A mitre is a traditional, ceremonial head-dress of ancient Jewish high priests and Christian bishops and other clergy.
Contents
Mitre may also refer to:
A mitre is a traditional, ceremonial head-dress of ancient Jewish high priests and Christian bishops and other clergy.
Mitre may also refer to:
Smith may refer to:

This article deals with the diplomatic affairs, foreign policy and international relations of the Argentine Republic. At the political level, these matters are handled by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, also known as the Cancillería, which answers to the President. The current Minister of Foreign Affairs, since December 2023, is Chancellor Diana Mondino.
Twin Peaks is an American television series, running from 1990 to 1991; and in 2017.
Bunnings Group Limited, trading as Bunnings Warehouse or Bunnings, is an Australian household hardware and garden centre chain. The chain has been owned by Wesfarmers since 1994, and has stores in Australia and New Zealand.

Mount Bona is one of the major mountains of the Saint Elias Mountains in eastern Alaska, and is the fifth-highest independent peak in the United States. It is either the tenth- or eleventh-highest peak in North America. Mount Bona and its adjacent neighbor Mount Churchill are both large ice-covered stratovolcanoes. Bona has the distinction of being the highest volcano in the United States and the fourth-highest in North America, outranked only by the three highest Mexican volcanoes, Pico de Orizaba, Popocatépetl, and Iztaccíhuatl. Its summit is a small stratovolcano on top of a high platform of sedimentary rocks.

Domingo María Cristóbal French was an Argentine revolutionary who took part in the May Revolution and the Argentine War of Independence.

Bernardo de Irigoyen was an Argentine lawyer, diplomat and politician.
This glossary of woodworking lists a number of specialized terms and concepts used in woodworking, carpentry, and related disciplines.

Carlos Tejedor was an Argentine jurist and politician, Governor of Buenos Aires Province between 1878 and 1880. Tejedor was a prominent figure in the movement against the Federalization of Buenos Aires.

Foreign relations between the Argentine Republic and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland have existed for over two centuries.
The following radio stations broadcast on FM frequency 88.9 MHz:
There are many landmarks in Buenos Aires, Argentina some of which are of considerable historical or artistic interest.
Argentina held nine presidential elections between 1862 and 1910, every six years.

The Argentine Civil Wars were a series of civil conflicts of varying intensity that took place through the territories of Argentina from 1814 to 1853. Beginning concurrently with the Argentine War of Independence (1810–1818), the conflict prevented the formation of a stable governing body until the signing of the Argentine Constitution of 1853, followed by low-frequency skirmishes that ended with the Federalization of Buenos Aires. The period saw heavy intervention from the Brazilian Empire that fought against state and provinces in multiple wars. Breakaway nations, former territories of the viceroyalty, such as the Banda Oriental, Paraguay and the Upper Peru were involved to varying degrees. Foreign powers such as the British and French empires put heavy pressure on the fledgling nations at times of international war.

Ángel Vicente "Chacho" Peñaloza was a military officer and provincial leader prominent in both the history of La Rioja province and the Argentine civil wars that preceded national unity.

The State of Buenos Aires was a secessionist republic resulting from the overthrow of the Argentine Confederation government in the Province of Buenos Aires on September 11, 1852. The State of Buenos Aires was never recognized by the Confederation; it remained, however, independent under its own government and constitution. Buenos Aires rejoined the Argentine Confederation after the former's victory at the Battle of Pavón in 1861.
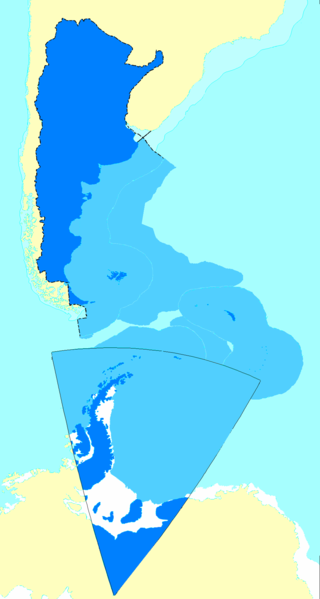
Argentine irredentism refers to the idea that Argentina has suffered large territorial losses early in the 19th century to neighboring countries, and that it must strive to regain control of them, forming "Great Argentina", envisioned with the same borders as the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata. This idea surged in popularity in the late 19th century, and peaked in influence in the late 1940s and early 1950s. All of these claims have been abandoned by Argentina, save for the Falkland Islands sovereignty dispute.
Gertrude Emily Benham was an English explorer and mountaineer. Born in London, she was the youngest of six children and began climbing mountains as a girl. She went on to climb mountains on almost every continent. Benham was also an intrepid hiker and walked from Valparaiso, Chile, to Buenos Aires, Argentina. She went on to hike across Kenya, and traverse Africa on foot.