
Macrocephaly is a condition in which the head is abnormally large; this includes the scalp, the cranial bone, and the contents of the cranium.

A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is a condition present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which there are problems with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which there are problems with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders.

Patau syndrome is a syndrome caused by a chromosomal abnormality, in which some or all of the cells of the body contain extra genetic material from chromosome 13. The extra genetic material disrupts normal development, causing multiple and complex organ defects.
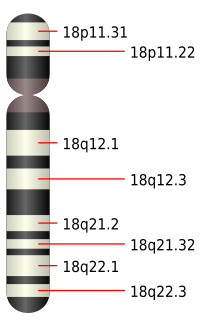
Edwards syndrome, also known as trisomy 18, is a genetic disorder caused by a third copy of all or part of chromosome 18. Many parts of the body are affected. Babies are often born small and have heart defects. Other features include a small head, small jaw, clenched fists with overlapping fingers, and severe intellectual disability.

Polyhydramnios is a medical condition describing an excess of amniotic fluid in the amniotic sac. It is seen in about 1% of pregnancies. It is typically diagnosed when the amniotic fluid index (AFI) is greater than 24 cm. There are two clinical varieties of polyhydramnios: chronic polyhydramnios where excess amniotic fluid accumulates gradually, and acute polyhydramnios where excess amniotic fluid collects rapidly.
Microphthalmia, also referred as microphthalmos, is a developmental disorder of the eye in which one or both eyes are abnormally small and have anatomic malformations. It is different from nanophthalmos in which the eye is small in size but has no anatomical alterations.
Trisomy 8, also known as Warkany syndrome 2, is a human chromosomal disorder caused by having three copies (trisomy) of chromosome 8. It can appear with or without mosaicism.
Neurodevelopmental disorders are a group of Disorders which affect the development of the nervous system, leading to abnormal brain function which may affect emotion, learning ability, self-control and memory. The effects of neurodevelopmental disorders tend to last for a person's entire lifetime.
ICD-10 is an international statistical classification used in health care and related industries.
ICD-10 is an international statistical classification used in health care and related industries.

DiGeorge syndrome, also known as 22q11.2 deletion syndrome, is a syndrome caused by the deletion of a small segment of chromosome 22. While the symptoms can vary, they often include congenital heart problems, specific facial features, frequent infections, developmental delay, learning problems and cleft palate. Associated conditions include kidney problems, hearing loss and autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis or Graves disease.

Dysmelia is a congenital disorder of a limb resulting from a disturbance in embryonic development.
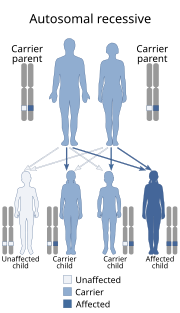
Fryns syndrome is an autosomal recessive multiple congenital anomaly syndrome that is usually lethal in the neonatal period. Fryns (1987) reviewed the syndrome.

Roberts syndrome, or sometimes called pseudothalidomide syndrome, is an extremely rare genetic disorder that is characterized by mild to severe prenatal retardation or disruption of cell division, leading to malformation of the bones in the skull, face, arms, and legs.
Malpuech facial clefting syndrome, also called Malpuech syndrome or Gypsy type facial clefting syndrome, is a rare congenital syndrome. It is characterized by facial clefting, a caudal appendage, growth deficiency, intellectual and developmental disability, and abnormalities of the renal system (kidneys) and the male genitalia. Abnormalities of the heart, and other skeletal malformations may also be present. The syndrome was initially described by Guilliaume Malpuech and associates in 1983. It is thought to be genetically related to Juberg-Hayward syndrome. Malpuech syndrome has also been considered as part of a spectrum of congenital genetic disorders associated with similar facial, urogenital and skeletal anomalies. Termed "3MC syndrome", this proposed spectrum includes Malpuech, Michels and Mingarelli-Carnevale (OSA) syndromes. Mutations in the COLLEC11 and MASP1 genes are believed to be a cause of these syndromes. The incidence of Malpuech syndrome is unknown. The pattern of inheritance is autosomal recessive, which means a defective (mutated) gene associated with the syndrome is located on an autosome, and the syndrome occurs when two copies of this defective gene are inherited.
Young–Madders syndrome, alternatively known as Pseudotrisomy 13 syndrome or holoprosencephaly–polydactyly syndrome, is a genetic disorder resulting from defective and duplicated chromosomes which result in holoprosencephaly, polydactyly, facial malformations and mental retardation, with a significant variance in the severity of symptoms being seen across known cases. Many cases often suffer with several other genetic disorders, and some have presented with hypoplasia, cleft lip, cardiac lesions and other heart defects. In one case in 1991 and another in 2000 the condition was found in siblings who were the product of incest. Many cases are diagnosed prenatally and often in siblings. Cases are almost fatal in the prenatal stage with babies being stillborn.

13q deletion syndrome is a rare genetic disease caused by the deletion of some or all of the large arm of human chromosome 13. It causes intellectual disability and congenital malformations that affect a variety of organ systems.












