
Deurne is a rural municipality and eponymous village in the province of North Brabant in the Netherlands. Including the villages of Liessel, Vlierden, Neerkant, and Helenaveen, Deurne had a population of 32,437 in 2021 and covers an area of 118.36 km2 (45.70 sq mi).

Hoofddorp is the main town of the municipality of Haarlemmermeer, in the province of North Holland, the Netherlands. In 2021, the population was 77,885. The town was founded in 1853, immediately after the Haarlemmermeer had been drained.

Henri Gerard Winkelman was a Dutch military officer who served as Commander-in-chief of the Armed forces of the Netherlands during the German invasion of the Netherlands.

The UNESCO World Heritage Site known as the Defence Line of Amsterdam is a 135-kilometre (84 mi) ring of fortifications around Amsterdam. It has 42 forts that are 10–15 kilometres (6.2–9.3 mi) from the centre and lowlands, which can easily be flooded in time of war. The flooding was designed to give a depth of about 30 centimetres (12 in), too little for boats to cross. Any buildings within 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) of the line had to be made of wood so that they could be burnt and the obstruction removed.
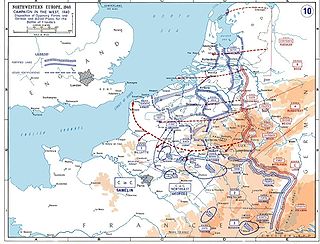
The Netherlands entered World War II on May 10, 1940, when invading German forces quickly overran the country. On December 7, 1941, after the attack on Pearl Harbor, the Netherlands government in exile also declared war on Japan. Operation Market Garden, which started in 1944, liberated the southern and eastern parts of the country, but full liberation did not come until the surrender of Germany on May 5, 1945.

The Dutch Waterline was a series of water-based defences conceived by Maurice of Nassau in the early 17th century, and realised by his half brother Frederick Henry. Combined with natural bodies of water, the Waterline could be used to transform Holland, the westernmost region of the Netherlands and adjacent to the North Sea, almost into an island. In the 19th century, the Line was extended to include Utrecht.

The German invasion of the Netherlands, otherwise known as the Battle of the Netherlands, was a military campaign part of Case Yellow, the Nazi German invasion of the Low Countries and France during World War II. The battle lasted from 10 May 1940 until the surrender of the main Dutch forces on 14 May. Dutch troops in the province of Zeeland continued to resist the Wehrmacht until 17 May, when Germany completed its occupation of the whole country.

The Koningshooikt–Wavre Line, abbreviated to KW Line and often known as the Dyle Line after the Dijle (Dyle) river, was a 60 kilometres (37 mi)-long fortified line of defence prepared by the Belgian Army between Koningshooikt and Wavre which was intended to protect Brussels from a possible German invasion. Construction on the KW Line began in September 1939 after World War II had begun but while Belgium itself remained a neutral state. It was subsequently extended southwards from Wavre towards Namur. The line itself consisted of bunkers, anti-tank ditches, and barricades including so-called Cointet-elements and played a key role in Allied strategy during the German invasion of Belgium in May 1940. However, its role in the actual fighting was ultimately minimal. In 2009 an inventory of surviving emplacements was begun.

The Grebbe Line was a forward defence line of the Dutch Water Line, based on inundation. The Grebbe Line ran from the Grebbeberg in Rhenen northwards until the IJsselmeer.

The Battle of Overloon was a battle fought in the Second World War battle between Allied forces and the German Army which took place in and around the village of Overloon in the south-east of the Netherlands between 30 September and 18 October 1944. The battle, which resulted in an Allied victory, ensued after the Allies launched Operation Aintree. The Allies went on to liberate the town of Venray.
The Dyle Plan or Plan D was the plan of the Commander-in-Chief of the French Army, Général d'armée Maurice Gamelin, to defeat a German attempt to invade France through Belgium. The Dyle (Dijle) river is 86 km (53 mi) long, from Houtain-le-Val through Flemish Brabant and Antwerp; Gamelin intended French, British and Belgian troops to halt a German invasion force along the line of the river. The Franco-Belgian Accord of 1920 had co-ordinated communication and fortification efforts of both armies. After the German Remilitarization of the Rhineland on 7 March 1936, the Belgian government abrogated the accord and substituted a policy of strict neutrality, now that the German Army was on the German–Belgian border.

The Battle of Fort Ében-Émael was a battle between Belgian and German forces that took place between 10 May and 11 May 1940, and was part of the Battle of Belgium and Fall Gelb, the German invasion of the Low Countries and France. An assault force of German paratroopers, Fallschirmjäger, was tasked with assaulting and capturing Fort Ében-Émael, a Belgian fortress whose strategic position and strong artillery emplacements dominated several important bridges over the Albert Canal. These carried roads which led into the Belgian heartland and were what the German forces intended to use to advance. As some of the German airborne forces assaulted the fortress and disabled the garrison and the artillery pieces inside it, others simultaneously captured three bridges over the Canal. Having disabled the fortress, the airborne troops were then ordered to protect the bridges against Belgian counter-attacks until they linked up with ground forces from the German 18th Army.

The Battle of the Grebbeberg was a major engagement during the Battle of the Netherlands, which was a part of the World War II Operation Fall Gelb in 1940.

The Frisian waterline started being built around 1580. The defence line goes from the Zuidersea, along the River Linde, to the De Blesse Bridge. Then, the defence line goes northward to Kuinre by way of Heerenveen, Terband, Gorredijk, Donkerbroek, Bakkeveen and Frieschepalen.

Ouvrage La Ferté, also known as Ouvrage Villy-La Ferté, is a petit ouvrage of the Maginot Line, located in the Fortified Sector of Montmédy, facing Belgium. The ouvrage lies between the towns of Villy and La Ferté-sur-Chiers. It possesses two combat blocks linked by an underground gallery. The westernmost position in its sector, it was a comparatively weakly armed fortification in an exposed position that left it vulnerable to isolation and attack. After a sustained attack during the Battle of France, the position was overwhelmed by German forces and was destroyed with its entire garrison killed. The fighting at La Ferté was the heaviest of any position in the Maginot Line. It is preserved as a war memorial.

The 256th Infantry Division was a German infantry division in World War II. They formed on August 1939 as part of the 4. Welle (wave). The division was destroyed at Vitebsk in June 1944 during Operation Bagration. The remnants of the division formed Divisions-Gruppe 256 which was assigned to Korps-Abteilung H.

The IJssel Line was the Dutch portion of the NATO Cold War line of defence for Western Europe during the 1950s and 1960s. It consisted of anti-aircraft and four-barrel machine gun bunkers, command and hospital bunkers, and many Ram and Sherman tank bunkers encased in concrete, leaving the turrets exposed. These elements were placed along the IJssel river.

The Battle of Mill was a day long struggle in and around the Dutch village of Mill along the Peel-Raam line on the first day of the invasion of the Netherlands in 1940. Although the Germans broke through, they suffered heavy casualties and were delayed in their advance by one day.

The West Brabant waterline is a Dutch military defense line based on inundation.






















