
Latin is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition.
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. Adding it to the beginning of one word changes it into another word. For example, when the prefix un- is added to the word happy, it creates the word unhappy. Particularly in the study of languages, a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the words to which it is affixed.
A noun is a word that generally functions as the name of a specific object or set of objects, such as living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, or ideas.
International scientific vocabulary (ISV) comprises scientific and specialized words whose language of origin may or may not be certain, but which are in current use in several modern languages.
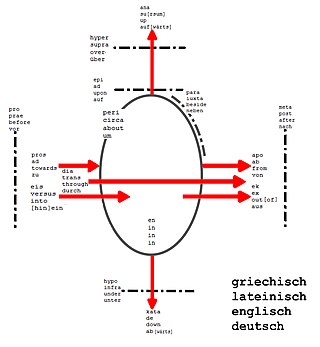
Prepositions and postpositions, together called adpositions, are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations or mark various semantic roles.

The following are lists of words in the English language that are known as "loanwords" or "borrowings," which are derived from other languages.
The Greek language has contributed to the English lexicon in five main ways:
Although English is a Germanic language, it has Latin influences. Its grammar and core vocabulary are inherited from Proto-Germanic, but a significant portion of the English vocabulary comes from Romance and Latinate sources. A portion of these borrowings come directly from Latin, or through one of the Romance languages, particularly Anglo-Norman and French, but some also from Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish; or from other languages into Latin and then into English. The influence of Latin in English, therefore, is primarily lexical in nature, being confined mainly to words derived from Latin and Greek roots.
Numeral or number prefixes are prefixes derived from numerals or occasionally other numbers. In English and many other languages, they are used to coin numerous series of words. For example:
Neoclassical compounds are compound words composed from combining forms derived from classical Latin or ancient Greek roots. New Latin comprises many such words and is a substantial component of the technical and scientific lexicon of English and other languages, via international scientific vocabulary (ISV). For example, bio- combines with -graphy to form biography.
In Indo-European studies, the term s-mobile designates the phenomenon where a PIE root appears to begin with an *s- which is sometimes but not always present. It is therefore represented in the reflex of the root in some attested derivatives but not others. The fact that there is no consistency about which language groups retain the s-mobile in individual cases is good evidence that it is an original Indo-European phenomenon, and not an element added or lost in the later history of particular languages.
The prefix ped- in English and various other Western languages has multiple Latin and Ancient Greek roots, and multiple meanings. Ped- is a prefix in English and many other Western languages, often with divergent spellings, such as pet-, pie-, pei-, etc.
Medical terminology is a language used to precisely describe the human body including all its components, processes, conditions affecting it, and procedures performed upon it. Medical terminology is used in the field of medicine
English prefixes are affixes that are added before either simple roots or complex bases consisting of (a) a root and other affixes, (b) multiple roots, or (c) multiple roots and other affixes. Examples of these follow:
Glosa is a constructed international auxiliary language based on Interglossa. The first Glosa dictionary was published 1978. The name of the language comes from the Greek root glossa meaning tongue or language.
Botanical Latin is a technical language based on New Latin, used for descriptions of botanical taxa. Until 2012, International Code of Botanical Nomenclature mandated Botanical Latin to be used for the descriptions of most new taxa. It is still the only language other than English accepted for descriptions. The names of organisms governed by the Code also have forms based on Latin.