
A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial form. A monitor usually comprises the display device, circuitry, casing, and power supply. The display device in modern monitors is typically a thin film transistor liquid crystal display (TFT-LCD) with LED backlighting having replaced cold-cathode fluorescent lamp (CCFL) backlighting. Older monitors used a cathode ray tube (CRT). Monitors are connected to the computer via VGA, Digital Visual Interface (DVI), HDMI, DisplayPort, Thunderbolt, low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) or other proprietary connectors and signals.

A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly, instead using a backlight or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome. LCDs are available to display arbitrary images or fixed images with low information content, which can be displayed or hidden, such as preset words, digits, and seven-segment displays, as in a digital clock. They use the same basic technology, except that arbitrary images are made up of a large number of small pixels, while other displays have larger elements. LCDs can either be normally on (positive) or off (negative), depending on the polarizer arrangement. For example, a character positive LCD with a backlight will have black lettering on a background that is the color of the backlight, and a character negative LCD will have a black background with the letters being of the same color as the backlight. Optical filters are added to white on blue LCDs to give them their characteristic appearance.
A plasma display panel (PDP) is a type of flat panel display that uses small cells containing plasma; ionized gas that responds to electric fields.

An LCD projector is a type of video projector for displaying video, images or computer data on a screen or other flat surface. It is a modern equivalent of the slide projector or overhead projector. To display images, LCD projectors typically send light from a metal-halide lamp through a prism or series of dichroic filters that separates light to three polysilicon panels – one each for the red, green and blue components of the video signal. As polarized light passes through the panels, individual pixels can be opened to allow light to pass or closed to block the light. The combination of open and closed pixels can produce a wide range of colors and shades in the projected image.

A display device is an output device for presentation of information in visual or tactile form. When the input information that is supplied has an electrical signal, the display is called an electronic display.
The refresh rate is the number of times in a second that a display hardware updates its buffer. This is distinct from the measure of frame rate. The refresh rate includes the repeated drawing of identical frames, while frame rate measures how often a video source can feed an entire frame of new data to a display.

The display resolution or display modes of a digital television, computer monitor or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by different factors in cathode ray tube (CRT) displays, flat-panel displays and projection displays using fixed picture-element (pixel) arrays.

Liquid-crystal-display televisions are television sets that use liquid-crystal displays to produce images. They are, by far, the most widely produced and sold television display type. LCD TVs are thin and light, but have some disadvantages compared to other display types such as high power consumption, poorer contrast ratio, and inferior color gamut.

A backlight is a form of illumination used in liquid crystal displays (LCDs). As LCDs do not produce light by themselves, they need illumination to produce a visible image. Backlights illuminate the LCD from the side or back of the display panel, unlike frontlights, which are placed in front of the LCD. Backlights are used in small displays to increase readability in low light conditions such as in wristwatches, and are used in smart phones, computer displays and LCD televisions to produce light in a manner similar to a CRT display. A review of some early backlighting schemes for LCDs is given in a report Engineering and Technology History by Peter J. Wild.
A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.
The Sony Ruvi is an analog video and still video camera released in 1998. The Ruvi was considerably smaller than any other camcorder available at the time, at 124 × 66 × 44.1 mm and 380g. This made the Ruvi small enough to keep inside a shirt pocket. Ruvi is an abbreviation of Recording Unit by Video.

An active shutter 3D system is a technique of displaying stereoscopic 3D images. It works by only presenting the image intended for the left eye while blocking the right eye's view, then presenting the right-eye image while blocking the left eye, and repeating this so rapidly that the interruptions do not interfere with the perceived fusion of the two images into a single 3D image.

A super-twisted nematic display (STN) is a type of monochrome passive-matrix liquid crystal display (LCD). This type of LCD was invented at the Brown Boveri Research Center, Baden, Switzerland, in 1983. For years a better scheme for multiplexing was sought. Standard twisted nematic (TN) LCDs with a 90 degrees twisted structure of the molecules have a contrast vs. voltage characteristic unsuitable for passive-matrix addressing as there is no distinct threshold voltage. STN displays, with the molecules twisted from 180 to 270 degrees, have superior characteristics. The main advantage of STN LCDs is their more pronounced electro-optical threshold allowing for passive-matrix addressing with many more lines and columns. For the first time, a prototype STN matrix display with 540x270 pixels was made by Brown Boveri in 1984, which was considered a breakthrough for the industry.

Defective pixels are pixels on a liquid crystal display (LCD) that are not performing as expected. The ISO standard ISO 13406-2 distinguishes between three different types of defective pixels, while hardware companies tend to have further distinguishing types.
Electronics on Plastic by Laser Release (EPLaR) is a method for manufacturing flexible electrophoretic displays using conventional AM-LCD manufacturing equipment, avoiding the need to build new factories. The technology can also be used to manufacture flexible OLED displays using standard OLED fabrication facilities.

A LED-backlit LCD is a flat panel display which uses LED backlighting instead of the cold cathode fluorescent (CCFL) backlighting. LED-backlit displays use the same TFT LCD technologies as CCFL-backlit displays, but offer reduced energy consumption, better contrast and brightness, greater color range, more rapid response to changes in scene, and photorefractive effects.
Electrically operated display devices have developed from electromechanical systems for display of text, up to all-electronic devices capable of full-motion 3D color graphic displays. Electromagnetic devices, using a solenoid coil to control a visible flag or flap, were the earliest type, and were used for text displays such as stock market prices and arrival/departure display times. The cathode ray tube was the workhorse of text and video display technology for several decades until being displaced by plasma, liquid crystal (LCD) and solid-state devices such as LEDs and OLEDs. With the advent of microprocessors and microelectronic devices, many more individual picture elements ("pixels") could be incorporated into one display device, allowing graphic displays and video.
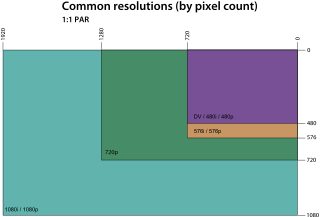
The graphics display resolution is the width and height dimension of an electronic visual display device, such as a computer monitor, in pixels. Certain combinations of width and height are standardized and typically given a name and an initialism that is descriptive of its dimensions. A higher display resolution in a display of the same size means that displayed photo or video content appears sharper, and pixel art appears smaller.
Multi-primary color (MPC) display is a display that can reproduce a wider gamut color than conventional displays. In addition to the standard RGB color subpixels, the technology utilizes additional colors, such as yellow, magenta and cyan, and thus increases the range of displayable colors that the human eye can see.














