The first USS Arizona was an iron-hulled, side-wheel merchant steamship. Seized by the Confederate States of America in 1862 during the American Civil War, she was captured later the same year by the United States Navy.
USS Abraham—formerly CSS Victoria—was a side-wheel steamer captured by the Union Navy from the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War.

The USS Queen of the West was a sidewheel steamer ram ship and the flagship of the United States Ram Fleet and the Mississippi Marine Brigade. It was built at Cincinnati, Ohio in 1854. It served as a commercial steamer until purchased by Colonel Charles Ellet Jr. in 1862 and converted for use as a ram ship. The ship operated in conjunction with the Mississippi River Squadron during the Union brown-water navy battle against the Confederate River Defense Fleet for control of the Mississippi River and its tributaries during the American Civil War.

The first USS Lafayette was a side wheel steamer, converted to an ironclad ram, in the United States Navy during the American Civil War.

USS Albatross was a screw steamer rigged as a three-masted schooner acquired by the Union Navy during the beginning of the American Civil War. She was outfitted as a gunboat with heavy guns and used in the Union blockade of the waterways of the Confederate States of America.

Laurent Millaudon was a wooden side-wheel river steamboat launched at Cincinnati, Ohio, in 1856 operating in the New Orleans, Louisiana, area, and captained by W. S. Whann. At the beginning of the American Civil War she was taken into service by the Confederate Navy as CSS General Sterling Price. On 6 June 1862, she was sunk at the Battle of Memphis. She was raised and repaired by the Union army, and on 16 June 1862 was moved into Union service as USS General Price and served until the end of the war.
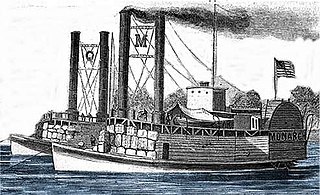
USS Monarch was a United States Army sidewheel ram that saw service in the American Civil War as part of the United States Ram Fleet and the Mississippi Marine Brigade. She operated on the Mississippi River and Yazoo River during 1862 and 1863.

USS General Bragg was a heavy (1,043-ton) steamer captured by Union Navy forces during the American Civil War. She was outfitted as a U.S. Navy gunboat and was assigned to enforce the Union blockade of the waterways of the Confederate States of America.

USS Signal – a small 190-ton steamship – was acquired during the second year of the American Civil War by the Union Navy and outfitted as a gunboat. She also served other types of duty, such as that of dispatch vessel and convoy escort.

USS Fern was a tugboat acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. Her task was to tow other ships and barges, and to provide other duties that a tug could easily do, such as dispatch running.
USS Ivy was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.

Little Rebel was a cotton-clad ram that had been converted from a Mississippi River steamer to serve as the flagship of the Confederate River Defense Fleet in the American Civil War. Sent from New Orleans to defend against the Federal descent of the Mississippi, she was among the force that engaged vessels of the Union Army's Western Gunboat Flotilla at the Battle of Plum Point Bend on May 10, 1862. On June 6, she again was involved in an action with the Federal gunboats, this time at the Battle of Memphis. In the battle, a shot from a Federal gun pierced her boiler, disabling her, and she was then pushed aground by the Federal ram USS Monarch and captured.

USS Rattler was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.

USS Cricket was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Springfield was a steamship purchased by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat assigned to patrol Confederate waterways.

USS St. Clair was a steamer purchased by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Juliet was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.

USS Alexandria was a side-wheel steamer captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a dispatch boat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.
The first USS Silver Cloud was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.

USS Sumter was a 525-ton sidewheel paddle steamer captured by the Union Navy during the Union blockade of the American Civil War.















