
USS Choctaw was a large (1,004-ton) steamer built for the merchant service, but acquired by the Union Navy during the second year of the American Civil War.
The first USS Arizona was an iron-hulled, side-wheel merchant steamship. Seized by the Confederate States of America in 1862 during the American Civil War, she was captured later the same year by the United States Navy.
USS Abraham—formerly CSS Victoria—was a side-wheel steamer captured by the Union Navy from the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War.

Laurent Millaudon was a wooden side-wheel river steamboat launched at Cincinnati, Ohio, in 1856 operating in the New Orleans, Louisiana, area, and captained by W. S. Whann. At the beginning of the American Civil War she was taken into service by the Confederate Navy as CSS General Sterling Price. On 6 June 1862, she was sunk at the Battle of Memphis. She was raised and repaired by the Union army, and on 16 June 1862 was moved into Union service as USS General Price and served until the end of the war.
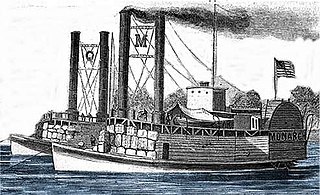
USS Monarch was a United States Army sidewheel ram that saw service in the American Civil War as part of the United States Ram Fleet and the Mississippi Marine Brigade. She operated on the Mississippi River and Yazoo River during 1862 and 1863.

USS General Bragg was a heavy (1,043-ton) steamer captured by Union Navy forces during the American Civil War. She was outfitted as a U.S. Navy gunboat and was assigned to enforce the Union blockade of the waterways of the Confederate States of America.

USS Covington was purchased by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was assigned as a simple gunboat with powerful rifled guns to intercept blockade runners attempting to run the Union blockade of the Confederate States of America.

USS Clifton was a shallow-draft side-wheel paddle steamer, built in 1861 at Brooklyn, as a civilian ferry. The Union Navy bought her early that December, and commissioned her after having her converted into a gunboat. In 1863 she ran aground, was captured and commissioned into the Texas Marine Department. Her career ended in 1864 when she ran aground and her Confederate crew burned her to prevent her recapture.

USS Calhoun was a captured Confederate steamer and blockade runner acquired by the Union Navy from the prize court during the American Civil War.

USS General Lyon, originally the De Soto, was recaptured from the Confederate States of America and renamed USS De Soto, and then USS General Lyon, after Brigadier General Nathaniel Lyon.
USS Patroon was a screw steamer acquired by the United States Navy during the American Civil War. The Union Navy used her to patrol off the coast of the Confederate States of America to enforce the Union blockade.

USS Isaac Smith was a screw steamer acquired by the United States Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederate States of America to prevent the Confederacy from trading with other countries. In 1863, she became the only warship in the American Civil War to be captured by enemy land forces. She then served in the Confederate States Navy as CSS Stono until she was wrecked.

USS Maria Denning was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy for various tasks, including carrying supplies, prisoners of war, and acting as a receiving ship for newly enlisted sailors or for sailors whose ship was sunk.
USS Mobile was a steamer captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as part of blockade forces to prevent Confederate forces from trading with other countries.

The first USS Barataria was a steamer captured by the Union Army during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.

USS Kinsman, sometimes called USS Colonel Kinsman, was a sidewheel steamer captured by the Union Army during the American Civil War. She was used by the Army and then by the Union Navy as a gunboat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways. On 23 February 1863, she hit a snag and sank.

USS Alexandria was a side-wheel steamer captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a dispatch boat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.

USS Rodolph was a steamer commissioned by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She served the Union Navy during its struggle against the Confederate States of America, both as a tugboat and a minesweeper, as well as a gunboat when the occasion demanded. Just as the war was ending, Rodolph struck a mine and sank, with four of her crew killed and a number of others wounded.

USS Sumter was a 525-ton sidewheel paddle steamer captured by the Union Navy during the Union blockade of the American Civil War.















