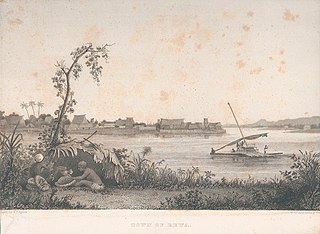Rotuma is a self-governing heptarchy, generally designated a dependency of Fiji. "Rotuma" commonly refers to Rotuma Island, the only permanently inhabited and by far the largest of all the islands in the Rotuma Group. Officially, the Rotuma Act declares that Rotuma consists of Rotuma Island as well as its neighbouring islands, rocks, and reefs across the entire Rotuma Group. The dependency is situated around 500 km west of the French islands of Wallis and Futuna and a similar distance north of the Fijian mainland. Its capital is Ahau, a hamlet consisting of a number of colonial-era buildings. Rotuma exists as a dependency of Fiji but itself contains its own socioreligious pene-enclave known traditionally as Faguta where the chiefs and their villages adhere to the practices of worship, festival dates, and French-based writing system of the Marists, based at Sumi.
Ratu is an Austronesian title used by male Fijians of chiefly rank. An equivalent title, adi, is used by females of chiefly rank. In the Malay language, the title ratu is also the traditional honorific title to refer to the ruling king or queen in Javanese culture. Thus in Java, a royal palace is called "keraton", constructed from the circumfix ke- -an and Ratu, to describe the residence of the ratu.
The House of Chiefs in Fiji consists of the Fijian nobility, composed of about seventy chiefs of various ranks, majority of which are related. It is not a formal political body and is not the same as the former Great Council of Chiefs, which was a political body with a prescribed constitutional role, although the membership of the two bodies did overlap to a great extent.
The culture of Fiji is a tapestry of native Fijian, Indian, European, Chinese and other nationalities. Culture polity traditions, language, food costume, belief system, architecture, arts, craft, music, dance, and sports will be discussed in this article to give you an indication of Fiji's indigenous community but also the various communities which make up Fiji as a modern culture and living. The indigenous culture is an active and living part of everyday life for the majority of the population.

Turaga na Vunivalu na Tui Kaba, shortened as Vunivalu, is the Paramount Chief of the Kubuna Confederacy of the island of Bau in Fiji. Loosely translated the title means Warlord of Bau or "Root of War". The succession to the title does not follow primogeniture, but the candidate must be a high-ranking member of the Tui Kaba clan.
Tui Nayau is the title held by the paramount chief of the Lau Islands in Fiji and is synonymous with the title holders over lordship of these islands. When translated, Tu’i Nayau means "Lord of Nayau", an island north of Lakeba.
RatuMeli Bolobolo was a Fijian chief and academic, who lectured at the Fiji Institute of Technology.
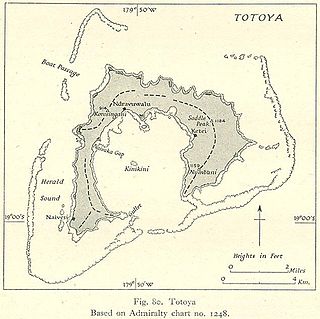
Totoya is a volcanic island in the Moala subgroup of Fiji's Lau archipelago. It occupies an area of 28 km2, making it the smallest of the Yasayasa Moala Group. Its maximum elevation is 366 metres above sea level. The main economic activity is coconut farming.
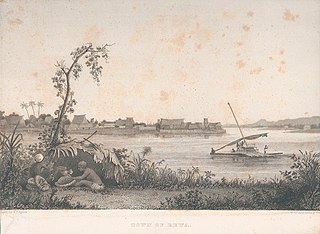
Rewa is a province of Fiji. With a land area of 272 square kilometers, it includes the capital city of Suva and is in two parts — one including part of Suva's hinterland to the west and a noncontiguous area to the east, separated from the rest of Rewa by Naitasiri Province. The province had a population of 108,016 at the 2017 census, making it Fiji's third most populous.

Lomaloma is a village at the south of the island of Vanua Balavu in the Lau archipelago of Fiji. The settlement is part of the tribal district of Tikina, Lomaloma and consists of 9 villages, 13 Yavusa (tribes), 42 Mataqali (clans), and 54 family units known as Tokatoka. The nine villages of Lomaloma Tikina are Lomaloma, Sawana, Susui, Narocivo, Namalata, Uruone, Levukana, Dakuilomaloma, and Tuvuca.
The Hupda are an Amazonian indigenous people who live in Brazil and Colombia. They speak the Hup language.

The Turu are an ethnic and linguistic group based in the Singida Region of north-central Tanzania who speak Bantu language Kinyaturu. In 1993, the Turu population was estimated to number 556,000. The current population of the Turu is now over 1,000,000. They speak the Turu language.
In Fijian, Turaga is the word for a man.
Fijian tradition and ceremony is a living way of life that has evolved as the Fijian nation has modernised over time, with various external influences from Pacific neighbours, and the European and Asian society. This general overview of various aspects of Fijian tradition, social structure and ceremony, much of it from the Bauan Fijian tradition although there are variations from province to province, uses "Fijian" to mean indigenous Fijians or I Taukei rather than all citizens of Fiji, and the Fijian terms are most often of the Bauan dialect. Many social intricacies depend on one's inherited social position and the occasion one is confronted with: each will have a particular social etiquette.
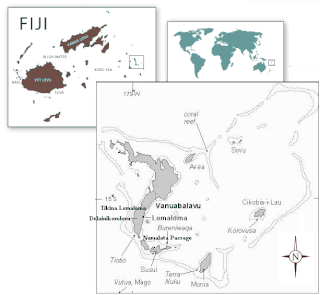
Turaga na Rasau is a traditional Fijian chiefly title of the Lau Islands. Prior to Fiji's colonial days, Fiji had many different Vanua with their own Paramount Chieftain which exercised no authority over the other; a saying from the island of Kadavu aptly summarises it "Nomu Turaga o sega na noqu Turaga" or "Your Chief is not my Chief" also the people of Beqa Island were of a similar opinion saying "Qali Cuva Ki Lagi" or "Subject only to heaven" and would bow to no outside Chieftain, but at the turn of the 20th century aspects of the traditional social structure remained, but for administrative purposes three main Matanitu were solidified and formed as they were the dominant consolidated powers at the time being that of Kubuna, Burebasaga and Tovata. With regard to the Rasau while its traditional origins were in Kubuna on Bau the titles traditional authority in modern Fiji is now in Tovata, Lau in particular Lomaloma Tikina on the Island of Vanua Balavu.
In many parts of West Africa, there is an old chieftaincy tradition, and the Akan people have developed their own hierarchy, which exists alongside the democratic structure of the country. The Akan word for the ruler or one of his various courtiers is "Nana". In colonial times, Europeans translated it as "chief", but that is not an exact equivalent. Other sources speak of "kings", which is also not entirely correct, especially in the case of the said courtiers. The term "chief" has become common even among modern Ghanaians, though it would be more correct to use the expression "Nana" without translation wherever possible.
Taukei ni Waluvu is a Fijian phrase for "Owner of the Flood." It is the traditional chiefly title of the warrior hill clan Siko-Natabutale of Nairukuruku village. The history of the clan from the mid- nineteenth century, represent the social structures of the chiefly system, religion and western culture that supported colonialism in Fiji. Tradition, Christianity and British indirect rule were combined to legitimize what was accepted as the right way to govern. Condemned by some modern day critics as exploitative, the Fijian chiefly system was the medium of native social interdependence and a traditional contract shared by the indigenous clans of pre-colonial Fiji, that was utilized for colonial rule. Since Independence the chiefly system has had to adapt to the demands of modernity. Anthropologist Arthur Capell in his study of early tribal migration within Fiji made the point that, "the history of Fiji is the history of chiefly families." The phrase in fact emphasized the hierarchical nature of Fijian traditional society where chiefly power was held sacred. The relationship between Chiefs and Westerners in especially Missionaries thus became a focal point for gathering insight into Fijian culture and tradition in the nineteenth century. James Turner a latter anthropologist found, "The chiefly families of Nairukuruku were the first in the eastern highlands of Viti Levu to declare their allegiance to the central government and as a result of this support their influence expanded throughout the area".
In Fiji, Turaga na Roko Tui Bau is a vassal chief of the Vunivalu of Bau. From his seat at the residence of Naicobocobo, the Roko Tui Bau rules the Vusaratu chiefs and has relationships with the Roko Tui Dreketi, Ratu Mai Verata, Roko Tui Namata, Roko Tui Veikau, Tui Vuya and other members of Fiji's House of Chiefs.

Camakau are a traditional watercraft of Fiji. Part of the broader Austronesian tradition, they are similar to catamarans, outrigger canoes, or smaller versions of the drua, but are larger than a takia. These vessels were built primarily for the purposes of travelling between islands and for trade. These canoes are single hulled, with an outrigger and a cama, a float, with both ends of the hull being symmetrical. They were very large, capable of travelling open ocean, and have been recorded as being up to 70 ft in length.

Navatu is a sub district in Cakaudrove; one of 3 provinces situated in Vanua Levu, the second largest island in Fiji. The sub-district, or "tikina" as it is known in the iTaukei language, comprises nine villages mainly occupying the eastern peninsular of the Natewa Bay. While Copra has been the main source of income for villages in the Navatu tikina, kava or yaqona is also becoming a fast growing commodity for villages within the Navatu sub-district.