In biochemistry, NAD(P) may refer to:
| This set index page lists chemical compounds articles associated with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
In biochemistry, NAD(P) may refer to:
| This set index page lists chemical compounds articles associated with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
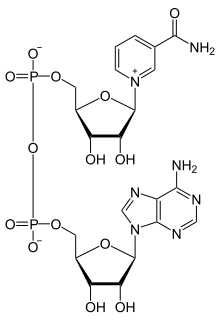
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a cofactor that is central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other nicotinamide. NAD exists in two forms: an oxidized and reduced form, abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH respectively.
DNA ligase (NAD+) (EC 6.5.1.2, polydeoxyribonucleotide synthase (NAD+), polynucleotide ligase (NAD+), DNA repair enzyme, DNA joinase, polynucleotide synthetase (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), deoxyribonucleic-joining enzyme, deoxyribonucleic ligase, deoxyribonucleic repair enzyme, deoxyribonucleic joinase, DNA ligase, deoxyribonucleate ligase, polynucleotide ligase, deoxyribonucleic acid ligase, polynucleotide synthetase, deoxyribonucleic acid joinase, DNA-joining enzyme, polynucleotide ligase (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)) is an enzyme with systematic name poly(deoxyribonucleotide):poly(deoxyribonucleotide) ligase (AMP-forming, NMN-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
In enzymology, a mannuronate reductase (EC 1.1.1.131) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a sorbose 5-dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.1.1.123) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 21-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (NAD+) (EC 1.1.1.150) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 21-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.1.1.151) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Aquacobalamin reductase (EC 1.16.1.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
CDP-4-dehydro-6-deoxyglucose reductase (EC 1.17.1.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a ferredoxin–NAD+ reductase (EC 1.18.1.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a rubredoxin—NAD(P)+ reductase (EC 1.18.1.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a rubredoxin-NAD+ reductase (EC 1.18.1.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Asparagusate reductase (EC 1.8.1.11) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Aspartate dehydrogenase (EC 1.4.1.21) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Beta-alanopine dehydrogenase (EC 1.5.1.26) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a NAD(P)+ transhydrogenase (Re/Si-specific (EC 1.6.1.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a NAD+ diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.22) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a NAD+ nucleosidase (EC 3.2.2.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a NAD(P)+ nucleosidase (EC 3.2.2.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a NAD(P)+-protein-arginine ADP-ribosyltransferase (EC 2.4.2.31) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction using nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
NAD(P)H-hydrate epimerase is an enzyme with systematic name (6R)-6beta-hydroxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydronicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide 6-epimerase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction