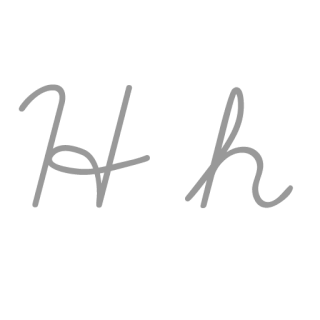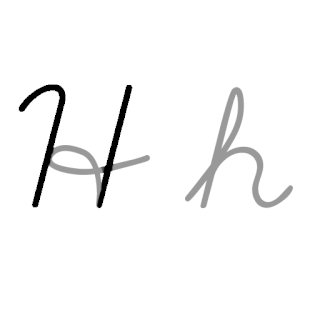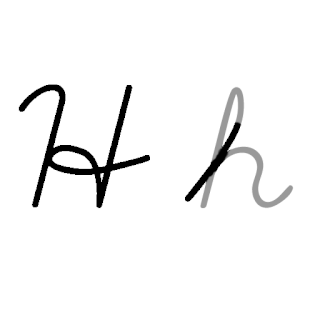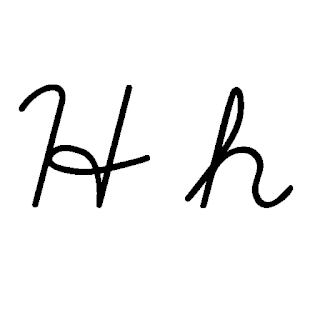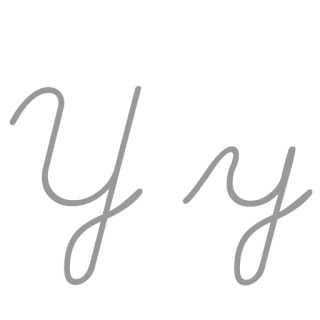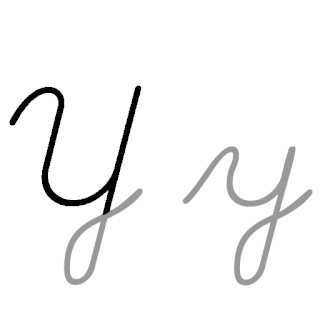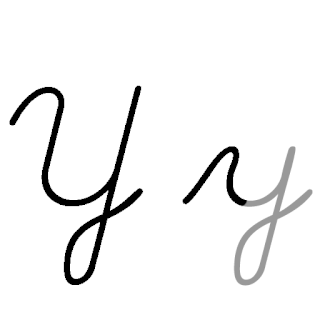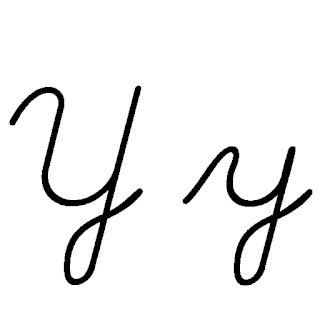A dictionary is a listing of words in one or more specific languages, often arranged alphabetically, which may include information on definitions, usage, etymologies, pronunciations, translation, etc. or a book of words in one language with their equivalents in another, sometimes known as a lexicon. It is a lexicographical reference that shows inter-relationships among the data.
English orthography is the system of writing conventions used to represent spoken English in written form that allows readers to connect spelling to sound to meaning.
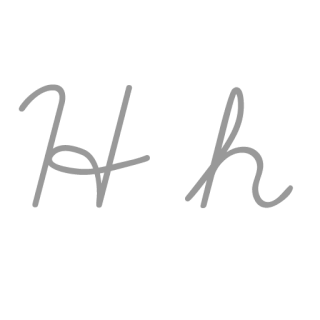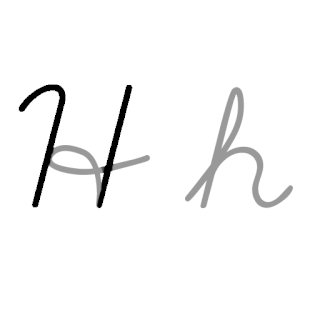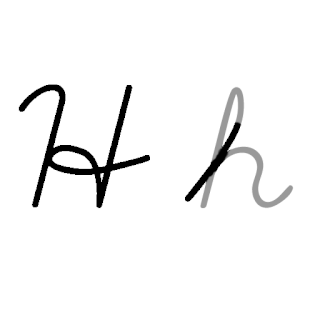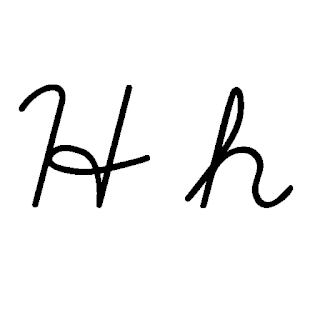
H or h is the eighth letter in the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Its name in English is aitch, or regionally haitch.
A rhyme is a repetition of similar sounds in the final stressed syllables and any following syllables of two or more words. Most often, this kind of perfect rhyming is consciously used for effect in the final positions of lines of poems and songs. More broadly, a rhyme may also variously refer to other types of similar sounds near the ends of two or more words. Furthermore, the word rhyme has come to be sometimes used as a shorthand term for any brief poem, such as a rhyming couplet or nursery rhyme.
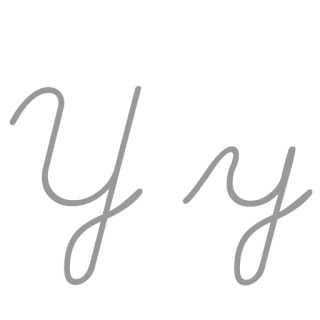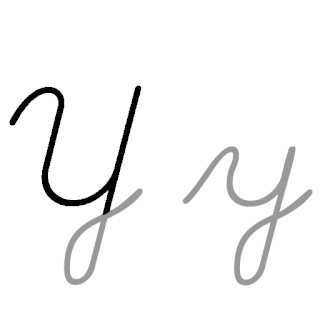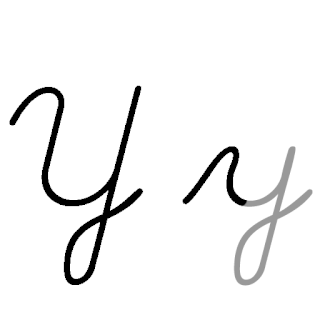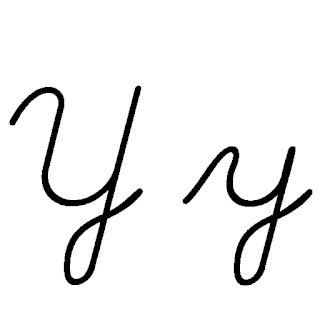
Y or y is the 25th and penultimate letter of the ISO basic Latin alphabet and the sixth vowel letter of the modern English alphabet. In the English writing system, it sometimes represents a vowel and sometimes a consonant, and in other orthographies it may represent a vowel or a consonant. Its name in English is wye, plural wyes.

Classical Chinese, also known as Literary Chinese is the language of the classic literature from the end of the Spring and Autumn period through to the end of the Han dynasty, a written form of Old Chinese. Classical Chinese is a traditional style of written Chinese that evolved from the classical language, making it different from any modern spoken form of Chinese. Literary Chinese was used for almost all formal writing in China until the early 20th century, and also, during various periods, in Japan, Korea and Vietnam. Among Chinese speakers, Literary Chinese has been largely replaced by written vernacular Chinese, a style of writing that is similar to modern spoken Mandarin Chinese, while speakers of non-Chinese languages have largely abandoned Literary Chinese in favor of local vernaculars.
Webster's Dictionary is any of the dictionaries edited by Noah Webster in the early nineteenth century, and numerous related or unrelated dictionaries that have adopted the Webster's name. "Webster's" has become a genericized trademark in the U.S. for dictionaries of the English language, and is widely used in English dictionary titles. Merriam-Webster is the corporate heir to Noah Webster's original works, which are in the public domain.
Œ is a Latin alphabet grapheme, a ligature of o and e. In medieval and early modern Latin, it was used to represent the Greek diphthong οι and in a few non-Greek words, usages that continue in English and French. In French, it is also used in some non-learned words, representing then mid-front rounded vowel-sounds, rather than sounding the same as é or è, those being its traditional French values in the words borrowed from or via Latin.
The modern English alphabet is a Latin alphabet consisting of 26 letters, each having an upper- and lower-case form. It originated around the 7th century from Latin script. Since then, letters have been added or removed to give the current Modern English alphabet of 26 letters. The word alphabet is a compound of the first two letters of the Greek alphabet, alpha and beta.

The Qieyun is a Chinese rhyme dictionary, published in 601 during the Sui dynasty. The book was a guide to proper reading of classical texts, using the fanqie method to indicate the pronunciation of Chinese characters. The Qieyun and later redactions, notably the Guangyun, are important documentary sources used in the reconstruction of historical Chinese phonology.
A spelling pronunciation is the pronunciation of a word according to its spelling, different from a standard or traditional pronunciation. Words spelled with silent letters, or traditionally pronounced with reduced vowels or omitted consonants, may be subject to a spelling pronunciation.
An eye rhyme, also called a visual rhyme or a sight rhyme, is a rhyme in which two words are spelled similarly but pronounced differently. An example is the names of English actor Sean Bean, whose spelling suggests the two names should rhyme, though they do not.
"I before E, except after C" is a mnemonic rule of thumb for English spelling. If one is not sure whether a word is spelled with the digraph ei or ie, the rhyme suggests that the correct order is ie unless the preceding letter is c, in which case it is ei. For example:
Early Modern English or Early New English is the stage of the English language from the beginning of the Tudor period to the English Interregnum and Restoration, or from the transition from Middle English, in the late 15th century, to the transition to Modern English, in the mid-to-late 17th century.
A rhyming dictionary is a specialist dictionary designed for use in writing poetry and lyrics. In a rhyming dictionary, words are categorized into equivalence classes that consist of words that rhyme with one another. They also typically support several different kinds of rhymes and possibly also alliteration as well.
For centuries, there has been a movement to reform the spelling of English language. It seeks to change English orthography so that it is more consistent, matches pronunciation better, and follows the alphabetic principle. Common motives for spelling reform include quicker, cheaper learning, thus making English more useful as an international auxiliary language.
Despite the various English dialects spoken from country to country and within different regions of the same country, there are only slight regional variations in English orthography, the two most notable variations being British and American spelling. Many of the differences between American and British English date back to a time before spelling standards were developed. For instance, some spellings seen as "American" today were once commonly used in Britain, and some spellings seen as "British" were once commonly used in the United States.
A pronunciation respelling for English is a notation used to convey the pronunciation of words in the English language, which does not have a phonemic orthography.
The English word twat is a vulgarism which literally means the vulva or vagina, and is used figuratively as a derogatory epithet. In British English the epithet denotes an obnoxious or stupid person of either sex, whereas in American English it is rarer and usually applied to a woman. In Britain the usual current pronunciation is ; the older pronunciation, still usual in America, is, reflected in the former variant spelling twot. The literal sense is first attested in 1656, the epithet in the 1930s. The word's etymology is uncertain. The American Heritage Dictionary suggests a conjectural Old English word *thwāt, "a cut", cognate with Old Norse þveit (thveit). Jonathon Green suggests a connection with twitchel, a dialect term for a narrow passage.
A reverse dictionary is a dictionary alphabetized by the reversal of each entry: