
USS Chemung (AO-30), a Cimarron-class fleet replenishment oiler serving in the United States Navy, was the second ship named for the Chemung River in New York State.

The third USS Merrimack (AO-37) (ex-Caddo) was one of five Kennebec-class fleet oilers built during World War II for service in the United States Navy. She also service in the Cold War. She was named after the Merrimack River in Massachusetts and New Hampshire.

USS Sabine (AO-25), a Cimarron-class fleet replenishment oiler serving in the United States Navy, was the second ship named for the Sabine River on the Texas-Louisiana border.
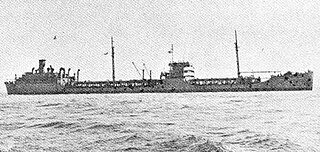
SS Mission Santa Ynez was a Type T2-SE-A2 tanker built for the United States Maritime Commission during World War II. After the war she was acquired by the United States Navy as USS Mission Santa Ynez (AO-134). Later the tanker transferred to the Military Sea Transportation Service as USNS Mission Santa Ynez (T-AO-134). A Mission Buenaventura-class oiler, she was named for Mission Santa Inés located in Solvang, California.

USS Neosho (AO–48) was a Kennebec-class type T2 fleet oiler of the United States Navy. The ship was laid down on 8 July 1941, as SS Catawba, by the Bethlehem-Sparrows Point Shipyard Inc., Sparrows Point, Maryland. The purchase came under Maritime Commission contract number 145 for the Socony-Vacuum Oil Company, later renamed Mobil Oil.

USS Patuxent (AO-44) was a Kennebec-class oiler in the United States Navy during World War II. She was the second U.S. Navy ship named for the Patuxent River in Maryland.

USS Saugatuck (AO-75) was a Suamico-class replenishment oiler of the United States Navy.

USS Schuylkill (AO-76), originally named the SS Louisburg, was a Type T2-SE-A1 Suamico-class fleet oiler of the United States Navy.

The USS Manatee (AO-58)—the second vessel of the United States Navy to bear the name—was a Cimarron-class fleet replenishment oiler named for a river in Florida. Cimarron-class oilers were named after American rivers in the southern United States.

USS Soubarissen (AO-93) was an Escambia-class fleet oiler converted to a water tanker, named for a chief of the "Neutral" Indian Nations which, although a part of the Iroquois confederation, were called "neutral" by the French because they took no part in the wars of the Iroquois and Hurons. The area he governed included the oil fields of northwestern Pennsylvania and western New York. The knowledge of the oil seepages there was well known among the Indians, and it was declared neutral ground so all Indians could obtain oil for medicinal and domestic purposes without danger or interference. In 1627, Joseph de La Roche Daillon heard of the oil springs and made an expedition to visit them. He was kindly received by Chief Soubarissen, shown the oil seepages, and duly reported his observations to his superiors. These observations contributed largely to the interest in the petroleum resources of the Pennsylvania region.

USS Niobrara (AO-72) was a T3 Kennebec-class oiler constructed for the United States Navy during World War II. She was the only U.S. Navy ship named for the Niobrara River in Nebraska.

USS Chikaskia (AO-54) was a Cimarron-class fleet oiler acquired by the U.S. Navy during World War II. She served her country primarily in the Pacific Ocean Theatre of Operations, and provided petroleum products where needed to combat ships. For her very dangerous work under combat conditions, she was awarded six battle stars for World War II and one for the Korean War.

USS Elokomin (AO-55) was a Cimarron-class fleet oiler acquired by the U.S. Navy during World War II. She served her country primarily in the Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea, and the North Atlantic Ocean Theatre of Operations, and provided petroleum products where needed to combat ships.

USS Cacapon (AO-52) was a T3 Cimarron-class fleet oiler acquired by the U.S. Navy during World War II. She served her country primarily in the Pacific Ocean Theater of Operations, and provided petroleum products where needed to combat ships. For performing this dangerous task, she was awarded battle stars and citations during World War II, the Korean War, and the Vietnam War.

USS Chipola (AO-63) was a Cimarron-class fleet oiler acquired by the U.S. Navy during World War II. She served her country primarily in the Pacific Theater of Operations, and provided petroleum products where needed to combat ships. For performing this dangerous task in combat areas, she was awarded three battle stars during World War II and thirteen campaign stars during the Vietnam War.

USS Housatonic (AO-35) was a Chicopee-class oiler acquired by the United States Navy for use during World War II. She was the third ship of the U.S. Navy named for the Housatonic River in Massachusetts and Connecticut.

USS Cohocton (AO-101) was lead ship of her class of fleet oiler acquired by the United States Navy for use during World War II. She had the dangerous but necessary task of providing fuel to vessels in combat and non-combat areas. She served in the Pacific Ocean Theatre of operations late in the war.

USS Severn (AO-61) was a Cimarron-class fleet oiler. She was constructed for the U.S. Navy during World War II and her assignment was to provide liquids, such as fuel or water, to ships in the forward battle areas. She survived this dangerous task and returned home post-war with two battle stars to her credit.

USS Enoree (AO-69) was a Chiwawa-class oiler constructed for the United States Navy during World War II. She was the only U.S. Navy ship named for the Enoree River in South Carolina.

The T3 tanker, or T3, are a class of seaworthy large tanker ships produced in the United States and used to transport fuel oil, gasoline or diesel before and during World War II, the Korean War and the Vietnam War. The T3 tanker classification is still used today. The T3 tanker has a full load displacement of about 24,830 tons.



















