct-attached storage. A SAN typically is a dedicated network of storage devices not accessible through the local area network (LAN).
Data center bridging (DCB) is a set of enhancements to the Ethernet local area network communication protocol for use in data center environments, in particular for use with clustering and storage area networks.
Fibre Channel over IP is an Internet Protocol (IP) created by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) for storage technology.

In computing, Linux-IO (LIO) Target is an open-source implementation of the SCSI target that has become the standard one included in the Linux kernel. Internally, LIO does not initiate sessions, but instead provides one or more Logical Unit Numbers (LUNs), waits for SCSI commands from a SCSI initiator, and performs required input/output data transfers. LIO supports common storage fabrics, including FCoE, Fibre Channel, IEEE 1394, iSCSI, iSCSI Extensions for RDMA (iSER), SCSI RDMA Protocol (SRP) and USB. It is included in most Linux distributions; native support for LIO in QEMU/KVM, libvirt, and OpenStack makes LIO also a storage option for cloud deployments.
Storage security is a specialty area of security that is concerned with securing data storage systems and ecosystems and the data that resides on these systems.






