
The traditional Chinese calendar (also known as the Agricultural Calendar [農曆; 农历; Nónglì; 'farming calendar'], Former Calendar [舊曆; 旧历; Jiùlì], Traditional Calendar [老曆; 老历; Lǎolì], is a lunisolar calendar which identifies years, months, and days according to astronomical phenomena. In China, it is defined by the Chinese national standard GB/T 33661–2017, "Calculation and Promulgation of the Chinese Calendar", issued by the Standardization Administration of China on May 12, 2017.
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun crosses the Earth's equator, which is to say, appears directly above the equator. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise "due east" and set "due west". This occurs twice each year, around 20 March and 23 September.

The Hebrew calendar, also called Jewish calendar, is a lunisolar calendar used today for Jewish religious observance, and as an official calendar of the state of Israel. It determines the dates for Jewish holidays and the appropriate public reading of Torah portions, yahrzeits, and daily Psalm readings, among many ceremonial uses. In Israel, it is used for religious purposes, provides a time frame for agriculture, and is an official calendar for civil holidays, alongside the Gregorian calendar.
The Julian calendar, proposed by Julius Caesar in AUC 708, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on 1 January AUC 709 , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandria.

A lunisolar calendar is a calendar in many cultures, combining lunar calendars and solar calendars. The date of Lunisolar calendars therefore indicates both the Moon phase and the time of the solar year, that is the position of the Sun in the Earth's sky. If the sidereal year is used instead of the solar year, then the calendar will predict the constellation near which the full moon may occur. As with all calendars which divide the year into months there is an additional requirement that the year have a whole number of months. In this case ordinary years consist of twelve months but every second or third year is an embolismic year, which adds a thirteenth intercalary, embolismic, or leap month.

The Metonic cycle or enneadecaeteris is a period of almost exactly 19 years after which the lunar phases recur at the same time of the year. The recurrence is not perfect, and by precise observation the Metonic cycle defined as 235 synodic months is just 2 hours, 4 minutes and 58 seconds longer than 19 tropical years. Meton of Athens, in the 5th century BC, judged the cycle to be a whole number of days, 6,940. Using these whole numbers facilitates the construction of a lunisolar calendar.

A year or annum is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked.

The Maya calendar is a system of calendars used in pre-Columbian Mesoamerica and in many modern communities in the Guatemalan highlands, Veracruz, Oaxaca and Chiapas, Mexico.
The heliacal rising or star rise of a star occurs annually, or the similar phenomenon of a planet, when it first becomes visible above the eastern horizon at dawn just before sunrise, after it has spent a season behind the sun rendering it invisible. Historically, the most important such rising is that of Sirius, which was an important feature of the Egyptian calendar and astronomical development. The rising of the Pleiades heralded the start of the Ancient Greek sailing season, using celestial navigation.

The Thai solar calendar was adopted by King Chulalongkorn in 1888 CE as the Siamese version of the Gregorian calendar, replacing the Thai lunar calendar as the legal calendar in Thailand. Years are now counted in the Buddhist Era (B.E.): พุทธศักราช, พ.ศ., which is 543 years ahead of the Gregorian calendar.

The ancient Egyptian calendar – a civil calendar – was a solar calendar with a 365-day year. The year consisted of three seasons of 120 days each, plus an intercalary month of five epagomenal days treated as outside of the year proper. Each season was divided into four months of 30 days. These twelve months were initially numbered within each season but came to also be known by the names of their principal festivals. Each month was divided into three 10-day periods known as decans or decades. It has been suggested that during the Nineteenth Dynasty and the Twentieth Dynasty the last two days of each decan were usually treated as a kind of weekend for the royal craftsmen, with royal artisans free from work.

As a moveable feast, the date of Easter is determined in each year through a calculation known as computus. Easter is celebrated on the first Sunday after the Paschal full moon, which is the first full moon on or after 21 March. Determining this date in advance requires a correlation between the lunar months and the solar year, while also accounting for the month, date, and weekday of the Julian or Gregorian calendar. The complexity of the algorithm arises because of the desire to associate the date of Easter with the date of the Jewish feast of Passover which, Christians believe, is when Jesus was crucified.
The Buddhist calendar is a set of lunisolar calendars primarily used in Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, and Thailand as well as in Malaysia, Singapore and Vietnam by Chinese populations for religious or official occasions. While the calendars share a common lineage, they also have minor but important variations such as intercalation schedules, month names and numbering, use of cycles, etc. In Thailand, the name Buddhist Era is a year numbering system shared by the traditional Thai lunisolar calendar and by the Thai solar calendar.
Citation of United Kingdom legislation includes the systems used for legislation passed by devolved parliaments and assemblies, for secondary legislation, and for prerogative instruments. It is relatively complex both due to the different sources of legislation in the United Kingdom, and because of the different histories of the constituent countries of the United Kingdom.
The ISO week date system is effectively a leap week calendar system that is part of the ISO 8601 date and time standard issued by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) since 1988 and, before that, it was defined in ISO (R) 2015 since 1971. It is used (mainly) in government and business for fiscal years, as well as in timekeeping. This was previously known as "Industrial date coding". The system specifies a week year atop the Gregorian calendar by defining a notation for ordinal weeks of the year.
A docket in the United States is the official summary of proceedings in a court of law. In the United Kingdom in modern times it is an official document relating to delivery of something, with similar meanings to these two elsewhere. In the late nineteenth century the term referred to a large folio book in which clerks recorded all filings and court proceedings for each case, although use has been documented since 1485.
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most of the world. It was introduced in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years differently so as to make the average calendar year 365.2425 days long, more closely approximating the 365.2422-day 'tropical' or 'solar' year that is determined by the Earth's revolution around the Sun. The rule for leap years is:
Every year that is exactly divisible by four is a leap year, except for years that are exactly divisible by 100, but these centurial years are leap years if they are exactly divisible by 400. For example, the years 1700, 1800, and 1900 are not leap years, but the years 1600 and 2000 are.
If the parties to a legal case anticipate that it will not take up a significant amount of time, they may apply for the court to designate it as a short cause. Cases on the "short cause" calendar will get priority since they will not tie up a courtroom for a long time.
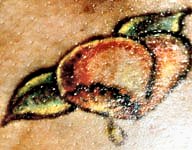
Peaches is an unidentified female whose torso was discovered on June 28, 1997, in Lakeview, New York, near Hempstead Lake State Park. The cause of the woman's death is listed as homicide, apparently by decapitation. As of 2022 she remains unidentified since her skull has yet to be found. The woman had a tattoo on her left breast depicting a heart-shaped peach with a bite taken out of it and two drops falling from its core, which resulted in her nickname. As of December 2016, additional skeletal remains found on Long Island in 2011 have been positively identified as belonging to Peaches, along with the remains of her child. As a result, Peaches is now linked to the Long Island serial killer as a potential victim.









