
The Antarctic Treaty and related agreements, collectively known as the Antarctic Treaty System (ATS), regulate international relations with respect to Antarctica, Earth's only continent without a native human population. It was the first arms control agreement established during the Cold War, designating the continent as a scientific preserve, establishing freedom of scientific investigation, and banning military activity; for the purposes of the treaty system, Antarctica is defined as all the land and ice shelves south of 60°S latitude. Since September 2004, the Antarctic Treaty Secretariat, which implements the treaty system, is headquartered in Buenos Aires, Argentina.

Norway, formally the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of Norway. Bouvet Island, located in the Subantarctic, is a dependency; Norway also claims the Antarctic territories of Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land. The capital and largest city in Norway is Oslo.

Svalbard, previously known as Spitsbergen or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it lies about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed in size by Nordaustlandet and Edgeøya. The largest settlement is Longyearbyen on the west coast of Spitsbergen.
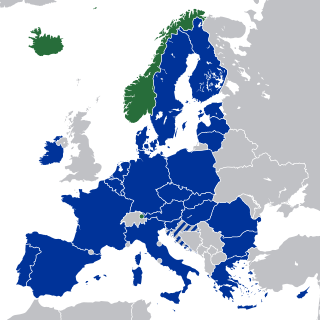
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the Agreement on the European Economic Area, an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade Association. The EEA links the EU member states and three of the four EFTA states into an internal market governed by the same basic rules. These rules aim to enable free movement of persons, goods, services, and capital within the European single market, including the freedom to choose residence in any country within this area. The EEA was established on 1 January 1994 upon entry into force of the EEA Agreement. The contracting parties are the EU, its member states, and Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway. New members of EFTA would not automatically become party to the EEA Agreement, as each EFTA State decides on its own whether it applies to be party to the EEA Agreement or not. According to Article 128 of the EEA Agreement, "any European State becoming a member of the Community shall, and the Swiss Confederation or any European State becoming a member of EFTA may, apply to become a party to this Agreement. It shall address its application to the EEA Council." EFTA does not envisage political integration. It does not issue legislation, nor does it establish a customs union. Schengen is not a part of the EEA Agreement. However, all of the four EFTA States participate in Schengen and Dublin through bilateral agreements. They all apply the provisions of the relevant Acquis.

Spitsbergen, is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway.

Sweden and Norway or Sweden–Norway, officially the United Kingdoms of Sweden and Norway, and known as the United Kingdoms, was a personal union of the separate kingdoms of Sweden and Norway under a common monarch and common foreign policy that lasted from 1814 until its peaceful dissolution in 1905.

The Svalbard Treaty recognises the sovereignty of Norway over the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard, at the time called Spitsbergen. The exercise of sovereignty is, however, subject to certain stipulations, and not all Norwegian law applies. The treaty restricts military uses of the archipelago, but it is not demilitarized. The signatories were given equal rights to engage in commercial activities on the islands. As of 2023, Norway and Russia make use of this right.
In 1814, the Kingdom of Norway made a brief and ultimately unsuccessful attempt to regain its independence. While Norway had always legally been a separate kingdom, since the 16th century it had shared a monarch with Denmark; Norway was a subordinate partner in the combined state, whose government was based in Copenhagen. Due to its alliance with France during the Napoleonic Wars, Denmark was forced to sign the Treaty of Kiel in January 1814 ceding Norway to Sweden.

The history of the European Communities between 1958 and 1972 saw the early development of the European Communities. The European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) had just been joined by the European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom) and the European Economic Community (EEC), the latter of which soon became the most important. In 1967 the EEC's institutions took over the other two with the EEC's Commission holding its first terms under Hallstein and Rey.
Events in the year 1814 in Norway.
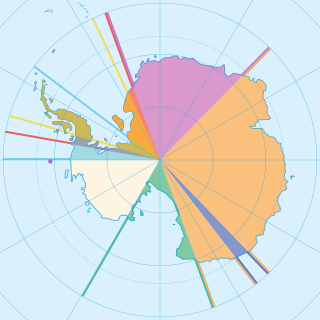
Seven sovereign states – Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway, and the United Kingdom – have made eight territorial claims in Antarctica. These countries have tended to place their Antarctic scientific observation and study facilities within their respective claimed territories; however, a number of such facilities are located outside of the area claimed by their respective countries of operation, and countries without claims such as China, India, Italy, Japan, Pakistan, Russia, South Africa (SANAE), Poland, and the United States have constructed research facilities within the areas claimed by other countries. There are overlaps among the territories claimed by Argentina, Chile, and the United Kingdom.

The history of the European Union between 1993 and 2004 was the period between its creation and the 2004 enlargement. The European Union was created at the dawn of the post–Cold War era and saw a series of successive treaties laying the ground for the euro, foreign policy and future enlargement. Three new member states joined the previous twelve in this period and the European Economic Area extended the reach of the EU's markets to three more.

Denmark–Norway was an early modern multi-national and multi-lingual real union consisting of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Kingdom of Norway, the Duchy of Schleswig, and the Duchy of Holstein. The state also claimed sovereignty over three historical peoples: Frisians, Gutes and Wends. Denmark–Norway had several colonies, namely the Danish Gold Coast, the Nicobar Islands, Serampore, Tharangambadi, and the Danish West Indies. The union was also known as the Dano-Norwegian Realm, Twin Realms (Tvillingerigerne) or the Oldenburg Monarchy (Oldenburg-monarkiet).
Events in the year 1751 in Norway.
Norway's elongated shape, its numerous internal geographical barriers and the often widely dispersed and separated settlements are all factors that have strongly influenced the structure of the country's administrative subdivisions. This structure has varied over time and is subject to continuous review. In 2017, the government decided to abolish some of the counties and to merge them with other counties to form larger ones, reducing the number of counties from 19 to 11, which was implemented on 1 January 2020. Following protests, the new government decided to abolish three of the new counties in 2022, and re-establish seven of the old ones. Taking effect on 1 January 2024 there are fifteen counties in Norway.

Queen Maud Land is a roughly 2.7-million-square-kilometre (1.0-million-square-mile) region of Antarctica claimed by Norway as a dependent territory. It borders the claimed British Antarctic Territory 20° west and the Australian Antarctic Territory 45° east. In addition, a small unclaimed area from 1939 was annexed in June 2015. Positioned in East Antarctica, it makes out about one-fifth of the continent, and is named after the Norwegian queen Maud of Wales (1869–1938).

The 1995 enlargement of the European Union saw Austria, Finland, and Sweden accede to the European Union (EU). This was the EU's fourth enlargement and came into effect on 1 January of that year. It is also known as the EFTAn Enlargement round All these states were previous members of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) and had traditionally been less interested in joining the EU than other European countries. Norway had negotiated to join alongside the other three but following the signing of the treaty, membership was turned down by the Norwegian electorate in the 1994 national referendum. Switzerland also applied for membership on 26 May 1992, but withdrew it after a negative referendum result on 6 December 1992.

The economy of Svalbard is dominated by coal mining, tourism and research. In 2007, there were 484 people working in the mining sector, 211 people working in the tourism sector and 111 people working in the education sector. The same year, mining gave a revenue of 2.008 billion kr, tourism NOK 317 million and research 142 million. In 2006, the average income for economically active people was NOK 494,700, or 23% higher than on the mainland. Almost all housing is owned by the various employers and institutions and rented to their employees; there are only a few privately owned houses, most of which are recreational cabins. Because of this, it is nearly impossible to live on Svalbard without working for an established institution. The Spitsbergen Treaty and Svalbard Act established Svalbard as an economic free zone and demilitarized zone in 1925.

The Treaty of Accession 1972 was the international agreement which provided for the accession of Denmark, Ireland, Norway and the United Kingdom to the European Communities. Norway did not ratify the treaty after it was rejected in a referendum held in September 1972. The treaty was ratified by Denmark, Ireland and the United Kingdom who became EC member states on 1 January 1973 when the treaty entered into force. The treaty remains an integral part of the constitutional basis of the European Union.
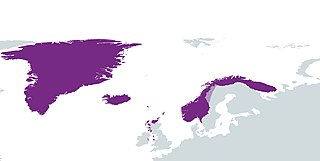
The term Norwegian Realm and Old Kingdom of Norway refer to the Kingdom of Norway's peak of power at the 13th century after a long period of civil war before 1240. The kingdom was a loosely unified nation including the territory of modern-day Norway, modern-day Swedish territory of Jämtland, Herjedalen, Ranrike (Bohuslän) and Idre and Särna, as well as Norway's overseas possessions which had been settled by Norwegian seafarers for centuries before being annexed or incorporated into the kingdom as 'tax territories'. To the North, Norway also bordered extensive tax territories on the mainland. Norway, whose expansionism starts from the very foundation of the Kingdom in 872, reached the peak of its power in the years between 1240 and 1319.
















