
Chain mail is a type of armour consisting of small metal rings linked together in a pattern to form a mesh. It was generally in common military use between the 3rd century BC and the 16th century AD in Europe, and longer in Asia and North Africa. A coat of this armour is often referred to as a hauberk, and sometimes a byrnie.
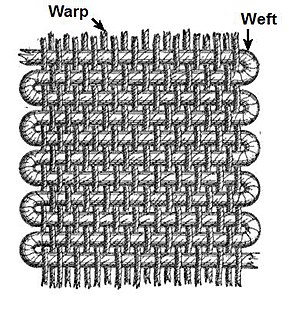
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal threads are called the warp and the lateral threads are the weft, woof, or filling. The method in which these threads are interwoven affects the characteristics of the cloth. Cloth is usually woven on a loom, a device that holds the warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. A fabric band that meets this definition of cloth can also be made using other methods, including tablet weaving, back strap loom, or other techniques that can be done without looms.

Hugo Wallace Weaving is an English actor. Born in Colonial Nigeria to English parents, he has resided in Australia for the entirety of his career. He is the recipient of six Australian Academy of Cinema and Television Arts Awards (AACTA) and has also been recognized as an Honorary Officer of the Order of Australia.

A carpet is a textile floor covering typically consisting of an upper layer of pile attached to a backing. The pile was traditionally made from wool, but since the 20th century, synthetic fibers such as polypropylene, nylon or polyester are often used, as these fibers are less expensive than wool. The pile usually consists of twisted tufts that are typically heat-treated to maintain their structure. The term carpet is often used in a similar context to the term rug, but rugs are typically considered to be smaller than a room and not attached to the floor.

A monkey's fist or monkey paw is a type of knot, so named because it looks somewhat like a small bunched fist or paw. It is tied at the end of a rope to serve as a weight, making it easier to throw, and also as an ornamental knot. This type of weighted rope can be used as a hand-to-hand weapon, called a slungshot by sailors. It was also used in the past as an anchor in rock climbing, by stuffing it into a crack. It is still sometimes used today in sandstone, as in the Elbe Sandstone Mountains in Germany.

Macramé is a form of textile produced using knotting techniques.

A Persian carpet or Persian rug, also known as Iranian carpet, is a heavy textile made for a wide variety of utilitarian and symbolic purposes and produced in Iran, for home use, local sale, and export. Carpet weaving is an essential part of Persian culture and Iranian art. Within the group of Oriental rugs produced by the countries of the "rug belt", the Persian carpet stands out by the variety and elaborateness of its manifold designs.

In civil engineering, grade separation is a method of aligning a junction of two or more surface transport axes at different heights (grades) so that they will not disrupt the traffic flow on other transit routes when they cross each other. The composition of such transport axes does not have to be uniform; it can consist of a mixture of roads, footpaths, railways, canals, or airport runways. Bridges, tunnels, or a combination of both can be built at a junction to achieve the needed grade separation.

A kilim is a flat tapestry-woven carpet or rug traditionally produced in countries of the former Persian Empire, including Iran, the Balkans and the Turkic countries. Kilims can be purely decorative or can function as prayer rugs. Modern kilims are popular floor coverings in Western households.

A shawl is an Indian simple item of clothing, loosely worn over the shoulders, upper body and arms, and sometimes also over the head. It is usually a rectangular or square piece of cloth, which is often folded to make a triangle, but can also be triangular in shape. Other shapes include oblong shawls.
Ayin is the sixteenth letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician ʿayin, Hebrew ʿayinע, Aramaic ʿē, Syriac ʿē ܥ, and Arabic ʿayn ع.

In the field of road transport, an interchange or a grade-separated junction is a road junction that uses grade separations to allow for the movement of traffic between two or more roadways or highways, using a system of interconnecting roadways to permit traffic on at least one of the routes to pass through the junction without interruption from crossing traffic streams. It differs from a standard intersection, where roads cross at grade. Interchanges are almost always used when at least one road is a controlled-access highway or a limited-access divided highway (expressway), though they are sometimes used at junctions between surface streets.

A directional interchange, colloquially known as a stack interchange, is a type of grade-separated junction between two controlled-access highways that allows for free-flowing movement to and from all directions of traffic. These interchanges eliminate the problems of weaving, have the highest vehicle capacity, and vehicles travel shorter distances when compared different types of interchanges.
An oriental rug is a heavy textile made for a wide variety of utilitarian and symbolic purposes and produced in "Oriental countries" for home use, local sale, and export.

A chain-link fence is a type of woven fence usually made from galvanized or LLDPE-coated steel wire. The wires run vertically and are bent into a zig-zag pattern so that each "zig" hooks with the wire immediately on one side and each "zag" with the wire immediately on the other. This forms the characteristic diamond pattern seen in this type of fence.

Segmented turning, also known as polychromatic turning, is a form of woodturning on a lathe where the initial workpiece is composed of multiple parts glued together. The process involves gluing several pieces of wood to create patterns and visual effects in turned projects.

Brick Stitch, also known as the Cheyenne Stitch or Comanche Stitch, is a bead weaving stitch in which individual beads are stacked horizontally in the same pattern as bricks are stacked in a wall.

A knotted-pile carpet is a carpet containing raised surfaces, or piles, from the cut off ends of knots woven between the warp and weft. The Ghiordes/Turkish knot and the Senneh/Persian knot, typical of Anatolian carpets and Persian carpets, are the two primary knots. A flat or tapestry woven carpet, without pile, is a kilim. A pile carpet is influenced by width and number of warp and weft, pile height, knots used, and knot density.

Soumak is a tapestry technique of weaving sturdy, decorative fabrics used for rugs, domestic bags and bedding, with soumak fabrics used for bedding known as soumak mafrash.
Fashion in Iran is divided into several historical periods. The exact date of the emergence of weaving in Iran is not yet known, but it is likely that it coincides with the emergence of civilization. Clothing in Iran is mentioned in Persian mythology. Ferdowsi and many historians have considered Keyumars as the inventors of the use of animals' skin and hair as clothing, while some mention Hushang as the first inventor of the use of living skins as clothing. Ferdowsi considers Tahmuras as initiators of textiles in Iran. There are historical discoveries in northern Iran from about 6,000 BC that refer to wool weaving at the time. Other discoveries in central Iran dating back to 4200 BC have shown that the animal skin has not been the only clothing worn on the Iranian plateau. The clothing of ancient Iran took an advanced form, and the fabric and colour of clothing became very important. Depending on the social status, eminence, climate of the region and the season, Persian clothing during the Achaemenian period took various forms. The philosophy used in this clothing, in addition to being functional, also played an aesthetic role.

















