
SOAP is a messaging protocol specification for exchanging structured information in the implementation of web services in computer networks. It uses XML Information Set for its message format, and relies on application layer protocols, most often Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), although some legacy systems communicate over Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), for message negotiation and transmission.
A web service (WS) is either:
The Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards is a nonprofit consortium that works on the development, convergence, and adoption of open standards for cybersecurity, blockchain, Internet of things (IoT), emergency management, cloud computing, legal data exchange, energy, content technologies, and other areas.
The Web Services Business Process Execution Language (WS-BPEL), commonly known as BPEL, is an OASIS standard executable language for specifying actions within business processes with web services. Processes in BPEL export and import information by using web service interfaces exclusively.
XForms is an XML format used for collecting inputs from web forms. XForms was designed to be the next generation of HTML / XHTML forms, but is generic enough that it can also be used in a standalone manner or with presentation languages other than XHTML to describe a user interface and a set of common data manipulation tasks.
The Financial Information eXchange (FIX) protocol is an electronic communications protocol initiated in 1992 for international real-time exchange of information related to securities transactions and markets. With trillions of dollars traded annually on the NASDAQ alone, financial service entities are employing direct market access (DMA) to increase their speed to financial markets. Managing the delivery of trading applications and keeping latency low increasingly requires an understanding of the FIX protocol.
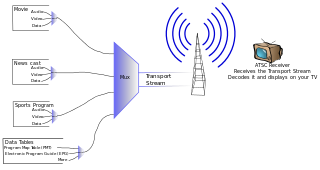
The Program and System Information Protocol (PSIP) is the MPEG and privately defined program-specific information originally defined by General Instrument for the DigiCipher 2 system and later extended for the ATSC digital television system for carrying metadata about each channel in the broadcast MPEG transport stream of a television station and for publishing information about television programs so that viewers can select what to watch by title and description. Its FM radio equivalent is Radio Data System (RDS).
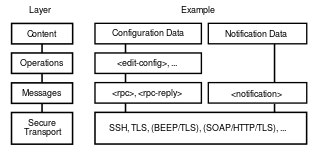
The Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF) is a network management protocol developed and standardized by the IETF. It was developed in the NETCONF working group and published in December 2006 as RFC 4741 and later revised in June 2011 and published as RFC 6241. The NETCONF protocol specification is an Internet Standards Track document.
The Common Information Model (CIM) is an open standard that defines how managed elements in an IT environment are represented as a common set of objects and relationships between them.
The Microsoft Open Specification Promise is a promise by Microsoft, published in September 2006, to not assert its patents, in certain conditions, against implementations of a certain list of specifications.
The Urban Traffic Management Control or UTMC programme is the main initiative in the United Kingdom for the development of a more open approach to Intelligent Transport Systems or ITS in urban areas. Originating as a Government research programme, the initiative is now managed by a community forum, the UTMC Development Group, which represents both local transport authorities and the systems industry.
TransXChange is a UK national XML based data standard for the interchange of bus route and timetable information between bus operators, the Vehicle and Operator Services Agency, local authorities and passenger transport executives, and others involved in the provision of passenger information.
The Standard Interface for Real-time Information or SIRI is an XML protocol to allow distributed computers to exchange real-time information about public transport services and vehicles.

The Web Services Description Language is an XML-based interface description language that is used for describing the functionality offered by a web service. The acronym is also used for any specific WSDL description of a web service, which provides a machine-readable description of how the service can be called, what parameters it expects, and what data structures it returns. Therefore, its purpose is roughly similar to that of a type signature in a programming language.
gSOAP is a C and C++ software development toolkit for SOAP/XML web services and generic XML data bindings. Given a set of C/C++ type declarations, the compiler-based gSOAP tools generate serialization routines in source code for efficient XML serialization of the specified C and C++ data structures. Serialization takes zero-copy overhead.
NeTEx is the CEN Technical standard for exchanging Public Transport Information as XML documents. It provides a W3C XML schema based on the Transmodel abstract model of common public transport concepts and data structures and can be used to exchange many different kinds of data between passenger information systems, including data describing for stops, facilities, timetabling and fares. Such data can be used by both operational management systems and customer facing systems for journey planning etc.
Datex II or Datex2 is a data exchange standard for exchanging traffic information between traffic management centres, traffic service providers, traffic operators and media partners. It contains for example traffic incidents, current road works and other special traffic-related events. These data is presented in XML-format and is modeled with UML. The standard is developed by the technical body Intelligent transport systems of the European Committee for Standardization.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.



