
The American Locomotive Company was an American manufacturer of locomotives, diesel generators, steel, and tanks that operated from 1901 to 1969. The company was formed by the merger of seven smaller locomotive manufacturers and Schenectady Locomotive Engine Manufactory of Schenectady, New York. A subsidiary, American Locomotive Automobile Company, designed and manufactured automobiles under the Alco brand from 1905 to 1913. ALCO also produced nuclear reactors from 1954 to 1962.

Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twentieth century following a December 1900 editorial in American Engineer and Railroad Journal.

Montreal Locomotive Works (MLW) was a Canadian railway locomotive manufacturer which existed under several names from 1883 to 1985, producing both steam and diesel locomotives. For a number of years it was a subsidiary of the American Locomotive Company. MLW's headquarters and manufacturing facilities were located in Montreal, Quebec.

Orenstein & Koppel was a major German engineering company specialising in railway vehicles, escalators, and heavy equipment. It was founded on April 1, 1876 in Berlin by Benno Orenstein and Arthur Koppel.

A booster engine for steam locomotives is a small two-cylinder steam engine back-gear-connected to the trailing truck axle on the locomotive or the lead truck on the tender. A rocking idler gear permits it to be put into operation by the driver (engineer). It drives one axle only and can be non-reversible, with one idler gear, or reversible, with two idler gears.

Lima Locomotive Works was an American firm that manufactured railroad locomotives from the 1870s through the 1950s. The company took the most distinctive part of its name from its main shop's location in Lima, Ohio. The shops were located between the Erie Railroad main line, the Baltimore & Ohio's Cincinnati-Toledo main line and the Nickel Plate Road main line and shops.

The ALCO S-1 and S-3 were 660 horsepower (490 kW) switcher diesel-electric locomotives produced by ALCO and their Canadian subsidiary Montreal Locomotive Works (MLW). The two locomotives differed only in trucks, with the S-1 using ALCO's own Blunt trucks, and the S-3 using AAR type A switcher trucks. The S-1 was built between April 1940 and June 1950, with a total of 543 completed, while the S-3 was constructed between February 1950 and November 1953 with total sales of 300. A modified version, the S-10, was built by MLW only; 13 were built between January and June 1958.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-10-0 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels, ten powered and coupled driving wheels, and no trailing wheels. Central Pacific Railroad's El Gobernador, built in 1883, was the only locomotive with this wheel arrangement to operate in the United States. The name "Mastodon" has also been applied to this type, though this nickname has also been mistakenly used for the 4-8-0 arrangement, leading to some confusion. Sources refer to the 4-8-0 as the Twelve-wheeler. Later, these locomotives were named "Super Mastodon's."
The USRA 0-8-0 was a USRA standard class of steam locomotive designed under the control of the United States Railroad Administration, the nationalized railroad system in the United States during World War I. This was the standard heavy switcher of the USRA types, and was of 0-8-0 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, or "D" in UIC classification.

South Australian Railways (SAR) was the statutory corporation through which the Government of South Australia built and operated railways in South Australia from 1854 until March 1978, when its non-urban railways were incorporated into Australian National, and its Adelaide urban lines were transferred to the State Transport Authority.
National Railway Equipment Company is an American railroad equipment rebuilding, leasing, and manufacturing company, headquartered in Mt. Vernon, Illinois. NREC sells new and rebuilt locomotives to railroad companies worldwide, with an emphasis on the North American market.
A builder's plate is usually a metal plate that is attached to rolling stock, bogies, construction equipment, trucks, automobiles, large household appliances, bridges, ships and more. It gives such information as the name of the manufacturer, the place and country of manufacture, the model number, the serial number, as well as the date of manufacture or date of fabrication of the item or unit.

The Siemens Charger is a family of diesel-electric passenger locomotives designed and manufactured by Siemens Mobility for the North American market.

The GN boxcab locomotives were the first electric locomotives purchased by the Great Northern Railway (GN) for use through the Cascade Tunnel. Four locomotives were supplied by the American Locomotive Company; they used electrical equipment from General Electric and weighed 115 short tons (104 t) each.

The South African Railways Katanga Mikado 2-8-2 of 1917 was a steam locomotive used in South Africa.
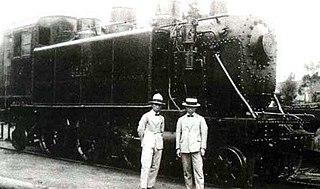
The Pureshi-class (プレシ) locomotives were a group of steam tank locomotives with 2-6-2 wheel arrangement of used by the Chosen Government Railway (Sentetsu) in Korea. The "Pure" name came from the American naming system for steam locomotives, under which locomotives with 2-6-2 wheel arrangement were called "Prairie".

The Manila Railroad 45 class of 1919 were twenty-one 4-6-0 Ten-wheeler steam locomotives. Twenty locomotives were built by American light duty locomotive manufacturer H.K. Porter, Inc. between 1919 and 1921 for the Manila Railroad Company (MRR). The so-called Porters were the most successful steam locomotive class in Philippine service. They carried express trains for passengers as well as short-range maintenance trains for 70 years and served both the MRR and its successor, the Philippine National Railways. However, like all tender engines from the Manila Railroad era, the last locomotive was scrapped in the 1990s without a single unit preserved.

The Manila Railway 100 class, of 1906 were five 4-4-2 Atlantic-type steam locomotives built by the North British Locomotive Company. They were the flagship locomotives of the Manila Railway during the late 1900s and throughout the 1910s, being the first tender-hauling locomotives in Philippine service. They hauled the Baguio Special, an express service between Manila and Baguio via Damortis station in Rosario, La Union.
















