Nisil is an alloy of nickel (95.5% wt.) and silicon (4.4% wt.) with traces of Mg (0.1% wt.), which is non-magnetic.
Nisil melts at 1341 - 1420 °C, has a density of 8.58 g/cm3, and electrical resistivity of 0.365 Ω⋅mm2/m at 20 °C.
It is often used in conjunction with Nicrosil in type N thermocouples. In this use, it serves as the negative leg of the thermocouple. It offers higher thermoelectric stability in air above 1000°C (1830°F) and better oxidation resistance than type E, J and K thermocouples. It can not be exposed to sulphur-containing gases.

Rhodium is a chemical element; it has symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is a very rare, silvery-white, hard, corrosion-resistant transition metal. It is a noble metal and a member of the platinum group. It has only one naturally occurring isotope, which is 103Rh. Naturally occurring rhodium is usually found as a free metal or as an alloy with similar metals and rarely as a chemical compound in minerals such as bowieite and rhodplumsite. It is one of the rarest and most valuable precious metals.

A thermocouple, also known as a "thermoelectrical thermometer", is an electrical device consisting of two dissimilar electrical conductors forming an electrical junction. A thermocouple produces a temperature-dependent voltage as a result of the Seebeck effect, and this voltage can be interpreted to measure temperature. Thermocouples are widely used as temperature sensors.
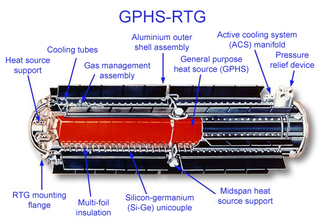
A radioisotope thermoelectric generator, sometimes referred to as a radioisotope power system (RPS), is a type of nuclear battery that uses an array of thermocouples to convert the heat released by the decay of a suitable radioactive material into electricity by the Seebeck effect. This type of generator has no moving parts and is ideal for deployment in remote and harsh environments for extended periods with no risk of parts wearing out or malfunctioning.

Carbon steel is a steel with carbon content from about 0.05 up to 2.1 percent by weight. The definition of carbon steel from the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) states:

Constantan, also known in various contexts as Eureka, Advance, and Ferry, refers to a copper-nickel alloy commonly used for its stable electrical resistance across a wide range of temperatures. It usually consists of 55% copper and 45% nickel. Its main feature is the low thermal variation of its resistivity, which is constant over a wide range of temperatures. Other alloys with similarly low temperature coefficients are known, such as manganin.

Carnauba, also called Brazil wax and palm wax, is a wax of the leaves of the carnauba palm Copernicia prunifera, a plant native to and grown only in the northeastern Brazilian states of Ceará, Piauí, Paraíba, Pernambuco, Rio Grande do Norte, Maranhão and Bahia. It is known as the "Queen of Waxes". In its pure state, it is usually available in the form of hard yellow-brown flakes. It is obtained by collecting and drying the leaves, beating them to loosen the wax, then refining and bleaching it. As a food additive, its E number is E903.
Resistance thermometers, also called resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), are sensors used to measure temperature. Many RTD elements consist of a length of fine wire wrapped around a heat-resistant ceramic or glass core but other constructions are also used. The RTD wire is a pure material, typically platinum (Pt), nickel (Ni), or copper (Cu). The material has an accurate resistance/temperature relationship which is used to provide an indication of temperature. As RTD elements are fragile, they are often housed in protective probes.

Tantalum carbides (TaC) form a family of binary chemical compounds of tantalum and carbon with the empirical formula TaCx, where x usually varies between 0.4 and 1. They are extremely hard, brittle, refractory ceramic materials with metallic electrical conductivity. They appear as brown-gray powders, which are usually processed by sintering.
Alumel is an alloy consisting of approximately 95% nickel, 2% aluminium, 2% manganese, and 1% silicon. This magnetic alloy is used to make the negative conductors of ANSI Type K (chromel-alumel) thermocouples and thermocouple extension wire. Alumel is a registered trademark of Concept Alloys, Inc.

A heat detector is a fire alarm device designed to respond when the convected thermal energy of a fire increases the temperature of a heat sensitive element. The thermal mass and conductivity of the element regulate the rate flow of heat into the element. All heat detectors have this thermal lag. Heat detectors have two main classifications of operation, "rate-of-rise" and "fixed temperature". The heat detector is used to help in the reduction of property damage.
Chromel is an alloy made of approximately 90% nickel and 10% chromium by weight that is used to make the positive conductors of ANSI Type E (chromel-constantan) and K (chromel-alumel) thermocouples. It can be used at temperatures up to 1,100 °C (2,010 °F) in oxidizing atmospheres. Chromel is a registered trademark of Concept Alloys, Inc.
The Systems Nuclear Auxiliary POWER (SNAP) program was a program of experimental radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) and space nuclear reactors flown during the 1960s by NASA.
Nicrosil is a nickel alloy containing about 14.4% chromium, 1.4% silicon, and 0.1% magnesium.

The Pirani gauge is a robust thermal conductivity gauge used for the measurement of the pressures in vacuum systems. It was invented in 1906 by Marcello Pirani.

A heat flux sensor is a transducer that generates an electrical signal proportional to the total heat rate applied to the surface of the sensor. The measured heat rate is divided by the surface area of the sensor to determine the heat flux.
A potentiometer is an instrument for measuring voltage or 'potential difference' by comparison of an unknown voltage with a known reference voltage. If a sensitive indicating instrument is used, very little current is drawn from the source of the unknown voltage. Since the reference voltage can be produced from an accurately calibrated voltage divider, a potentiometer can provide high precision in measurement. The method was described by Johann Christian Poggendorff around 1841 and became a standard laboratory measuring technique.

A thermal profile is a complex set of time-temperature data typically associated with the measurement of thermal temperatures in an oven. The thermal profile is often measured along a variety of dimensions such as slope, soak, time above liquidus (TAL), and peak.

The piston-cylinder apparatus is a solid media device, used in Geosciences and Material Sciences, for generating simultaneously high pressure and temperature. Modifications of the normal set-up can push these limits to even higher pressures and temperatures. A particular type of piston-cylinder, called Griggs apparatus, is also able to add a deviatoric stress on the sample.
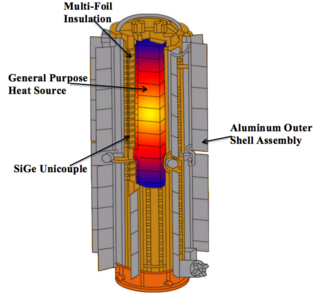
Silicon-germanium (SiGe) thermoelectrics have been used for converting heat into electrical power in spacecraft designed for deep-space NASA missions since 1976. This material is used in the radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) that power Voyager 1, Voyager 2, Galileo, Ulysses, Cassini, and New Horizons spacecraft. SiGe thermoelectric material converts enough radiated heat into electrical power to fully meet the power demands of each spacecraft. The properties of the material and the remaining components of the RTG contribute towards the efficiency of this thermoelectric conversion.

Thermopile laser sensors are used for measuring laser power from a few µW to several W. The incoming radiation of the laser is converted into heat energy at the surface. This heat input produces a temperature gradient across the sensor. Making use of the thermoelectric effect a voltage is generated by this temperature gradient. Since the voltage is directly proportional to the incoming radiation, it can be directly related to the irradiation power.