The United States Navy, United States Coast Guard, and United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) use a hull classification symbol to identify their ships by type and by individual ship within a type. The system is analogous to the pennant number system that the Royal Navy and other European and Commonwealth navies use.

Deep Submergence Vessel NR-1 was a unique United States Navy (USN) nuclear-powered ocean engineering and research submarine, built by the Electric Boat Division of General Dynamics at Groton, Connecticut. NR-1 was launched on 25 January 1969, completed initial sea trials 19 August 1969, and was home-ported at Naval Submarine Base New London. NR-1 was the smallest nuclear submarine ever put into operation. The vessel was casually known as "Nerwin" and was never officially named or commissioned. The U.S. Navy is allocated a specific number of warships by the U.S. Congress. Admiral Hyman Rickover avoided using one of those allocations, and he also wanted to avoid the oversight that a warship receives from various bureaus.

A naval ship is a military ship used by a navy. Naval ships are differentiated from civilian ships by construction and purpose. Generally, naval ships are damage resilient and armed with weapon systems, though armament on troop transports is light or non-existent.

A ship's tender, usually referred to as a tender, is a boat, or a larger ship used to service or support other boats or ships, generally by transporting people or supplies to and from shore or another ship. Smaller boats may also have tenders, usually called dinghies.
Underwater divers may be employed in any branch of an armed force, including the navy, army, marines, air force and coast guard. Scope of operations includes: Search and recovery, search and rescue, underwater surveys, explosive ordnance disposal, demolition, underwater engineering, salvage, ships husbandry, reconnaissance, infiltration, sabotage, counterifiltration, underwater combat and security.

The United States Navy's Military Sealift Command (MSC) is an organization that controls the replenishment and military transport ships of the Navy. Military Sealift Command has the responsibility for providing sealift and ocean transportation for all US military services as well as for other government agencies. It first came into existence on 9 July 1949 when the Military Sea Transportation Service (MSTS) became solely responsible for the Department of Defense's ocean transport needs. The MSTS was renamed the Military Sealift Command in 1970.

The SEAL Delivery Vehicle (SDV) is a manned submersible and a type of swimmer delivery vehicle used to deliver United States Navy SEALs and their equipment for special operations missions. It is also operated by the Royal Navy's Special Boat Service, which operates 3 SDV's.

The Scorpio is a brand of underwater submersible Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) manufactured by Perry Tritech used by sub-sea industries such as the oil industry for general operations, and by the Royal Navy and the United States Navy for submarine rescue services. Originally developed by AMETEK Straza of El Cajon, United States, they were subsequently developed by Perry Tritech. Although the design of the original Scorpio is over several decades old, it forms the basis for a current generation of Scorpio-branded ROVs. Scorpio ROVs are named in a sequence following the order of manufacture, such as "Scorpio 17" or "Scorpio 45" which refer to specific ROVs.

USNS Salvor (ARS-52) is a Safeguard-class salvage ship, the second United States Navy ship of that name.

USNS Mount Baker (T-AE-34) was the seventh of eight Kilauea-class ammunition ships. She served in the United States Navy from 1972 to 1996 and with the Military Sealift Command from 1996 to 2010. She was scrapped in 2012.
Operations Specialist is a United States Navy and United States Coast Guard occupational rating. It is a sea duty-intensive rating in the Navy while the majority of Coast Guard OS's are at ashore Command Centers.

The Type 925 Dajiang (大江) is a type of naval auxiliary ship belonging to the People's Republic of China. Each ship is usually equipped with up to two Type 7103 DSRV class Deep Submergence Rescue Vehicles (DSRVs). The lead ship of the Dajiang class is the Changxingdao. The Type 925 is a submarine tender that can also be used as a submarine rescue ship, and hence, it is designated as a submarine support ship by Chinese.
MV Kellie Chouest is a Deep Submergence Elevator Support Ship operated under the Military Sealift Command's Special Mission Ship Program and leased from Edison Chouest Offshore. It is assigned to COMSUBDEVRON FIVE for deep water rescue, salvage and research missions.

The fourth USS Scout (MCM-8) is an Avenger-class mine countermeasures ship of the United States Navy.
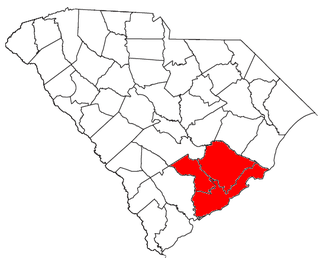
The Charleston metropolitan area is an area centered on Charleston, South Carolina. The U.S. Office of Management and Budget designates the area as the Charleston–North Charleston, SC Metropolitan Statistical Area, a metropolitan statistical area used for statistical purposes only by the United States Census Bureau and other federal agencies. The OMB defines the area as comprising Berkeley, Charleston and Dorchester counties, an area with 664,607 in the 2010 census. Principal cities include Charleston, North Charleston, and Summerville. The area is commonly referred to as the Tri-County Area or the Lowcountry, though the latter term has historically referred to South Carolina coast in general.

MV Carolyn Chouest is a chartered submarine support ship for the United States Navy assigned to the Special Missions Program to support NR-1, the deep submergence craft. She towed NR-1 between work areas, served as a floating supply warehouse and provided quarters for extra crew until the NR-1 was removed from service in 2008.
The Type 7103 deep-submergence rescue vehicle (DSRV) is a submarine rescue submersible of the People's Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) of the People's Republic of China (PRC).
Operation Nanook is an annual military exercise of the Canadian Armed Forces in the Arctic. The exercise is intended to train the different elements of the Canadian Armed Forces along with other government organizations, such as the Canadian Coast Guard and Royal Canadian Mounted Police in disaster training and sovereignty patrols in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago and northern Canada.
Naval Support Activity Charleston, originally designated Naval Weapons Station Charleston, is a base of the United States Navy located on the west bank of the Cooper River, in the cities of Goose Creek and Hanahan South Carolina. The base encompasses more than 17,000 acres (69 km²) of land with 10,000 acres (40 km²) of forest and wetlands, 16-plus miles of waterfront, four deep-water piers, 38.2 miles (61.5 km) of railroad and 292 miles (470 km) of road. The current workforce numbers more than 11,000 with an additional 3,600 people in on-base family housing.















