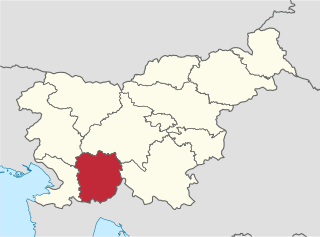
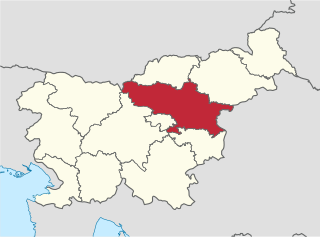
| Western Slovenia Zahodna Slovenija | |
|---|---|
| Region | |
 | |
| Country | |
| Area [1] | |
| • Total | 8,061 km2 (3,112 sq mi) |
| Population [2] | |
| • Total | 933,800 |
| • Density | 120/km2 (300/sq mi) |
| NUTS code | SI02 |
| GDP per capita (PPS) | € 24,900 (2006) [3] |
Western Slovenia (Zahodna Slovenija) is one of the two NUTS-2 Regions of Slovenia. The region forms the western part of the country and includes the cities of Ljubljana, Koper, Kranj and Nova Gorica. It is the richer of the two regions of Slovenia and its GDP per capita is 105.4% of the European Union average (€24,900 per year).
The Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics is a geocode standard for referencing the subdivisions of countries for statistical purposes. The standard is developed and regulated by the European Union, and thus only covers the member states of the EU in detail. The Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics is instrumental in the European Union's Structural Fund delivery mechanisms and for locating the area where goods and services subject to European public procurement legislation are to be delivered.

Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a sovereign state located in southern Central Europe at a crossroads of important European cultural and trade routes. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and the Adriatic Sea to the southwest. It covers 20,273 square kilometers (7,827 sq mi) and has a population of 2.07 million. One of the successor states of the former Yugoslavia, Slovenia is a parliamentary republic and a member of the United Nations, of the European Union, and of NATO. The capital and largest city is Ljubljana.

Ljubljana is the capital and largest city of Slovenia. It has been the cultural, educational, economic, political, and administrative centre of independent Slovenia since 1991.
Western Slovenia (SI02) is divided into the following statistical regions:
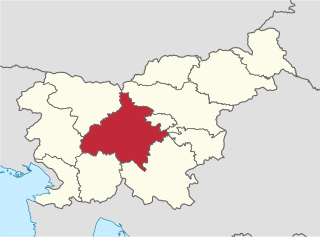
The Central Slovenia Statistical Region is a statistical region in central Slovenia.

The Upper Carniola Statistical Region is a statistical region in northwest Slovenia. It is a region with high mountains, including Mount Triglav, and is almost entirely Alpine. A large part of this statistical region is protected as a national park. The relief and climate are good bases for tourism. In 2013, the region recorded almost 19% of tourist nights in Slovenia, of which 78% were by foreign tourists. The region ranked second in Slovenia in number of tourist beds per 1,000 population, even though it had just over half as many beds as the Coastal–Karst Statistical Region. In 2013, the registered unemployment rate here was the lowest in Slovenia, 3 percentage points lower than the national average and more than 8 percentage points lower than in the Mura Statistical Region, where the registered unemployment rate was the highest. Although agriculture in this region is not among the most important activities, the farms are among the largest in the country both in terms of average utilised agricultural area per farm and in terms of the number of livestock per farm.

The Gorizia Statistical Region is a statistical region in western Slovenia, along the border with Italy. It is named after the Italian town of Gorizia. The Julian Alps, the Soča River, and the Vipava Valley are the most prominent natural features of this region. It contributed just over 5% to total national GDP in 2012, but in terms of GDP per capita it ranked fourth in the country. In the same year, disposable income per capita in the region the highest, in second place behind the Central Slovenia Statistical Region. Housing stock estimates indicate that at the end of 2013 the region had the highest share of dwellings with three or more rooms. The share of single-room dwellings was less than 10%. Dwellings here are larger than the Slovenian average, with 37 m² of usable floor space per person on average. The number of cars per 1,000 population is also the highest in Slovenia, with an average of 100 cars more per 1,000 people than in the Central Sava Statistical Region. However, the cars here and in the Lower Sava Statistical Region are also the oldest.