
The United States Asiatic Fleet was a fleet of the United States Navy during much of the first half of the 20th century. Before World War II, the fleet patrolled the Philippine Islands. Much of the fleet was destroyed by the Japanese by February 1942, after which it was dissolved, and the remnants incorporated into the naval component of the South West Pacific Area command, which eventually became the Seventh Fleet.

The Philadelphia Naval Shipyard was an important naval shipyard of the United States for almost two centuries.

USS Ringgold (DD-89) was a Wickes-class destroyer in the United States Navy during World War I and the interwar period. During World War II, the vessel was transferred to the Royal Navy as a Town-class destroyer named HMS Newark, being scrapped after the end of the war in 1947.

USS Williams (DD-108) was a Wickes-class destroyer in the United States Navy entering service in 1919, and was the second ship to bear the name. Following a brief stint in active service, the ship was laid up for 17 years before being reactivated during World War II. Williams transferred to the Royal Canadian Navy during World War II as part of Lend-Lease and was renamed HMCS St. Clair (I65), surviving the war and being scrapped in 1946.

USS Osborne (DD-295) was a Clemson-class destroyer in the United States Navy following World War I. She was named for Weedon Osborne.

The first USS Talbot was a torpedo boat in the United States Navy.
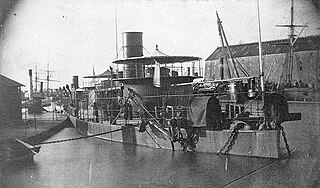
The Miantonomoh class consisted of four monitors built for the Union Navy during the U.S. Civil War, but only one ship was completed early enough to participate in the war. They were broken up in 1874–1875.

USS Monmouth County (LST-1032) was an LST-542-class tank landing ship built for the United States Navy during World War II. Named after Monmouth County, New Jersey, she was the only U.S. Naval vessel to bear the name.

Asbury Park was a high-speed coastal steamer built in Philadelphia, and intended to transport well-to-do persons from New York to summer homes on the New Jersey shore. This vessel was sold to West Coast interests in 1918, and later converted to an automobile ferry, serving on various routes San Francisco Bay, Puget Sound and British Columbia. This vessel was known by a number of other names, including City of Sacramento, Kahloke, Langdale Queen, and Lady Grace.

The second USS Wando, later YT-17, later YT-123, later YTB-123, was a United States Navy tug in commission from 1917 to 1946.
Lillian Anne (YFB-41) was a United States Navy ferry in service from 1942 to 1943.
The fourth USS Despatch, originally USS Steam Cutter No. 423, later USS Hustle (YFB-6), was a ferry launch that served in the United States Navy from 1902 to 1921.

USS Charles (ID-1298) was a troop transport that served in the United States Navy from 1918 to 1920 and was briefly in commission as USS Harvard in 1918 and 1920. She was better known in her role as passenger liner SS Harvard, one of the premier West Coast steamships operated by the Los Angeles Steamship Company.

USS Dart (YFB-308) was a United States Navy ferry launch in service from 1900 to 1930, when she was transferred to the United States Lighthouse Service, and renamed the Locust, she was later transferred to the United States Coast Guard, until she was decommissioned in 1954.

The first USS Moosehead (ID-2047), later the fourth USS Porpoise (YFB-2047), was a steamer that served in the United States Navy from 1918 to 1930.
USS Pilgrim II (YFB-30) was a United States Navy motor launch employed as a river patrol boat during her naval service from 1942 to 1947.

The first USS Patchogue (ID-1227), later YFB-1227, was a United States Navy ferry in service from 1917 to 1922.

The City of Seattle was a side-wheel driven steam-powered ferry built in 1888. This vessel was the first ferry to operate on Puget Sound. City of Seattle was also used in the San Francisco Bay area starting in 1913. The ferry was known as YFB54 when owned by the U.S. navy in World War II, and as Magdalena during naval service and for a time following the war. The upper works of the ferry have been mounted on a barge hull, and are now in use as a houseboat in Sausalito, California.

San Felipe (YFB-12) (ex-Engineer) was a United States Army steel tugboat that later served as a ferryboat in the U.S. Navy and as an Imperial Japanese Army transport during World War II.

USS Pima County (LST-1081) was an LST-542-class tank landing ship of the United States Navy. Built by the American Bridge Company in Ambridge, Pennsylvania from 13 November 1944 she was commissioned into the navy on 30 January 1945. LST-1081 saw service as a logistics vessel in the latter stages of the Pacific War but was placed into reserve and decommissioned after the war. She was recommissioned in 1950 after the outbreak of the Korean War and served with the Atlantic Fleet, including a deployment in the Mediterranean Sea during which she was renamed USS Pima County. She returned to the reserve in 1956 and was decommissioned on 12 December of that year.
















