
A microRNA is a small non-coding RNA molecule found in plants, animals and some viruses, that functions in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. miRNAs function via base-pairing with complementary sequences within mRNA molecules. As a result, these mRNA molecules are silenced, by one or more of the following processes: (1) Cleavage of the mRNA strand into two pieces, (2) Destabilization of the mRNA through shortening of its poly(A) tail, and (3) Less efficient translation of the mRNA into proteins by ribosomes.
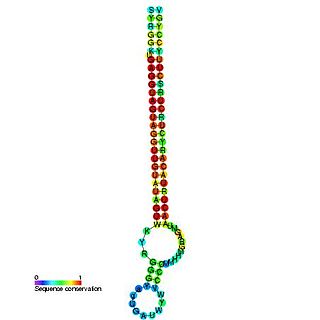
The Let-7 microRNA precursor was identified from a study of developmental timing in C. elegans, and was later shown to be part of a much larger class of non-coding RNAs termed microRNAs. miR-98 microRNA precursor from human is a let-7 family member. Let-7 miRNAs have now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of species (MIPF0000002). miRNAs are initially transcribed in long transcripts called primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs), which are processed in the nucleus by Drosha and Pasha to hairpin structures of about 70 nucleotide. These precursors (pre-miRNAs) are exported to the cytoplasm by exportin5, where they are subsequently processed by the enzyme Dicer to a ~22 nucleotide mature miRNA. The involvement of Dicer in miRNA processing demonstrates a relationship with the phenomenon of RNA interference.

In molecular biology lin-4 is a microRNA (miRNA) that was identified from a study of developmental timing in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. It was the first to be discovered of the miRNAs, a class of non-coding RNAs involved in gene regulation. miRNAs are transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give a 21 nucleotide product. The extents of the hairpin precursors are not generally known and are estimated based on hairpin prediction. The products are thought to have regulatory roles through complete or partial complementarity to mRNA. The lin-4 gene has been found to lie within a 4.11kb intron of a separate host gene.
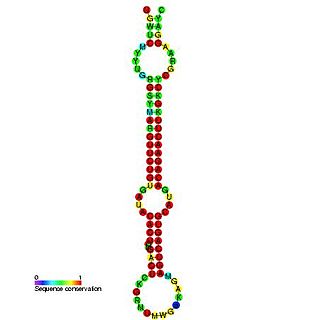
In molecular biology, miR-148 is a microRNA whose expression has been demonstrated in human, mouse, rat and zebrafish. miR-148 has also been predicted in chicken.
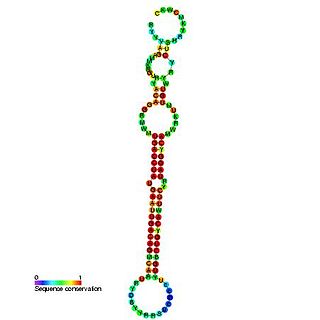
The miR-192 microRNA precursor, is a short non-coding RNA gene involved in gene regulation. miR-192 and miR-215 have now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in mouse and human.

The miR-8 microRNA precursor, is a short non-coding RNA gene involved in gene regulation. miR-8 in Drosophila melanogaster is expressed from the 3' arm of related precursor hairpins, along with miR-200, miR-236, miR-429 and human and mouse homolog miR-141. Members of this precursor family have now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of species. The bounds of the precursors are predicted based on conservation and base pairing and are not generally known.

The miR-9 microRNA, is a short non-coding RNA gene involved in gene regulation. The mature ~21nt miRNAs are processed from hairpin precursor sequences by the Dicer enzyme. The dominant mature miRNA sequence is processed from the 5' arm of the mir-9 precursor, and from the 3' arm of the mir-79 precursor. The mature products are thought to have regulatory roles through complementarity to mRNA. In vertebrates, miR-9 is highly expressed in the brain, and is suggested to regulate neuronal differentiation. A number of specific targets of miR-9 have been proposed, including the transcription factor REST and its partner CoREST.

The miR-10 microRNA precursor is a short non-coding RNA gene involved in gene regulation. It is part of an RNA gene family which contains miR-10, miR-51, miR-57, miR-99 and miR-100. miR-10, miR-99 and miR-100 have now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of species. mir-51 and mir-57 have currently only been identified in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.

The miR-124 microRNA precursor is a small non-coding RNA molecule that has been identified in flies, nematode worms, mouse and human. The mature ~21 nucleotide microRNAs are processed from hairpin precursor sequences by the Dicer enzyme, and in this case originates from the 3' arm. miR-124 has been found to be the most abundant microRNA expressed in neuronal cells. Experiments to alter expression of miR-124 in neural cells did not appear to affect differentiation. However these results are controversial since other reports have described a role for miR-124 during neuronal differentiation.

In molecular biology, miR-130 microRNA precursor is a small non-coding RNA that regulates gene expression. This microRNA has been identified in mouse, and in human. miR-130 appears to be vertebrate-specific miRNA and has now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a range of vertebrate species. Mature microRNAs are processed from the precursor stem-loop by the Dicer enzyme. In this case, the mature sequence is excised from the 3' arm of the hairpin. It has been found that miR-130 is upregulated in a type of cancer called hepatocellular carcinoma. It has been shown that miR-130a is expressed in the hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell compartment but not in mature blood cells.

MicroRNA (miRNA) precursor miR156 is a family of plant non-coding RNA. This microRNA has now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a range of plant species. Animal miRNAs are transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give a ~22 nucleotide product. In plants the precursor sequences may be longer, and the carpel factory (caf) enzyme appears to be involved in processing. In this case the mature sequence comes from the 5' arm of the precursor, and both Arabidopsis thaliana and rice genomes contain a number of related miRNA precursors which give rise to almost identical mature sequences. The extents of the hairpin precursors are not generally known and are estimated based on hairpin prediction. The products are thought to have regulatory roles through complementarity to mRNA.
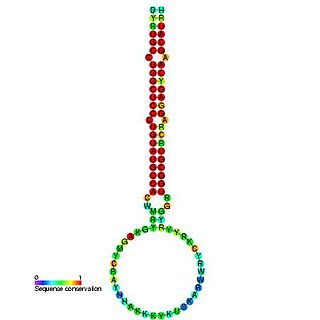
In molecular biology, mir-160 is a microRNA that has been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a range of plant species including Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa (rice). miR-160 is predicted to bind complementary sites in the untranslated regions of auxin response factor genes to regulate their expression. The hairpin precursors are predicted based on base pairing and cross-species conservation; their extents are not known. In this case, the mature sequence is excised from the 5' arm of the hairpin.

The mir-172 microRNA is thought to target mRNAs coding for APETALA2-like transcription factors. It has been verified experimentally in the model plant, Arabidopsis thaliana. The mature sequence is excised from the 3' arm of the hairpin.
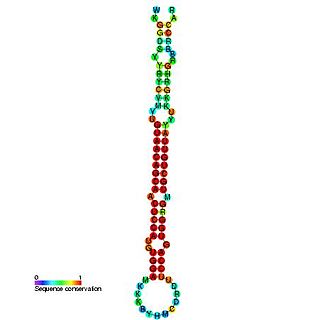
In molecular biology, miR-194 microRNA precursor is a small non-coding RNA gene that regulated gene expression. Its expression has been verified in mouse and in human. mir-194 appears to be a vertebrate-specific miRNA and has now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a range of vertebrate species. The mature microRNA is processed from the longer hairpin precursor by the Dicer enzyme. In this case, the mature sequence is excised from the 5' arm of the hairpin.

miR-196 is a non-coding RNA called a microRNA that has been shown to be expressed in humans and mice. miR-196 appears to be a vertebrate specific microRNA and has now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of vertebrate species. In many species the miRNA appears to be expressed from intergenic regions in HOX gene clusters. The hairpin precursors are predicted based on base pairing and cross-species conservation—their extents are not known. In this case the mature sequence is excised from the 5' arm of the hairpin.
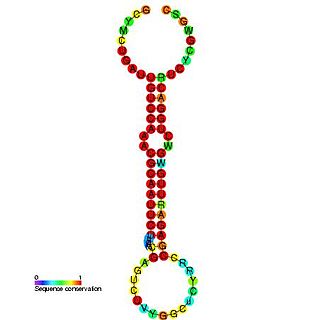
In molecular biology, the microRNA miR-219 was predicted in vertebrates by conservation between human, mouse and pufferfish and cloned in pufferfish. It was later predicted and confirmed experimentally in Drosophila. Homologs of miR-219 have since been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of species, including the platyhelminth Schmidtea mediterranea, several arthropod species and a wide range of vertebrates. The hairpin precursors are predicted based on base pairing and cross-species conservation; their extents are not known. In this case, the mature sequence is excised from the 5' arm of the hairpin.

The mir-2 microRNA family includes the microRNA genes mir-2 and mir-13. Mir-2 is widespread in invertebrates, and it is the largest family of microRNAs in the model species Drosophila melanogaster. MicroRNAs from this family are produced from the 3' arm of the precursor hairpin. Leaman et al. showed that the miR-2 family regulates cell survival by translational repression of proapoptotic factors. Based on computational prediction of targets, a role in neural development and maintenance has been suggested.

The mir-6 microRNA precursor is a precursor microRNA specific to Drosophila species. In Drosophila melanogaster there are three mir-6 paralogs called dme-mir-6-1, dme-mir-6-2, dme-mir-6-3, which are clustered together in the genome. The extents of these hairpin precursors are estimated based on hairpin prediction. Each precursor is generated following the cleavage of a longer primary transcript in the nucleus, and is exported in the cytoplasm. In the cytoplasm, precursors are further processed by the enzyme Dicer, generating ~22 nucleotide products from each arm of the hairpin. The products generated from the 3' arm of each mir-6 precursor have identical sequences. Both 5' and 3' mature products are experimentally validated. Experimental data suggests that the mature products of mir-6 hairpins are expressed in the early embryo of Drosophila and target apoptotic genes such as hid, grim and rpr.
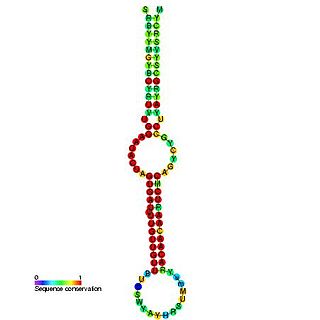
This family represents the microRNA (miRNA) precursor mir-7. This miRNA has been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of species. miRNAs are transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give a ~22 nucleotide product. In this case the mature sequence comes from the 5' arm of the precursor. The extents of the hairpin precursors are not generally known and are estimated based on hairpin prediction. The involvement of Dicer in miRNA processing suggests a relationship with the phenomenon of RNA interference.

miR-338 is a family of brain-specific microRNA precursors found in mammals, including humans. The ~22 nucleotide mature miRNA sequence is excised from the precursor hairpin by the enzyme Dicer. This sequence then associates with RISC which effects RNA interference.




















