
USS Black Hawk (1848) was a large steamer purchased by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
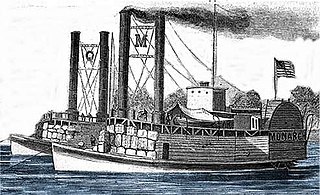
USS Monarch was a United States Army sidewheel ram that saw service in the American Civil War as part of the United States Ram Fleet and the Mississippi Marine Brigade. She operated on the Mississippi River and Yazoo River during 1862 and 1863.

USS General Bragg (1851) was a heavy (1,043-ton) steamer captured by Union Navy forces during the American Civil War. She was outfitted as a U.S. Navy gunboat and was assigned to enforce the Union blockade of the waterways of the Confederate States of America.

USS Signal (1862) – a small 190-ton steamship – was acquired during the second year of the American Civil War by the Union Navy and outfitted as a gunboat. She also served other types of duty, such as that of dispatch vessel and convoy escort.

USS Octorara was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Navy to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the Confederates from trading with other countries.

USS Calhoun was a captured Confederate steamer and blockade runner acquired by the Union Navy from the prize court during the American Civil War.

USS Fort Hindman was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was placed in service and used by the Navy to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the South from trading with other countries.
USS Ivy (1862) was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Tristram Shandy (1864) was a 444-ton steamer and blockade runner captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.

USS Ouachita (1863) was a steamer captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Navy to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the South from trading with other countries.

USS Rattler (1862) was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Cowslip (1863) was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.

USS Silver Lake (1862) was a steamer purchased by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Brilliant (1862) was a steamer purchased by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat assigned to patrol Confederate waterways.
USS Reindeer (1863) was a steamer purchased by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.

USS Eastport was a steamer captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a convoy and patrol vessel on Confederate waterways.
USS Exchange (1862) was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.

USS New Era (1862) was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways. New Era was also a name initially carried by a timbercladUSS Essex.
USS Avenger (1863) was a large steamer with powerful guns acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways. Because of her large size, she was also used, at times, as a cargo ship.
USS Philippi (1863) was a blockade runner captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She served the Union Navy’s struggle against the Confederate States of America as a picket, patrol and dispatch vessel.












