
USS Santee was a wooden-hulled, three-masted sailing frigate of the United States Navy. She was the first U.S. Navy ship to be so named and was one of its last sailing frigates in service. She was acquired by the Union Navy at the start of the American Civil War, outfitted with heavy guns and a crew of 480, and was assigned as a gunboat in the Union blockade of the Confederate States. She later became a training ship then a barracks ship for the U.S. Naval Academy.

CSSEllis was a gunboat in the Confederate States Navy and the United States Navy during the American Civil War. It was lost during a raid while under command of famed Navy officer Lieutenant William B. Cushing.

USS Stars and Stripes was a 407-ton steamer acquired by the U.S. Navy and put to use by the Union during the American Civil War.
The Stone Fleet consisted of a fleet of aging ships purchased in New Bedford and other New England ports, loaded with stone, and sailed south during the American Civil War by the Union Navy for use as blockships. They were to be deliberately sunk at the entrance of Charleston Harbor, South Carolina in the hope of obstructing blockade runners, then supplying Confederate interests. Although some sank along the way and others were sunk near Tybee Island, Georgia, to serve as breakwaters, wharves for the landing of Union troops, the majority were divided into two lesser fleets. One fleet was sunk to block the south channel off Morris Island, and the other to block the north channel near Rattlesnake Shoals off the present day Isle of Palms in what proved to be failed efforts to block access the main shipping channels into Charleston Harbor.
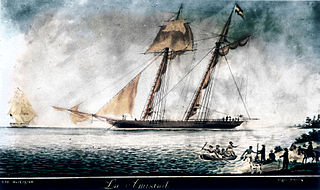
Washington was a revenue cutter that served in the United States Revenue Cutter Service and in the United States Navy. She discovered, boarded, and captured La Amistad after the slaves onboard had seized control of that schooner in an 1839 mutiny.

USS Morning Light was a sailing ship acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Navy to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the South from trading with other countries.
USS Dan Smith was a schooner used by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Navy to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the South from trading with other countries.

USS Maria J. Carlton was a schooner acquired by the United States Navy on October 15, 1861, during the American Civil War. Built before the war, the vessel was converted into a mortar schooner by the Navy. She was then transferred to the mouth of the Mississippi River in early 1862, as part of a force tasked with neutralizing Confederate forts guarding New Orleans, Louisiana. Maria J. Carlton participated in the Battle of Forts Jackson and St. Philip on April 18, but, the battle continuing, was sunk the next day by a shot from Fort Jackson. She was the only Union warship sunk solely by artillery fire from Confederate forts on the Mississippi River during the war.
USS Massachusetts was a large steamer acquired by the U.S. Navy prior to the American Civil War.

USS Tahoma was a Unadilla-class gunboat built by order of the United States Navy for service during the American Civil War.
USS G. W. Blunt was a Sandy Hook pilot boat acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War in 1861. See George W. Blunt (1856) for more details. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat as well as a dispatch boat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.
USS Hero (1861), a wooden schooner, was purchased by the Union Navy during the American Civil War at Baltimore, Maryland, 13 August 1861 to obstruct inlets to Pamlico Sound, North Carolina, near Cape Hatteras.
USS Orion (1861), a wooden schooner, was purchased by the Union Navy during the American Civil War at Baltimore, Maryland, on 13 August 1861.
USS Patriot was a schooner acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Rescue was a small (111-ton) steamer commissioned by the United States Navy during the American Civil War.
The third USS Union was a heavy (1,114-ton) steamer with a powerful 12-inch rifled gun purchased by the United States Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Somerfield (1861) was a Chesapeake Bay schooner purchased by the Union Navy at Baltimore, Maryland, on 13 August 1861 for the purpose of obstructing the North Carolina sounds.
USS South Wind (1861) was a schooner purchased by the Union Navy on 13 August 1861 at Baltimore, Maryland, for the "Stone Fleet" of American Civil War fame.
USS W. F. Bartlett was a schooner acquired by the United States Navy in 1861.






