Tellurium iodide may refer to:
- Tellurium monoiodide, TeI
- Tellurium tetraiodide, TeI4
Tellurium iodide may refer to:

Tellurium is a chemical element with the symbol Te and atomic number 52. It is a brittle, mildly toxic, rare, silver-white metalloid. Tellurium is chemically related to selenium and sulfur, all three of which are chalcogens. It is occasionally found in native form as elemental crystals. Tellurium is far more common in the Universe as a whole than on Earth. Its extreme rarity in the Earth's crust, comparable to that of platinum, is due partly to its formation of a volatile hydride that caused tellurium to be lost to space as a gas during the hot nebular formation of Earth.

Cadmium telluride (CdTe) is a stable crystalline compound formed from cadmium and tellurium. It is mainly used as the semiconducting material in cadmium telluride photovoltaics and an infrared optical window. It is usually sandwiched with cadmium sulfide to form a p–n junction solar PV cell.

Tellurium dioxide (TeO2) is a solid oxide of tellurium. It is encountered in two different forms, the yellow orthorhombic mineral tellurite, β-TeO2, and the synthetic, colourless tetragonal (paratellurite), α-TeO2. Most of the information regarding reaction chemistry has been obtained in studies involving paratellurite, α-TeO2.
There are 39 known isotopes and 17 nuclear isomers of tellurium (52Te), with atomic masses that range from 104 to 142. These are listed in the table below.

Sodium tellurite is an inorganic tellurium compound with formula Na2TeO3. It is a water-soluble white solid and a weak reducing agent. Sodium tellurite is an intermediate in the extraction of the element, tellurium; it is a product obtained from anode slimes and is a precursor to tellurium.
Tellurium hexafluoride is the inorganic compound of tellurium and fluorine with the chemical formula TeF6. It is a colorless, highly toxic gas with an unpleasant odor.

Tellurium tetrafluoride, TeF4, is a stable, white, hygroscopic crystalline solid and is one of two fluorides of tellurium. The other binary fluoride is tellurium hexafluoride. The widely reported Te2F10 has been shown to be F5TeOTeF5 There are other tellurium compounds that contain fluorine, but only the two mentioned contain solely tellurium and fluorine. Tellurium difluoride, TeF2, and ditellurium difluoride, Te2F2 are not known.

Tellurium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the empirical formula TeCl4. The compound is volatile, subliming at 200 °C at 0.1 mmHg. Molten TeCl4 is ionic, dissociating into TeCl3+ and Te2Cl102−.

Ditellurium bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula Te2Br. It is one of the few stable lower bromides of tellurium. Unlike sulfur and selenium, tellurium forms families of polymeric subhalides where the halide/chalcogen ratio is less than 2.

Tritellurium dichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula Te3Cl2. It is one of the more stable lower chlorides of tellurium.
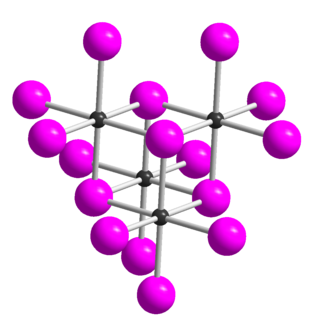
Tellurium tetraiodide (TeI4) is an inorganic chemical compound. It has a tetrameric structure which is different from the tetrameric solid forms of TeCl4 and TeBr4. In TeI4 the Te atoms are octahedrally coordinated and edges of the octahedra are shared.
The word cute is usually associated with the concept of cuteness, a form of attractiveness associated with youthful traits.
Organotellurium chemistry describes the synthesis and properties of chemical compounds containing a carbon-tellurium chemical bond. Organotellurium chemistry is a lightly studied area, in part because of the few applications.
Tellurium chloride may refer to either of the following compounds:
Tellurium iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula TeI. Two forms are known. Their structures differ from the other monohalides of tellurium. There are three subiodides of tellurium, α-TeI, β-TeI, and Te2I, and one tellurium tetraiodide.
Tellurium oxide may refer to:

Molybdenum(IV) telluride, molybdenum ditelluride or just molybdenum telluride is a compound of molybdenum and tellurium with formula MoTe2, corresponding to a mass percentage of 27.32% molybdenum and 72.68% tellurium. It can crystallise in two dimensional sheets which can be thinned down to monolayers that are flexible and almost transparent. It is a semiconductor, and can fluoresce. It is part of a class of materials called transition metal dichalcogenides. As a semiconductor the band gap lies in the infrared region. This raises the potential use as a semiconductor in electronics or an infrared detector.
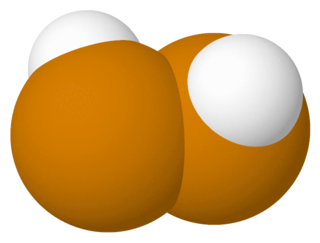
Hydrogen ditelluride or ditellane is an unstable hydrogen dichalcogenide containing two tellurium atoms per molecule, with structure HTeTeH or (TeH)2. Hydrogen ditelluride is interesting to theorists because its molecule is simple yet asymmetric (with no centre of symmetry) and is predicted to be one of the easiest to detect parity violation, in which the left handed molecule has differing properties to the right handed one due to the effects of the weak force.
Copper telluride may refer to:
The telluride bromides are chemical compounds that contain both telluride ions (Te2−) and bromide ions (Br−). They are in the class of mixed anion compounds or chalcogenide halides.