| Look up seizure in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Seizure may refer to:
| Look up seizure in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Seizure may refer to:

Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. These episodes can result in physical injuries, either directly such as broken bones or through causing accidents. In epilepsy, seizures tend to recur and may have no immediate underlying cause. Isolated seizures that are provoked by a specific cause such as poisoning are not deemed to represent epilepsy. People with epilepsy may be treated differently in various areas of the world and experience varying degrees of social stigma due to their condition.

An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with loss of consciousness, to shaking movements involving only part of the body with variable levels of consciousness, to a subtle momentary loss of awareness. Most of the time these episodes last less than two minutes and it takes some time to return to normal. Loss of bladder control may occur.

A convulsion is a medical condition where body muscles contract and relax rapidly and repeatedly, resulting in uncontrolled shaking. Because epileptic seizures typically include convulsions, the term convulsion is sometimes used as a synonym for seizure. However, not all epileptic seizures lead to convulsions, and not all convulsions are caused by epileptic seizures. Convulsions are also consistent with an electric shock and improper enriched air scuba diving. For non-epileptic convulsions, see non-epileptic seizures.
Trigger may refer to:
Embrace may refer to:
Epilepsia partialis continua is a rare type of brain disorder in which a patient experiences recurrent motor epileptic seizures that are focal, and recur every few seconds or minutes for extended periods.

Psychogenic non-epileptic seizures (PNES) are events resembling an epileptic seizure, but without the characteristic electrical discharges associated with epilepsy. PNES fall under the category of disorders known as functional neurological disorders (FND), also known as conversion disorders. A more recent term to describe these events is dissociative non-epileptic seizures. These are typically treated by psychologists or psychiatrists. The terms pseudoseizure, psychogenic seizure and hysterical seizure are older terms that have been used for PNES in the past and should not be used today.
Non-epileptic seizures (NES), also known as non-epileptic events, are paroxysmal events that appear similar to an epileptic seizure but do not involve abnormal, rhythmic discharges of neurons in the brain. Symptoms may include shaking, loss of consciousness, and loss of bladder control.
Breakthrough or break through may refer to:

Temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) is a chronic disorder of the nervous system which is characterized by recurrent, unprovoked focal seizures that originate in the temporal lobe of the brain and last about one or two minutes. TLE is the most common form of epilepsy with focal seizures. A focal seizure in the temporal lobe may spread to other areas in the brain when it may become a focal to bilateral seizure.
Frontal lobe epilepsy (FLE) is a neurological disorder that is characterized by brief, recurring seizures that arise in the frontal lobes of the brain, often while the patient is sleeping. It is the second most common type of epilepsy after temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE), and is related to the temporal form by the fact that both forms are characterized by the occurrence of partial (focal) seizures. Partial seizures occurring in the frontal lobes can occur in one of two different forms: either simple partial seizures or complex partial seizures. The symptoms and clinical manifestations of frontal lobe epilepsy can differ depending on which specific area of the frontal lobe is affected.

A seizure response dog (SRD) is a dog demonstrating specific assisting behaviour during or immediately after a person's epileptic seizure or other seizure. When reliably trained such dogs can serve as service dogs for people with epilepsy. Tasks for seizure dogs may include, but are not limited to:
Myoclonic epilepsy refers to a family of epilepsies that present with myoclonus. When myoclonic jerks are occasionally associated with abnormal brain wave activity, it can be categorized as myoclonic seizure. If the abnormal brain wave activity is persistent and results from ongoing seizures, then a diagnosis of myoclonic epilepsy may be considered.
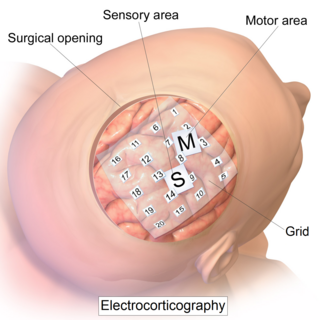
Electrocorticography (ECoG), or intracranial electroencephalography (iEEG), is a type of electrophysiological monitoring that uses electrodes placed directly on the exposed surface of the brain to record electrical activity from the cerebral cortex. In contrast, conventional electroencephalography (EEG) electrodes monitor this activity from outside the skull. ECoG may be performed either in the operating room during surgery or outside of surgery. Because a craniotomy is required to implant the electrode grid, ECoG is an invasive procedure.
Seizure types most commonly follow the classification proposed by the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) in 1981. These classifications have been updated in 2017. Distinguishing between seizure types is important since different types of seizure may have different causes, outcomes and treatments.
Racine stages are a categorization of epileptic seizures proposed by Ronald J. Racine in 1972. Prior to Racine's research in epilepsy, a quantifiable means to describe seizure intensities and their causes was not readily available. Racine's work allowed for epilepsy to be understood on a level previously thought impossible.

Generalized epilepsy is a form of epilepsy characterised by generalised seizures with no apparent cause. Generalized seizures, as opposed to focal seizures, are a type of seizure that impairs consciousness and distorts the electrical activity of the whole or a larger portion of the brain.
Ohtahara syndrome (OS), also known as early infantile epileptic encephalopathy (EIEE) is a progressive epileptic encephalopathy. The syndrome is outwardly characterized by tonic spasms and partial seizures within the first few months of life, and receives its more elaborate name from the pattern of burst activity on an electroencephalogram (EEG). It is an extremely debilitating progressive neurological disorder, involving intractable seizures and severe intellectual disabilities. No single cause has been identified, although in many cases structural brain damage is present.
Epilepsy and driving is a personal and safety issue. A person with a seizure disorder that causes lapses in consciousness may be putting the public at risk from their operation of a motor vehicle. Not only can a seizure itself cause an accident, but anticonvulsants often have side effects that include drowsiness. People with epilepsy are more likely to be involved in a traffic accident than people who do not have the condition, although reports range from minimally more likely up to seven times more likely.
Migralepsy is a rare condition in which a migraine is followed, within an hour period, by an epileptic seizure. Because of the similarities in signs, symptoms, and treatments of both conditions, such as the neurological basis, the psychological issues, and the autonomic distress that is created from them, they individually increase the likelihood of causing the other. However, also because of the sameness, they are often misdiagnosed for each other, as migralepsy rarely occurs.