The 12th Louisiana Regiment Infantry (African Descent) was a regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War. [1] [2]
The regiment was organized between May and July 1863 and was attached to the African Brigade in the Northeast Louisiana District until July 1863. The unit was posted at Vicksburg, Mississippi until March 1864.
The designation of the regiment was changed to 50th Regiment Infantry, U.S. Colored Troops on March 11, 1864. [3]

United States Colored Troops (USCT) were Union Army regiments during the American Civil War that primarily comprised African Americans, with soldiers from other ethnic groups also serving in USCT units. Established in response to a demand for more units from Union Army commanders, USCT regiments, which numbered 175 in total by the end of the war in 1865, constituted about one-tenth of the manpower of the army, according to historian Kelly Mezurek, author of For Their Own Cause: The 27th United States Colored Troops. "They served in infantry, artillery, and cavalry." Approximately 20 percent of USCT soldiers were killed in action or died of disease and other causes, a rate about 35 percent higher than that of white Union troops. Numerous USCT soldiers fought with distinction, with 16 receiving the Medal of Honor. The USCT regiments were precursors to the Buffalo Soldier units which fought in the American Indian Wars.

The 28th United States Colored Infantry, also called the 28th Indiana Infantry (Colored),1 was an African American infantry regiment from the state of Indiana that fought in the American Civil War.
The 1st Kansas Colored Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. It was the first black regiment to be organized in a northern state to see combat during the Civil War. At the Battle of Poison Spring, the regiment lost nearly half its number, and suffered the highest losses of any Kansas regiment during the war.
The 7th Louisiana Regiment Infantry (African Descent) was a regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War. The regiment served in Mississippi, Louisiana and Arkansas and mustered out March 13, 1866.
The 9th Louisiana Infantry (African Descent), later reorganized as 1st Mississippi Colored Heavy Artillery and then renamed 5th U.S. Colored Heavy Artillery, was an African-American regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War. It famously fought in the Battle of Milliken's Bend; one of the earliest Civil War battles with African-American troops involved.
The 8th Louisiana Regiment Infantry (African Descent) was an infantry regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War. It was composed primarily of freed or escaped slaves from Louisiana's plantations and was commanded by white officers.
The 10th Louisiana Infantry (African descent) was a regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War. It was composed primarily of freed or escaped slaves from Louisiana's plantations and was commanded by white officers.
The 10th United States Colored Heavy Artillery Regiment was an artillery regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War that served in the New Orleans defenses. The unit was organized in New Orleans in November 1862 as the 1st Louisiana Heavy Artillery Regiment (African Descent), and redesignated as the 1st Corps d'Afrique Heavy Artillery Regiment a year later. It briefly became the 7th United States Colored Heavy Artillery Regiment in April 1864, then assumed its final designation in May.
The 3rd Louisiana Regiment Native Guard Infantry was a regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War.
The 2nd Louisiana Regiment Native Guard Infantry was a regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War. It was organized in New Orleans and was tasked with defending the city until being redeployed to Ship Island in Mississippi. Its higher-ranking officers were white and lower grade officers and enlisted men were mixed heritage and African American.
The 49th United States Colored Infantry, first established as the 11th Louisiana Infantry (African descent) was an infantry regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War.

The 3rd Missouri Colored Infantry Regiment was an African-American infantry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. It was redesignated as the 67th U.S. Colored Troops Regiment on March 11, 1864.

The 46th United States Colored Infantry was an infantry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. The unit was originally designated as the 1st Arkansas Infantry Regiment. The regiment was composed of African American enlisted men commanded by white officers and was authorized by the Bureau of Colored Troops which was created by the United States War Department on May 22, 1863.
The 54th United States Colored Infantry was an infantry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. The regiment was composed of African American enlisted men commanded by white officers and was authorized by the Bureau of Colored Troops which was created by the United States War Department on May 22, 1863.
The 2nd United States Colored Infantry was an infantry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. The regiment was composed of African American enlisted men commanded by white officers and was authorized by the Bureau of Colored Troops which was created by the United States War Department on May 22, 1863.
The 52nd United States Colored Infantry was an infantry regiment composed of African-American troops recruited from Mississippi that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. On July 4, 1864, the 52nd Colored Infantry fought a battle at Coleman's Plantation in Jefferson County, Mississippi. This engagement is notable as it is most likely the first time that Black soldiers from Mississippi fought against white Confederates from the same state.
The 53rd United States Colored Infantry was an infantry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Originally formed as the 3rd Regiment Mississippi Volunteers (African Descent), the regiment was composed of African American enlisted men commanded by white officers. The 53rd served on garrison duty in Louisiana, Mississippi, and Arkansas before being mustered out of service in 1866.
The 58th United States Colored Infantry was an infantry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Originally organized as the 6th Mississippi Infantry (African Descent) on August 27, 1863, the regiment was redesignated as the 58th USCT Infantry on March 11, 1864. The regiment was composed of African American enlisted men from Mississippi commanded by white officers.
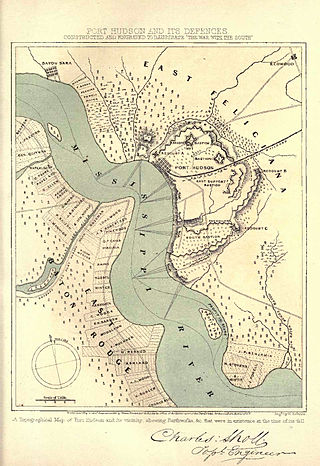
The 80th United States Colored Infantry Regiment was an African-American unit of the United States Colored Troops during the American Civil War. It was organized from the 8th Corps d'Afrique Infantry and attached to the Port Hudson garrison in Louisiana. The 80th Colored Infantry Regiment operated throughout Louisiana until 1866, when the troops scouted in Texas until the men mustered out in March 1867.
The 61st United States Colored Infantry was an infantry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. The regiment was composed of African American enlisted men commanded by white officers and was authorized by the Bureau of Colored Troops which was created by the United States War Department on May 22, 1863. The non-commissioned officers (sergeants and corporals) and enlisted men were African Americans. The regiment was originally organized as the 2nd Tennessee Volunteer Infantry (African Descent) and was also referred to as the 2nd West Tennessee Infantry Regiment (African Descent).