Paroxysmal attacks or paroxysms are a sudden recurrence or intensification of symptoms, such as a spasm or seizure. These short, frequent symptoms can be observed in various clinical conditions. They are usually associated with multiple sclerosis or pertussis, but they may also be observed in other disorders such as encephalitis, head trauma, stroke, asthma, trigeminal neuralgia, breath-holding spells, epilepsy, malaria, tabes dorsalis, and Behçet's disease, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). It has also been noted as a symptom of gratification disorder in children.

Interferon beta-1a is a cytokine in the interferon family used to treat multiple sclerosis (MS). It is produced by mammalian cells, while interferon beta-1b is produced in modified E. coli. Some claims have been made that Interferons produce about an 18–38% reduction in the rate of MS relapses.
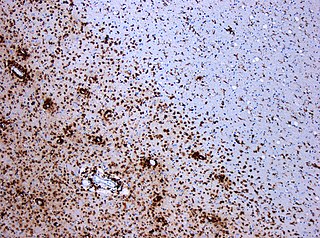
A demyelinating disease is any disease of the nervous system in which the myelin sheath of neurons is damaged. This damage impairs the conduction of signals in the affected nerves. In turn, the reduction in conduction ability causes deficiency in sensation, movement, cognition, or other functions depending on which nerves are involved.

Ocular microtremor (OMT) is a constant, physiological, high frequency, low amplitude eye tremor.
Oscillopsia is a visual disturbance in which objects in the visual field appear to oscillate. The severity of the effect may range from a mild blurring to rapid and periodic jumping. Oscillopsia is an incapacitating condition experienced by many patients with neurological disorders. It may be the result of ocular instability occurring after the oculomotor system is affected, no longer holding images steady on the retina. A change in the magnitude of the vestibulo-ocular reflex due to vestibular disease can also lead to oscillopsia during rapid head movements. Oscillopsia may also be caused by involuntary eye movements such as nystagmus, or impaired coordination in the visual cortex and is one of the symptoms of superior canal dehiscence syndrome. Sufferers may experience dizziness and nausea. Oscillopsia can also be used as a quantitative test to document aminoglycoside toxicity. Permanent oscillopsia can arise from an impairment of the ocular system that serves to maintain ocular stability. Paroxysmal oscillopsia can be due to an abnormal hyperactivity in the peripheral ocular or vestibular system.
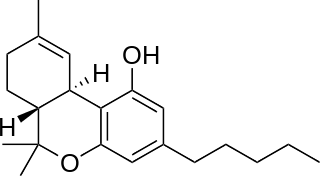
Nabiximols is a specific Cannabis extract that was approved in 2010 as a botanical drug in the United Kingdom despite a lack of convincing evidence of effectiveness for spasticity reduction. Nabiximols is sold as a mouth spray intended to alleviate neuropathic pain, spasticity, overactive bladder, and other symptoms of multiple sclerosis; it was developed by the UK company GW Pharmaceuticals. The drug is a pharmaceutical product standardized in composition, formulation, and dose. Its principal active cannabinoid components are the cannabinoids: tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Each spray delivers a dose of 2.7 mg THC and 2.5 mg CBD.
Interferon beta-1b is a cytokine in the interferon family used to treat the relapsing-remitting and secondary-progressive forms of multiple sclerosis (MS). It is approved for use after the first MS event. Closely related is interferon beta 1a, also indicated for MS, with a very similar drug profile.
Ocular myasthenia gravis (MG) is a disease of the neuromuscular junction resulting in hallmark variability in muscle weakness and fatigability. MG is an autoimmune disease where anomalous antibodies are produced against the naturally occurring acetylcholine receptors in voluntary muscles. MG may be limited to the muscles of the eye, leading to abrupt onset of weakness/fatigability of the eyelids or eye movement. MG may also involve other muscle groups.

Photopsia is the presence of perceived flashes of light in the field of vision.
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, sometimes experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) is an animal model of brain inflammation. It is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system (CNS). It is mostly used with rodents and is widely studied as an animal model of the human CNS demyelinating diseases, including multiple sclerosis and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM). EAE is also the prototype for T-cell-mediated autoimmune disease in general.
Intention tremor, is a dyskinetic disorder characterized by a broad, coarse, and low frequency tremor. The amplitude of an intention tremor increases as an extremity approaches the endpoint of deliberate and visually guided movement. An intention tremor is usually perpendicular to the direction of movement. When experiencing an intention tremor, one often overshoots or undershoots their target, a condition known as dysmetria. Intention tremor is the result of dysfunction of the cerebellum, particularly on the same side as the tremor in the lateral zone, which controls visually guided movements. Depending on the location of cerebellar damage, these tremors can be either unilateral or bilateral.
Skew deviation is an unusual ocular deviation (strabismus), wherein the eyes move upward (hypertropia), but in opposite directions. Skew deviation is caused by abnormal prenuclear vestibular input to the ocular motor nuclei, most commonly due to brainstem or cerebellar stroke. Other causes include multiple sclerosis and head trauma. Skew deviation is usually characterized by torticollis and binocular torsion. The exact pathophysiology of skew deviation remains incompletely understood. Skew deviation appears to be a perturbation of the ocular tilt reaction, which is itself probably a vestigial righting response used to keep fish and other lateral-eyed animals properly oriented.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory demyelinating disease that affects the central nervous system (CNS). Several therapies for it exist, although there is no known cure.

Multiple sclerosis can cause a variety of symptoms: changes in sensation (hypoesthesia), muscle weakness, abnormal muscle spasms, or difficulty moving; difficulties with coordination and balance; problems in speech (dysarthria) or swallowing (dysphagia), visual problems, fatigue and acute or chronic pain syndromes, bladder and bowel difficulties, cognitive impairment, or emotional symptomatology. The main clinical measure in progression of the disability and severity of the symptoms is the Expanded Disability Status Scale or EDSS.
![Blurred vision Symptom, lack of sharpness of vision resulting in the inability to see fine detail. http://purl.obolibrary.org/obo/HP_0000622 [HPO: probinson].](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7d/Pesto_ingredients.jpg/320px-Pesto_ingredients.jpg)
Blurred vision is an ocular symptom.

Tumefactive multiple sclerosis is a condition in which the central nervous system of a person has multiple demyelinating lesions with atypical characteristics for those of standard multiple sclerosis (MS). It is called tumefactive as the lesions are "tumor-like" and they mimic tumors clinically, radiologically and sometimes pathologically.

Retinal vasculitis is inflammation of the vascular branches of the retinal artery, caused either by primary ocular disease processes, or as a specific presentation of any systemic form of vasculitis such as Behçet's disease, sarcoidosis, multiple sclerosis, or any form of systemic necrotizing vasculitis such as temporal arteritis, polyarteritis nodosa, and granulomatosis with polyangiitis, or due to lupus erythematosus, or rheumatoid arthritis. Eales disease, pars planitis, birdshot retinochoroidopathy, and Fuchs heterochromic iridocyclitis (FHI) can also cause retinal vasculitis. Infectious pathogens such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, visceral larva migrans can also cause retinal vasculitis.
Radiologically isolated syndrome (RIS) is a clinical situation in which a person has white matter lesions suggestive of multiple sclerosis (MS), as shown on an MRI scan that was done for reasons unrelated to MS symptoms. The nerve lesions in these people show dissemination in space with an otherwise normal neurological examination and without historical accounts of typical MS symptoms.







![Blurred vision Symptom, lack of sharpness of vision resulting in the inability to see fine detail. http://purl.obolibrary.org/obo/HP_0000622 [HPO: probinson].](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7d/Pesto_ingredients.jpg/320px-Pesto_ingredients.jpg)

