
The first USS Pawnee was a sloop-of-war in the United States Navy during the American Civil War. She was named for the Pawnee Indian tribe.

The first USS Miami was a side-wheel steamer, double-ender gunboat in the United States Navy during the American Civil War.

USS Southfield was a double-ended, sidewheel steam gunboat of the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was sunk in action against the Confederate ironclad ram CSS Albemarle during the Battle of Plymouth (1864).

USS Ceres was a small 150-long-ton (152 t) steamboat acquired by the Union Navy during the beginning of the American Civil War. She was outfitted as a gunboat and used in the Union blockade of the waterways of the Confederate States of America.

USS Stars and Stripes was a 407-ton steamer acquired by the U.S. Navy and put to use by the Union during the American Civil War.

USS Wyalusing was a double-ended, side-wheel gunboat that served in the United States Navy during the American Civil War. She was named for the borough of Wyalusing in Bradford County, Pennsylvania.

USS Commodore Perry was a 512-long-ton (520-tonne) steamer acquired by the Union Navy in 1861, the first year of the American Civil War. She was named after Commodore Oliver Hazard Perry (1785–1819), a naval officer who had commanded American forces on Lake Erie in the War of 1812. In January–February 1862, Commodore Perry was part of the North Atlantic Blockading Squadron, taking part in the attack, in cooperation with the Union Army, which resulted in the surrender of Roanoke Island by the Confederate States of America. She participated in several other campaigns through 1862, including the capture of Elizabeth City, North Carolina, and army–navy expeditions against Franklin, Virginia, and Hertford, North Carolina. From 1863 until the end of the war, she was engaged in patrols, both inland and in Virginia coastal waters.

USSWhitehead, a screw steamer built in 1861 at New Brunswick, New Jersey, served as a gunboat in the United States Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Yankee was a steam-powered side-wheel tugboat acquired by the Union Navy just prior to the outbreak of the American Civil War.

USS Delaware was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy for use during the American Civil War. She had a very active naval career as a gunboat for over three years, and after the war served as a revenue cutter for over 37 years. The steamer was sold to the private sector in 1903, and disappeared from shipping registers in 1919.
USS John L. Lockwood was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was needed by the Navy to be part of the fleet of ships to prevent blockade runners from entering ports in the Confederacy.
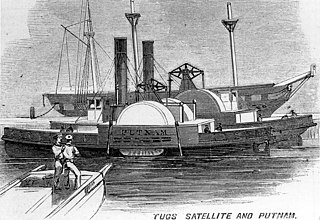
USS General Putnam – also known as the USS William G. Putnam – was acquired by the Union Navy during the first year of the American Civil War and outfitted as a gunboat and assigned to the Union blockade of the Confederate States of America. She also served as a tugboat and as a ship's tender when so required.

USS Underwriter was a 341-ton sidewheel steamer that was purchased for military use by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Shawsheen was a steam operated tugboat acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Western World was a ship acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Navy to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the South from trading with other countries.
USS Isaac N. Seymour, also referred to variously as Seymour, I. N. Seymour and J. N. Seymour, was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy for use as a gunboat during the American Civil War. She was used by the Navy as a littoral ship in fire support, supply and blockading roles.
USS Shamrock was a large seaworthy steamer with powerful guns, acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.
USS Gemsbok was a bark acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Navy as a gunboat, but, later in the war, she was also used as a collier and as a storeship.
USS Henry Brinker was a small steamship acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was placed into service as a gunboat and assigned to the blockade of ports of the Confederate States of America.
The third USS Union was a heavy (1,114-ton) steamer with a powerful 12-inch rifled gun purchased by the United States Navy during the American Civil War.










