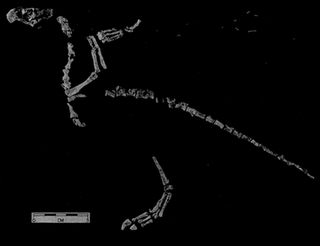
Protoavis is a problematic taxon known from fragmentary remains from Late Triassic Norian stage deposits near Post, Texas. The animal's true classification has been the subject of much controversy, and there are many different interpretations of what the taxon actually is. When it was first described, the fossils were described as being from a primitive bird which, if the identification is valid, would push back avian origins some 60-75 million years.
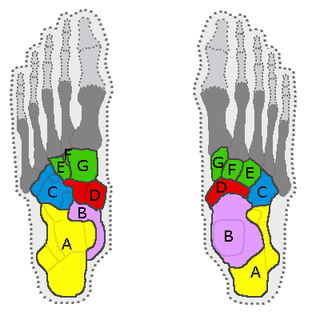
In the human body, the tarsus is a cluster of seven articulating bones in each foot situated between the lower end of the tibia and the fibula of the lower leg and the metatarsus. It is made up of the midfoot and hindfoot.

Avisaurus is a genus of enantiornithine bird from the Late Cretaceous of North America.

Hulsanpes is a genus of halszkaraptorine theropod dinosaurs that lived during the Late Cretaceous in what is now the Barun Goyot Formation of Mongolia, about 75-72 million years ago. The remains were found in 1970 and formally described in 1982 by Halszka Osmólska, who noted that the genus is represented by an immature individual. Hulsanpes represents the first record of the basal dromaeosaurid subfamily Halszkaraptorinae.

Sapeornis is a monotypic genus of avialan dinosaurs which lived during the early Cretaceous period. Sapeornis contains only one species, Sapeornis chaoyangensis.

Yungavolucris is a genus of enantiornithean birds. It contains the single species Yungavolucris brevipedalis, which lived in the Late Cretaceous. The fossil bones were found in the Lecho Formation at estancia El Brete, Argentina."Yungavolucris brevipedalis" means "Short-footed Yungas bird". The generic name, Yungavolucris is after the Yungas region + the Latin volucris, which translates to "bird". The specific name brevipedalis is from the Latin brevis, which means "short", + pedalis, from the Latin pes, meaning "foot".
The tibiotarsus is the large bone between the femur and the tarsometatarsus in the leg of a bird. It is the fusion of the proximal part of the tarsus with the tibia.

Glacialisaurus is a genus of sauropodomorph dinosaur. It lived during the Pliensbachian stage of the Early Jurassic period around 186 to 182 million years ago in what is now the central region of the Transantarctic Mountains of Antarctica. It is known from two specimens; the holotype, a partial tarsus (ankle) and metatarsus, and a partial left femur. The fossils were collected by a team led by paleontologist William R. Hammer during a 1990–91 field expedition to the Hanson Formation of Antarctica. They were described in 2007, and made the basis of the new genus and species Glacialisaurus hammeri. The genus name translates as “icy” or "frozen lizard”, and the species name honors Hammer.

Avisauridae is a family of extinct enantiornithine dinosaurs from the Cretaceous period, distinguished by several features of their ankle bones. Depending on the definition used, Avisauridae is either a broad and widespread group of advanced enantiornithines, or a small family within that group, restricted to species from the Late Cretaceous of North and South America.

Ceratonykus is a monospecific genus of alvarezsaurid dinosaur from Mongolia that lived during the Late Cretaceous in what is now the Barun Goyot Formation. The type and only species, Ceratonykus oculatus, is known from a fragmentary skeleton, including an incomplete skull, of an adult individual. It was named and described in 2009 by Vladimir Alifanov and Rinchen Barsbold. Its describers questioned the traditional placement of alvarezsaurs in Theropoda, instead suggesting they were ornithischians, but this has not been accepted since. Ceratonykus has an estimated length of 75 centimetres and weight of 760 grams. It has been considered as a possible junior synonym of Parvicursor.

Balaur is a genus of theropod dinosaur from the late Cretaceous period, in what is now Romania. It is the type species of the monotypic genus Balaur, after the balaur, a dragon of Romanian folklore. The specific name bondoc means "stocky", so Balaur bondoc means "stocky dragon" in Romanian. This name refers to the greater musculature that Balaur had compared to its relatives. The genus, which was first described by scientists in August 2010, is known from two partial skeletons.

Bauxitornis is an extinct genus of avisaurid enantiornithean birds which lived in what is now Hungary during the late Cretaceous period. Although first mentioned in a 2008 review of Hungarian Cretaceous bird fossils, it was named in a more comprehensive review by Gareth J. Dyke and Attila Ősi in 2010. The type species is Bauxitornis mindszentyae. The generic name "Bauxitornis" refers to the locality at which it was discovered, a Bauxite mine. The specific name "mindszentyae" honors Andrea Mindszenty, Ősi's advisor.

Albinykus is a genus of alvarezsaurid dinosaur. Fossils have been found from Late Cretaceous-age (Santonian) Javkhlant Formation in the Gobi Desert of Mongolia. The type species A. baatar was named by Sterling J. Nesbitt, Julia A. Clarke, Alan H. Turner and Mark A. Norell in 2011.

Pamparaptor is an extinct genus of maniraptoran theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Portezuelo Formation of the Neuquén province in Argentine Patagonia. Its precise classification is uncertain, but it is definitely a member of Paraves and probably a deinonychosaur. The authors who described it have argued that it is a dromaeosaurid. The genus contains a single species, P. micros, which is known from a single specimen consisting of a mostly complete and fully-articulated left foot, which preserves the iconic dromaeosaur-like “killing claw”.

Philovenator is an extinct genus of troodontid paravian dinosaurs from the Wulansuhai Formation of Inner Mongolia, China. Its specific name honors Phillip J. Currie.

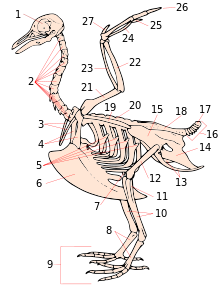
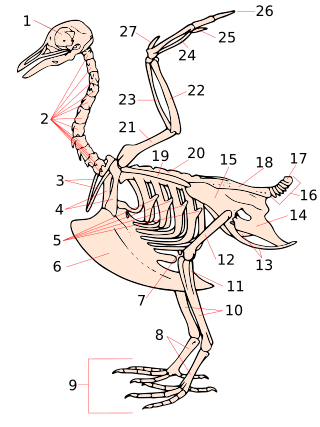
The anatomy of bird legs and feet is diverse, encompassing many accommodations to perform a wide variety of functions.

Zhongjianosaurus is a genus of dromaeosaurid belonging to the Microraptoria. Believed to hail from the Yixian Formation, specifically the middle of the Jehol Biota, it is the smallest known microraptorine thus far discovered and one of the smallest non-avian theropod dinosaurs.
Gettyia is an extinct genus of avisaurid enantiornithean bird from the Late Cretaceous of North America.

Imperobator is a genus of paravian theropod, a group of large, three-toed carnivorous dinosaurs, that lived during the Maastrichtian age of the Late Cretaceous period in what is now James Ross Island in Antarctica. Imperobator is one of only two non-avian theropods known from Antarctica, crossing over to the landmass when it was part of Gondwana. The only described specimen was found in 2003 by an expedition launched by the University of California Museum of Paleontology and initially described as a dromaeosaur in 2007. However, later searches reported more fossils from the site including teeth and skull bones. The fossils were formally described as a new genus of giant paravian in 2019.
Citipes is an extinct genus of caenagnathid theropod from the Late Cretaceous Dinosaur Park Formation in Alberta, Canada. The genus contains only one species, the type species, C. elegans. The generic name of Citipes is Latin for "fleet-footed", and the specific epithet "elegans" is Latin for "elegant". The type specimen of Citipes has a convoluted taxonomic history, and has been previously assigned to the genera Ornithomimus, Macrophalangia, Elmisaurus, Chirostenotes, and Leptorhynchos before being given its own genus in 2020.