
In modern physics, antimatter is defined as matter which is composed of the antiparticles of the corresponding particles of 'ordinary' matter. Minuscule numbers of antiparticles are generated daily at particle accelerators – total production has been only a few nanograms – and in natural processes like cosmic ray collisions and some types of radioactive decay, but only a tiny fraction of these have successfully been bound together in experiments to form anti-atoms. No macroscopic amount of antimatter has ever been assembled due to the extreme cost and difficulty of production and handling.
A pet is an animal kept primarily for company, protection or entertainment.

Positron emission tomography (PET) is an imaging technique that uses radioactive substances to visualize and measure metabolic processes in the body. PET is mainly used in the area of medical imaging for detecting or measuring changes in physiological activities like metabolism, blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption, and therefore, also called a functional imaging technique.
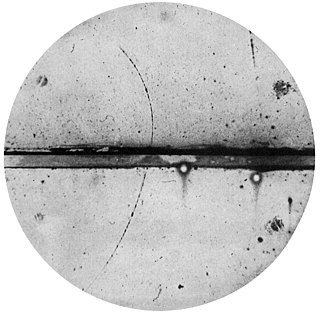
The positron or antielectron is the antiparticle or the antimatter counterpart of the electron. The positron has an electric charge of +1 e, a spin of 1/2, and has the same mass as an electron. When a positron collides with an electron, annihilation occurs. If this collision occurs at low energies, it results in the production of two or more photons.

The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN, is a European research organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, the organization is based in a northwest suburb of Geneva on the Franco–Swiss border and has 23 member states. Israel is the only non-European country granted full membership. CERN is an official United Nations Observer.
Aleph is the first letter of many Semitic abjads (alphabets).
A positronic brain is a fictional technological device, originally conceived by science fiction writer Isaac Asimov. It functions as a central processing unit (CPU) for robots, and, in some unspecified way, provides them with a form of consciousness recognizable to humans. When Asimov wrote his first robot stories in 1939 and 1940, the positron was a newly discovered particle, and so the buzz word "positronic" added a scientific connotation to the concept. Asimov's 1942 short story "Runaround" elaborates his fictional Three Laws of Robotics, which are ingrained in the positronic brains of nearly all of his robots.

Positron emission or beta plus decay is a subtype of radioactive decay called beta decay, in which a proton inside a radionuclide nucleus is converted into a neutron while releasing a positron and an electron neutrino (νe). Positron emission is mediated by the weak force. The positron is a type of beta particle (β+), the other beta particle being the electron (β−) emitted from the β− decay of a nucleus.
A supercollider is a high energy particle accelerator.

PAMELA was a cosmic ray research module attached to an Earth orbiting satellite. PAMELA was launched on 15 June 2006 and was the first satellite-based experiment dedicated to the detection of cosmic rays, with a particular focus on their antimatter component, in the form of positrons and antiprotons. Other objectives included long-term monitoring of the solar modulation of cosmic rays, measurements of energetic particles from the Sun, high-energy particles in Earth's magnetosphere and Jovian electrons. It was also hoped that it may detect evidence of dark matter annihilation. PAMELA operations were terminated in 2016, as were the operations of the host-satellite Resurs-DK1. The experiment was a recognized CERN experiment (RE2B).
There are 21 recognized isotopes of sodium (11Na), ranging from 18
Na to 39
Na and two isomers. 23
Na is the only stable isotope. It is considered a monoisotopic element and it has a standard atomic weight of 22.98976928(2). Sodium has two radioactive cosmogenic isotopes. With the exception of those two, all other isotopes have half-lives under a minute, most under a second. The shortest-lived is 18
Na, with a half-life of 1.3(4)×10−21 seconds.

The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, also designated AMS-02, is a particle physics experiment module that is mounted on the International Space Station (ISS). The experiment is a recognized CERN experiment (RE1). The module is a detector that measures antimatter in cosmic rays; this information is needed to understand the formation of the Universe and search for evidence of dark matter.

The Energetic Gamma Ray Experiment Telescope (EGRET) was one of four instruments outfitted on NASA's Compton Gamma Ray Observatory satellite. Since lower energy gamma rays cannot be accurately detected on Earth's surface, EGRET was built to detect gamma rays while in space. EGRET was created for the purpose of detecting and collecting data on gamma rays ranging in energy level from 30 MeV to 30 GeV.

iS: internal section is a video game developed by Positron and published by Square and released in 1999.
Positron Records is an independent record label based in Chicago, Illinois. The label was founded in 1998 by Chris Randall, frontman of the industrial band Sister Machine Gun. Positron describes itself as an "anti-label" because they release only a handful of albums and give as much support to each release as they can. The label also features a Creative Commons license for some of its albums, allowing individuals to upload those songs to peer-to-peer websites as well as sample parts of those songs for private or commercial usage.
Positron is a fixed shooter written by Gary Partis for the BBC Micro and Acorn Electron and published by Micro Power in 1983. It was developed on a pre-release Electron and was one of the few games available for the machine on its launch.

The Antiproton Decelerator (AD) is a storage ring at the CERN laboratory near Geneva. It was built as a successor to the Low Energy Antiproton Ring (LEAR) and started operation in the year 2000. Antiprotons are created by impinging a proton beam from the Proton Synchrotron on a metal target. The AD decelerates the resultant antiprotons to an energy of 5.3 MeV, which are then ejected to one of several connected experiments.

Tiny Tank is a third-person shooter platformer video game developed by AndNow and Appaloosa Interactive. Initially meant to be published by MGM Interactive, they dropped the title and gave it to Sony Computer Entertainment America. It was released on September 1, 1999 for the PlayStation.
This is the discography page for the industrial band Sister Machine Gun.

Ghostbusters is a 1990 platform shoot 'em up video game developed and published by Sega for the Sega Genesis/Mega Drive. It features an original story based on the Ghostbusters films, and is unrelated to a 1984 Ghostbusters game by Activision. The game was released in the United States in August 1990, and was released in the United Kingdom later that year. A Brazilian version by Tec Toy was released for the console in 1991.











