
The third USS Water Witch was a wooden-hulled, sidewheel gunboat in the United States Navy during the American Civil War. She is best known as the ship fired on by Paraguay in 1855. In 1864 she was captured by the Confederate States Navy, and subsequently was taken into that Navy as CSS Water Witch.

The first USS San Jacinto was an early screw frigate in the United States Navy during the mid-19th century. She was named for the San Jacinto River, site of the Battle of San Jacinto during the Texas Revolution. She is perhaps best known for her role in the Trent Affair of 1861.
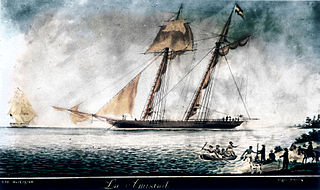
Washington was a revenue cutter that served in the United States Revenue Cutter Service and in the United States Navy. She discovered, boarded, and captured La Amistad after the slaves onboard had seized control of that schooner in an 1839 mutiny.
See also USS Sam Houston (SSBN-609).
The first USS Onward was a clipper in the Union Navy.

USS General Putnam – also known as the USS William G. Putnam – was acquired by the Union Navy during the first year of the American Civil War and outfitted as a gunboat and assigned to the Union blockade of the Confederate States of America. She also served as a tugboat and as a ship's tender when so required.
USS Two Sisters was a small 54-ton captured Confederate schooner acquired by the Union Navy from the prize court during the American Civil War.
USS Wild Cat was a captured Confederate schooner acquired by the Union Navy from the prize court during the American Civil War. She was put into service by the Union Navy to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the South from trading with other countries.
USS Rosalie was a captured Confederate sloop acquired by the Union Navy from the prize court during the American Civil War.
USS Restless was a barque acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.

USS Calhoun was a captured Confederate steamer and blockade runner acquired by the Union Navy from the prize court during the American Civil War.
USS Charlotte was a schooner captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the South from trading with other countries.
USS Brockenborough was a sloop captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Annie was a schooner captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a ship's tender in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways. Her service during the Union naval blockade of Confederate waters peaked during the Second Chesapeake Affair (1863–64) as a "fresh reinforcement from the south" in the search and capture of the U.S.S Chesapeake.

The first USS Wanderer was a high-speed schooner originally built for pleasure. It was used in 1858 to illegally import slaves from Africa. It was seized for service with the United States Navy during the American Civil War. In U.S. Navy service from 1861 to 1865, and under outright U.S. Navy ownership from 1863 to 1865, she was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat, as a tender, and as a hospital ship. She was decommissioned, put into merchant use, and lost off Cuba in 1871.
USS G. W. Blunt was a Sandy Hook pilot boat acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War in 1861. See George W. Blunt (1856) for more details. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat as well as a dispatch boat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.
USS Sarah and Caroline was a schooner captured by the Union Navy during the beginning of the American Civil War.
USS Stonewall was a small 30-ton blockade-running schooner captured by the Union Navy during the Union blockade of the American Civil War.
USS Swift was a small 12-ton schooner captured by the Union Navy during the Union blockade of the American Civil War.

The third USS Virginia was a 581-ton blockade-running steamer captured by the United States Navy and put to use by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. Virginia served the U.S. Navy primarily as a mortar gunboat. Her ordnance included six 24-pounder howitzers and a 12-pounder rifled gun.






