
The United States Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) is a Cabinet department in the Executive branch of the United States federal government. Although its beginnings were in the House and Home Financing Agency, it was founded as a Cabinet department in 1965, as part of the "Great Society" program of President Lyndon Johnson, to develop and execute policies on housing and metropolises.
The Low-Income Housing Tax Credit is a dollar-for-dollar tax credit in the United States for affordable housing investments. It was created under the Tax Reform Act of 1986 (TRA86) and gives incentives for the utilization of private equity in the development of affordable housing aimed at low-income Americans. LIHTC accounts for the majority of all affordable rental housing created in the United States today. As the maximum rent that can be charged is based upon the Area Median Income ("AMI"), LIHTC housing remains unaffordable to many low-income renters. The credits are also commonly called Section 42 credits in reference to the applicable section of the Internal Revenue Code. The tax credits are more attractive than tax deductions as the credits provide a dollar-for-dollar reduction in a taxpayer's federal income tax, whereas a tax deduction only provides a reduction in taxable income. The "passive loss rules" and similar tax changes made by TRA86 greatly reduced the value of tax credits and deductions to individual taxpayers. Less than 10% of current credit expenditures are claimed by individual investors.
The term New Frontier was used by Democratic presidential candidate John F. Kennedy in his acceptance speech in the 1960 United States presidential election to the Democratic National Convention at the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum as the Democratic slogan to inspire America to support him. The phrase developed into a label for his administration's domestic and foreign programs.
We stand today on the edge of a New Frontier—the frontier of the 1960s, the frontier of unknown opportunities and perils, the frontier of unfilled hopes and unfilled threats. ... Beyond that frontier are uncharted areas of science and space, unsolved problems of peace and war, unconquered problems of ignorance and prejudice, unanswered questions of poverty and surplus.
Section 8 of the Housing Act of 1937, often called Section 8, as repeatedly amended, authorizes the payment of rental housing assistance to private landlords on behalf of approximately 4.8 million low-income households, as of 2008, in the United States. The largest part of the section is the Housing Choice Voucher program which pays a large portion of the rents and utilities of about 2.1 million households. The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development manages Section 8 programs.
New Community Corporation (NCC) is a not-for-profit community development corporation based in Newark, New Jersey. NCC focuses on community organizing, provision of a variety of community-enhancing services, and resident participation in agency operation. Early prototypes of the community action movement included local housing and service agencies started by the Ford Foundation Gray Areas Initiative and the United States Office of Economic Opportunity, and the federal / private Mobilization for Youth in New York City.
The HOME Investment Partnerships Program (HOME) is a type of United States federal assistance provided by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) to States in order to provide decent and affordable housing, particularly housing for low- and very low-income Americans. It is the largest Federal block grant to States and local governments designed exclusively to create affordable housing for low-income families, providing approximately US$2 billion each year.
Secondary suite is an urban planning term used mainly in North American English for a self-contained apartment in an owner occupied single-family home / lot that is either attached to the principal dwelling or in a separate structure on the same property. In British English the term "annexe" is used instead. Reasons for wanting to add a secondary suite to a property may be to receive additional income, provide social and personal support to a family member, or obtain greater security.

The Texas Department of Housing and Community Affairs (TDHCA) is the state's lead agency responsible for homeownership, affordable rental housing, community and energy assistance programs, and colonia activities serving primarily low income Texans. The Manufactured Housing Division of TDHCA regulates the manufactured housing industry in Texas.

Public housing in the United States is administered by federal, state and local agencies to provide subsidized assistance for low-income households. Public housing is priced much below the market rate, allowing people to live in more convenient locations rather than move away from the city in search of lower rents. Now increasingly provided in a variety of settings and formats, originally public housing in the U.S. consisted primarily of one or more concentrated blocks of low-rise and/or high-rise apartment buildings. These complexes are operated by state and local housing authorities which are authorized and funded by the United States Department of Housing and Urban Development. More than 1.2 million households currently live in public housing of some type.
Section 523 loans are a mutual self-help rural housing program authorized under Section 523 of the Housing Act of 1949 and administered by the Rural Housing Service (RHS). Nonprofit organizations may obtain 2-year loans to purchase and develop land that is to be subdivided into building sites for housing. The interest rate is 3% for these loans. Applicants must demonstrate a need for the proposed building sites in the locality. Sponsors also may obtain technical assistance (TA) grants to pay for all or part of the cost of developing, administering, and coordinating programs of technical and supervisory assistance to the families who are building their own homes. Each family is expected to contribute at least 700 hours of labor in building homes for each other. Applicants must demonstrate that:
Section 521 rental assistance is rental assistance authorized under Section 521 of the Housing Act of 1949. Owners of housing financed under Section 515 or Section 514 may receive rental assistance payments from the Rural Housing Service (RHS). The assistance payments enable eligible tenants to make monthly rent payments that do not exceed the greater of: (1) 30% of monthly adjusted family income; (2) 10 percent of monthly income; or, (3) the portion of the family’s welfare payment that is designated for housing costs. The rental assistance payments, which are made directly to the borrowers, make up the difference between the tenants’ payments and the RHS-approved rent for the units. Borrowers must agree to operate the property on a limited profit or nonprofit basis. The term of the rental assistance agreement is 20 years for new construction projects and 5 years for existing projects. Agreements may be renewed for up to 5 years. An eligible borrower who does not participate in the program may be petitioned to participate by 20 percent or more of the tenants eligible for rental assistance.
Section 502 loans are a rural housing loan program, administered by the Rural Housing Service (RHS), authorized under Section 502 of the Housing Act of 1949. Borrowers may obtain loans for purchasing or repairing new or existing single-family housing. Loans are made directly by RHS or by private lenders with a USDA guarantee. Borrowers with income of 80% or less of the area median may be eligible for 33- year direct loans and may receive interest credit to bring the interest rate to as low as 1%. In a given fiscal year, at least 40% of the units financed under this section must be made available only to very low-income families or individuals with terms up to 38 years. Borrowers must have the means to repay the loans, but be unable to secure reasonable credit terms elsewhere. Borrowers with income of up to 115% of the area median may be eligible for 30-year guaranteed loans from private lenders. Priority is given to first-time home buyers, and the RHS may require that borrowers complete a home ownership counseling program.
The Pennsylvania Department of Aging is a cabinet-level agency charged with providing aid to Pennsylvania's approximately 3 million individuals age 60 and older. Although the bureau operates some services directly, such as the Pharmaceutical Contact for the Elderly (PACE) prescription drug program, it generally serves as a clearinghouse of funding and information for county-level Area Agencies on Aging. The department was formed under the governorship of Milton Shapp.
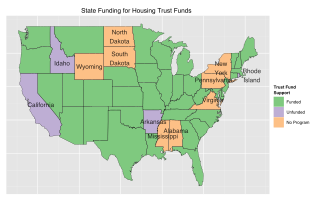
Housing trust funds are established sources of funding for affordable housing construction and other related purposes created by governments in the United States (U.S.). Housing Trust Funds (HTF) began as a way of funding affordable housing in the late 1970s. Since then, elected government officials from all levels of government in the U.S. have established housing trust funds to support the construction, acquisition, and preservation of affordable housing and related services to meet the housing needs of low-income households. Ideally, HTFs are funded through dedicated revenues like real estate transfer taxes or document recording fees to ensure a steady stream of funding rather than being dependent on regular budget processes. As of 2016, 400 state, local and county trust funds existed across the U.S.

A USDA Home Loan from the USDA loan program, also known as the USDA Rural Development Guaranteed Housing Loan Program, is a mortgage loan offered to rural property owners by the United States Department of Agriculture.

Howard County Housing is the umbrella organization for the Howard County Department of Housing and Community Development and the Howard County Housing Commission. The Department is Howard County Government’s housing agency and the Commission is a public housing authority and non-profit. Both have boards that meet monthly.
The Texas State Affordable Housing Corporation (TSAHC) is a nonprofit affordable housing provider in Texas.
The Rental Assistance Demonstration is a federal housing program that was enacted as part of the Consolidated and Further Continuing Appropriations Act, 2012, and is administered by the U.S. Department of Housing & Urban Development (HUD). Broadly, the purpose of the Rental Assistance Demonstration is to provide a set of tools to address the unmet capital needs of deeply affordable, federally assisted rental housing properties in order to maintain both the viability of the properties and their long-term affordability. It also simplifies the administrative oversight of the properties by the federal government. Specifically, RAD authorizes the conversion of a property's federal funding from one form to another, where the initial form presents structural impediments to private capital investment and the new form is not only familiar to lenders and investors but, since its enactment in 1974, has leveraged billions in private investment for the development and rehabilitation of deeply affordable rental housing.
Affordable housing is housing which is deemed affordable to those with a median household income as rated by the national government or a local government by a recognized housing affordability index. The challenges of promoting affordable housing varies by location.







