
2060 Chiron is a small Solar System body in the outer Solar System, orbiting the Sun between Saturn and Uranus. Discovered in 1977 by Charles Kowal, it was the first-identified member of a new class of objects now known as centaurs—bodies orbiting between the asteroid belt and the Kuiper belt.
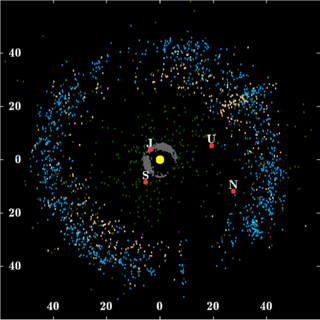
In planetary astronomy, a centaur is a small Solar System body that orbits the Sun between Jupiter and Neptune and crosses the orbits of one or more of the giant planets. Centaurs generally have unstable orbits because they cross or have crossed the orbits of the giant planets; almost all their orbits have dynamic lifetimes of only a few million years, but there is one known centaur, 514107 Kaʻepaokaʻawela, which may be in a stable orbit. Centaurs typically exhibit the characteristics of both asteroids and comets. They are named after the mythological centaurs that were a mixture of horse and human. Observational bias toward large objects makes determination of the total centaur population difficult. Estimates for the number of centaurs in the Solar System more than 1 km in diameter range from as low as 44,000 to more than 10,000,000.

Comet 4P/Faye is a periodic Jupiter-family comet discovered in November 1843 by Hervé Faye at the Royal Observatory in Paris. Its most recent perihelia were on November 15, 2006; May 29, 2014; and September 8, 2021.
39P/Oterma is a currently inactive periodic comet with an orbital period of nearly 20 years that stays outside the orbit of Jupiter. The nucleus has a diameter around 4–5 km. It was last observed in August 2021 and came to perihelion in July 2023 while 1.2 AU from Jupiter. It will finish the modest approach to Jupiter in January 2025 and will next come to perihelion in July 2042 at distance of 5.9 AU from the Sun. Opposition has occurred on 11 November 2023.

49P/Arend–Rigaux is a periodic comet in the Solar System.

78P/Gehrels, also known as Gehrels 2, is a Jupiter-family periodic comet in the Solar System with a current orbital period of 7.22 years.
111P/Helin–Roman–Crockett is a periodic comet in the Solar System. It was discovered by Eleanor and Ron Helin on 5 January 1989 from images obtained on the 3rd and 4th of that month. It is a Jupiter family comet known for extremely close approaches to Jupiter being a Quasi-Hilda comet. During these approaches, it actually orbits Jupiter. The last such approach was in 1976, the next will be in 2071. The Jovian orbits are highly elliptical and subject to intense Solar perturbation at apojove which eventually pulls the comet out of Jovian orbit for the cycle to begin anew.
152P/Helin–Lawrence is a periodic comet in the Solar System.
165P/LINEAR is a periodic comet in the Solar System. 165P/LINEAR has a perihelion distance of 6.8 AU, and is a Chiron-type comet with.
167P/CINEOS (P/2004 PY42) is a large periodic comet and active, grey centaur, approximately 66 kilometers (41 miles) in diameter, orbiting the Sun outside the orbit of Saturn. It was discovered on August 10, 2004, by astronomers with the CINEOS survey at Gran Sasso in Italy. It is one of only a handful known Chiron-type comets.
169/NEAT is a periodic comet in the Solar System. It is the parent body of the alpha Capricornids meteor shower in Late July. 169/NEAT may be related to comet P/2003 T12 (SOHO). It comes to perihelion on 9 July 2022. On 13 July 2022 passed 0.1395 AU (20.87 million km) from Venus. On 11 August 2026 it will pass 0.1672 AU (25.01 million km) from Earth and then come to perihelion on 21 September 2026.

11P/Tempel–Swift–LINEAR is a periodic Jupiter-family comet in the Solar System.

Comet Finlay is a periodic comet with an orbital period of 6 years discovered by William Henry Finlay on September 26, 1886. The next perihelion passage is July 13, 2021 when the comet will have a solar elongation of 54 degrees at approximately apparent magnitude 10. It last came to perihelion on December 27, 2014, at around magnitude 10. Of the numbered periodic comets, the orbit of 15P/Finlay has one of the smallest minimum orbit intersection distances with the orbit of Earth (E-MOID). In October 2060 the comet will pass about 5 million km from Earth.
178P/Hug–Bell is a periodic comet in the Solar System. It was discovered by Northeast Kansas Amateur Astronomers' League members Gary Hug and Graham Bell and is thought to be the first periodic comet to be discovered by amateurs. It was declared a comet less than two days after its initial discovery, after having its course confirmed on previous images.
118401 LINEAR, provisional designation 1999 RE70, is an asteroid and main-belt comet (176P/LINEAR) that was discovered by the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research (LINEAR) 1-metre telescopes in Socorro, New Mexico on September 7, 1999. (118401) LINEAR was discovered to be cometary on November 26, 2005, by Henry H. Hsieh and David C. Jewitt as part of the Hawaii Trails project using the Gemini North 8-m telescope on Mauna Kea and was confirmed by the University of Hawaii's 2.2-m (88-in) telescope on December 24–27, 2005, and Gemini on December 29, 2005. Observations using the Spitzer Space Telescope have resulted in an estimate of 4.0±0.4 km for the diameter of (118401) LINEAR.

45P/Honda–Mrkos–Pajdušáková is a short-period comet discovered by Minoru Honda December 3, 1948. It is named after Minoru Honda, Antonín Mrkos, and Ľudmila Pajdušáková. The object revolves around the Sun on an elliptical orbit with a period of 5.25 years. The nucleus is 1.3 kilometers in diameter. On August 19 and 20, 2011, it became the fifteenth comet detected by ground radar telescope.
163P/NEAT is a periodic comet discovered on November 5, 2004 by Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking (NEAT) using the 1.2 meter Samuel Oschin telescope at Palomar Observatory.

62P/Tsuchinshan, also known as Tsuchinshan 1, is a periodic comet discovered on 1965 January 1 at Purple Mountain Observatory, Nanking. It will next come to perihelion on 25 December 2023 at around apparent magnitude 8, and will be 0.53 AU (79 million km) from Earth and 110 degrees from the Sun.

246P/NEAT is a periodic comet discovered on 2004 March 28 by Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking (NEAT) using the 1.2-metre (47 in) reflector at Haleakala. It was given the permanent number 246P on 2011 January 14.
51P/Harrington is a periodic comet in the Solar System.












