
USS Vermont was originally intended to be a ship of the line for the U.S. Navy when laid down in 1818, but was not commissioned until 1862, when she was too outdated to be used as anything but a stores and receiving ship.
The first USS Mohican was a steam sloop-of-war in the United States Navy during the American Civil War. She was named for the Mohican tribe and was the first ship of her class.

The first USS Pocahontas, a screw steamer built at Medford, Massachusetts in 1852 as City of Boston, and purchased by the Navy at Boston, Massachusetts on 20 March 1855, was the first United States Navy ship to be named for Pocahontas, the Algonquian wife of Virginia colonist John Rolfe. She was originally commissioned as USS Despatch – the second U.S. Navy ship of that name – on 17 January 1856, with Lieutenant T. M. Crossan in command, and was recommissioned and renamed in 1860, seeing action in the American Civil War. As Pocahontas, one of her junior officers was Alfred Thayer Mahan, who would later achieve international fame as a military writer and theorist of naval power.
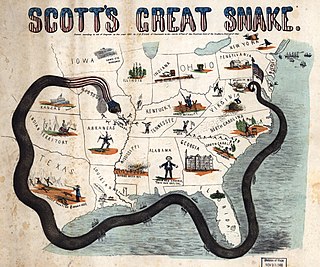
The Union blockade in the American Civil War was a naval strategy by the United States to prevent the Confederacy from trading.

USS Aries was an 820-ton iron screw steamer built at Sunderland, England, during 1861–1862, intended for employment as a blockade runner during the American Civil War. She was captured by Union Navy forces during the Union blockade of the Confederate States of America, and was commissioned as a Union gunboat. Aries was named for the constellation.

USS Alabama was a 1,261 long tons (1,281 t) wooden side-wheel steamer, built at New York City in 1850 and operated thereafter in commercial service in the western Atlantic.
USS Western World was a ship acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Navy to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the South from trading with other countries.
USS Laburnum was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Navy as a tugboat and dispatch boat to serve Union ships on blockade duty.

USS Lodona was a British steamship of the same name captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She had been built in England for shipowner Zachariah Pearson and attempted to break the United States' blockade of Confederate ports. USS Lodona was used by the Navy to patrol waters off those ports. After the war she returned to commercial ownership.
USS Marigold was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a tugboat, dispatch boat and also as a gunboat in the blockade of the Confederacy.
USS Mary Sanford was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Britannia was a steamer captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat and patrol vessel in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.
The first USS Adirondack was a large and powerful screw-assisted sloop of war with heavy guns, contracted by the Union Navy early in the American Civil War. She was intended for use by the Union Navy as a warship in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways. Her career with the Navy proved to be short, yet active and historically important. USS Adirondack was one of four sister ships which included the Housatonic, Ossipee and Juniata.
USS Althea was a screw steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. The Union Navy used her as a tugboat, a torpedo boat, and as a ship's tender in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.
USS Amaranthus was a screw steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a tugboat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.
USS Augusta Dinsmore was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat in support of the Union naval blockade of Confederate waterways. Because of her relatively large size, she was also sometimes used as a cargo ship.
USS Azalea was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as an armed tugboat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.
USS State of Georgia was a large steamer with powerful guns acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. State of Georgia, with her crew of 113 sailors and officers, was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.
USS Glasgow was originally a British cross-Channel sidewheel steamer named Eugenie owned by the South Eastern Railway that was built during the early 1860s. She was sold for blockade-running duties in 1863 and was captured by the Union Navy later that year during the American Civil War. Incorporated into the Navy, she was principally used as a dispatch boat and storeship in support of the Union blockade of the ports of the Confederate States of America. Renamed Glasgow in 1864, she sank after striking an obstacle the following year, but was refloated and repaired. The ship was sold back into commercial service in 1869 and was scrapped 20 years later.
The third USS Union was a heavy (1,114-ton) steamer with a powerful 12-inch rifled gun purchased by the United States Navy during the American Civil War.





