
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amine (-NH2) and carboxyl (-COOH) functional groups, along with a side chain (R group) specific to each amino acid. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N), although other elements are found in the side chains of certain amino acids. About 500 naturally occurring amino acids are known (though only 20 appear in the genetic code) and can be classified in many ways. They can be classified according to the core structural functional groups' locations as alpha- (α-), beta- (β-), gamma- (γ-) or delta- (δ-) amino acids; other categories relate to polarity, pH level, and side chain group type (aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid residues form the second-largest component (water is the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis.

Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. Biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life.

Metabolism is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main purposes of metabolism are: the conversion of food to energy to run cellular processes; the conversion of food/fuel to building blocks for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of nitrogenous wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments..

Proteins are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells, and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity.

Phenylalanine is an essential α-amino acid with the formula C
9H
11NO
2. It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of alanine. This essential amino acid is classified as neutral, and nonpolar because of the inert and hydrophobic nature of the benzyl side chain. The L-isomer is used to biochemically form proteins, coded for by DNA. Phenylalanine is a precursor for tyrosine, the monoamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), and the skin pigment melanin. It is encoded by the codons UUU and UUC.

Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula HO2CCH(NH2)CH2SH. The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions, as a nucleophile. The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. When used as a food additive, it has the E number E920. It is encoded by the codons UGU and UGC.

The chickpea or chick pea is an annual legume of the family Fabaceae, subfamily Faboideae. Its different types are variously known as gram or Bengal gram, garbanzo or garbanzo bean, Egyptian pea, chana, and chole. Chickpea seeds are high in protein. It is one of the earliest cultivated legumes, and 7500-year-old remains have been found in the Middle East.

A protease is an enzyme that catalyzes proteolysis, the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids. They do this by cleaving the peptide bonds within proteins by hydrolysis, a reaction where water breaks bonds. Proteases are involved in many biological functions, including digestion of ingested proteins, protein catabolism, and cell signalling.

Methionine is an essential amino acid in humans. As the substrate for other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical role in the metabolism and health of many species, including humans. It is encoded by the codon AUG.

Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain lysyl ((CH2)4NH2), classifying it as a basic, charged (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is encoded by the codons, AAA and AAG. Like almost all other amino acids, the α-carbon is chiral and lysine may refer to either enantiomer or a racemic mixture of both. For the purpose of this article, lysine will refer to the biologically active enantiomer L-lysine, where the α-carbon is in the S configuration.

Vegetarian nutrition is the set of health-related challenges and advantages of vegetarian diets.

Phytic acid is a six-fold dihydrogenphosphate ester of inositol, also called inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) or inositol polyphosphate. At physiological pH, the phosphates are partially ionized, resulting in the phytate anion.

A coffee bean is a seed of the Coffea plant and the source for coffee. It is the pit inside the red or purple fruit often referred to as a cherry. Just like ordinary cherries, the coffee fruit is also a so-called stone fruit. Even though the coffee beans are not technically beans, they are referred to as such because of their resemblance to true beans. The fruits – coffee cherries or coffee berries – most commonly contain two stones with their flat sides together. A small percentage of cherries contain a single seed, instead of the usual two. This is called a "peaberry". The peaberry occurs only between 10 and 15% of the time, and it is a fairly common belief that they have more flavour than normal coffee beans. Like Brazil nuts and white rice, coffee beans consist mostly of endosperm.

A phytase is any type of phosphatase enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of phytic acid – an indigestible, organic form of phosphorus that is found in grains and oil seeds – and releases a usable form of inorganic phosphorus. While phytases have been found to occur in animals, plants, fungi and bacteria, phytases have been most commonly detected and characterized from fungi.

Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All the proteins of the albumin family are water-soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Albumins are commonly found in blood plasma and differ from other blood proteins in that they are not glycosylated. Substances containing albumins are called albuminoids.
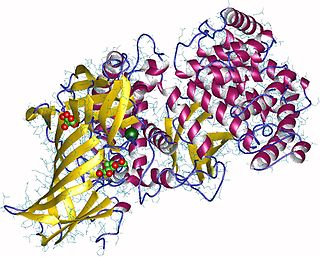
Aminopeptidases are enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of amino acids from the amino terminus (N-terminus) of proteins or peptides (exopeptidases).They are widely distributed throughout the animal and plant kingdoms and are found in many subcellular organelles, in cytosol, and as membrane components. Aminopeptidases are used in essential cellular functions. Many, but not all, of these peptidases are zinc metalloenzymes.
Prolamins are a group of plant storage proteins having a high proline amino acid content. They are found in plants, mainly in the seeds of cereal grains such as wheat (gliadin), barley (hordein), rye (secalin), corn (zein), sorghum (kafirin), and oats (avenin). They are characterised by a high glutamine and proline content, and have poor solubility in water. They solubilise best in strong alcohol [70-80%], light acid, and alkaline solutions. The prolamins of the tribe Triticeae, such as wheat gliadin, and related proteins are known to trigger coeliac disease, an autoimmune condition, in genetically predisposed individuals.
Soy protein is a protein that is isolated from soybean. It is made from soybean meal that has been dehulled and defatted. Dehulled and defatted soybeans are processed into three kinds of high protein commercial products: soy flour, concentrates, and isolates. Soy protein isolate has been used since 1959 in foods for its functional properties.

F-box proteins are proteins containing at least one F-box domain. The first identified F-box protein is one of three components of the SCF complex, which mediates ubiquitination of proteins targeted for degradation by the 26S proteasome.

Zingibain, zingipain, or ginger protease is a cysteine protease enzyme found in ginger rhizomes. It catalyses the preferential cleavage of peptides with a proline residue at the P2 position. It has two distinct forms, ginger protease I (GP-I) and ginger protease II (GP-II).















