A paymaster is someone appointed by a group of buyers, sellers, investors or lenders to receive, hold, and dispense funds, commissions, fees, salaries (renumeration) or other trade, loan, or sales proceeds within the private sector or public sector. Specific titles within the British government are Paymaster of the Forces, Paymaster-General and Paymaster of Pensions.
A pay-as-you-earn tax (PAYE) or pay-as-you-go is a withholding tax on income payments to employees. Amounts withheld are treated as advance payments of income tax due. They are refundable to the extent they exceed tax as determined on tax returns. PAYE may include withholding the employee portion of insurance contributions or similar social benefit taxes. In most countries, they are determined by employers but subject to government review. PAYE is deducted from each paycheck by the employer and must be remitted promptly to the government. Most countries refer to income tax withholding by other terms, including pay-as-you-go tax.
Unemployment benefits are payments made by authorized bodies to unemployed people. In the United States, benefits are funded by a compulsory governmental insurance system, not taxes on individual citizens. Depending on the jurisdiction and the status of the person, those sums may be small, covering only basic needs, or may compensate the lost time proportionally to the previous earned salary.
Self-insurance is a situation in which a person or business does not take out any third-party insurance, but rather a business that is liable for some risk, such as health costs, chooses to bear the risk itself rather than take out insurance through an insurance company.
Garnishment is a legal process for collecting a monetary judgment on behalf of a plaintiff from a defendant. Garnishment allows the plaintiff to take the money or property of the debtor from the person or institution that holds that property. A similar legal mechanism called execution allows the seizure of money or property held directly by the debtor.
A stipend is a regular fixed sum of money paid for services or to defray expenses, such as for scholarship, internship, or apprenticeship. It is often distinct from an income or a salary because it does not necessarily represent payment for work performed; instead it represents a payment that enables somebody to be exempt partly or wholly from waged or salaried employment in order to undertake a role that is normally unpaid or voluntary, or which cannot be measured in terms of a task .
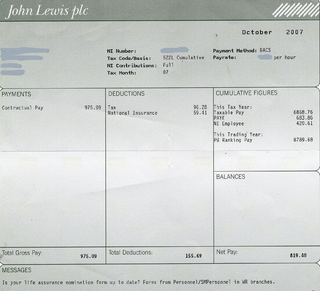
A paycheck, also spelled pay check or pay cheque, is traditionally a paper document issued by an employer to pay an employee for services rendered. In recent times, the physical paycheck has been increasingly replaced by electronic direct deposits to the employee's designated bank account or loaded onto a payroll card. Employees may still receive a pay slip to detail the calculations of the final payment amount.
Union dues are a regular payment of money made by members of unions. Dues are the cost of membership; they are used to fund the various activities which the union engages in. Nearly all unions require their members to pay dues.
Social Security Disability Insurance is a payroll tax-funded federal insurance program of the United States government. It is managed by the Social Security Administration and designed to provide income supplements to people who are physically restricted in their ability to be employed because of a notable disability. SSD can be supplied on either a temporary or permanent basis, usually directly correlated to whether the person's disability is temporary or permanent.

A work-at-home scheme is a get-rich-quick scam in which a victim is lured by an offer to be employed at home, very often doing some simple task in a minimal amount of time with a large amount of income that far exceeds the market rate for the type of work. The true purpose of such an offer is for the perpetrator to extort money from the victim, either by charging a fee to join the scheme, or requiring the victim to invest in products whose resale value is misrepresented.
The Inland Revenue or Inland Revenue Department is the public service department of New Zealand charged with advising the government on tax policy, collecting and disbursing payments for social support programmes, and collecting tax.
Social security, in Australia, refers to a system of social welfare payments provided by Commonwealth Government of Australia. These payments are administered by Centrelink, a branch of the Department of Human Services. In Australia, most benefits are means tested.
This article includes information about the child support policies of several countries.
42 U.S.C. § 652(k) is a United States law sometimes requires the denial or revocation of passports for individuals who are fail to pay child support. The law was enacted as part of the Personal Responsibility and Work Opportunity Act in 1996.

The Paycheck Fairness Act is a proposed United States labor law that would add procedural protections to the Equal Pay Act of 1963 and the Fair Labor Standards Act as part of an effort to address the gender pay gap in the United States. A Census Bureau report published in 2008 stated that women's median annual earnings were 77.5% of men's earnings. However, newer studies suggest that when the data is controlled for certain variables, the residual gap is around 5-7%; the same study concludes that the residual is because "hours of work in many occupations are worth more when given at particular moments and when the hours are more continuous. That is, in many occupations, earnings have a nonlinear relationship with respect to hours."
The British Columbia Family Maintenance Enforcement Program (FMEP) is a Provincial Government service established by the British Columbia Ministry of Justice in 1988, and currently administered by the Ministry of Attorney General. The program monitors and enforces maintenance orders and agreements for child support and spousal support. Annually, the program assists approximately 45,000 families, 58,000 children and collects and disburses over $200 million (CAD) in maintenance payments each year.
The Office of Child Support Enforcement (OCSE) is a United States government office responsible for overseeing the U.S. child support program. Child support is the obligation on parents to provide financial support for their children. OCSE was established with the Federal Government’s enactment of Child Support Enforcement and Paternity Establishment Program (CSE) in 1975, which was enacted to reduce welfare expenses by collecting child support from non-custodial parents.
In the United States, the combination of payroll taxes withheld from a household employee and the employment taxes paid by their employer are commonly referred to as the nanny tax. Under US law, any family or individual that pays a household employee more than $2,100 a year must withhold and pay Social Security and Medicare taxes, also known as FICA. The law mandates that all domestic workers, such as cooks, nannies, housekeepers and gardeners, are subject to the nanny tax. Federal unemployment insurance taxes must also be paid if the household pays any number of employees a total of $1,000 or more in a calendar quarter. State unemployment insurance taxes have the same requirement with the exceptions of California ($750), New York ($500), and Washington, D.C. ($500) have lower thresholds.

The Adoption Assistance and Child Welfare Act of 1980 (AACWA) was enacted by the US Government on June 17, 1980. Its purpose is to establish a program of adoption assistance; strengthen the program of foster care assistance for needy and dependent children; and improve the child welfare, social services, and aid to families with dependent children programs. This act amended titles IV-B and XX of the Social Security Act.




