Related Research Articles

The prehistory of Papua New Guinea can be traced to about 50,000–60,000 years ago, when people first migrated towards the Australian continent. The written history began when European navigators first sighted New Guinea in the early part of the 17th century.

Transport in Papua New Guinea is mainly based around roads and air travel. It is in many cases heavily limited by the mountainous terrain and copious amount of rainfall and frequent severe weather occurring in many locations, such as Lae. The capital, Port Moresby, is not linked by road to any of the other major towns and many highland villages can only be reached by light aircraft or on foot.

Sandaun Province is the northwesternmost mainland province of Papua New Guinea. It covers an area of 35,920 km2 and has a population of 248,411. The capital is Vanimo. In July 1998 the area surrounding the town Aitape was hit by an enormous tsunami caused by a Magnitude 7.0 earthquake which killed over 2,000 people. The five villages along the west coast of Vanimo towards the International Border are namely; Lido, Waromo, Yako, Musu and Wutung.

For administrative purposes, Papua New Guinea is divided into administrative divisions called provinces. There are 22 provincial-level divisions, which include 20 provinces, the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, and the National Capital District of Port Moresby.

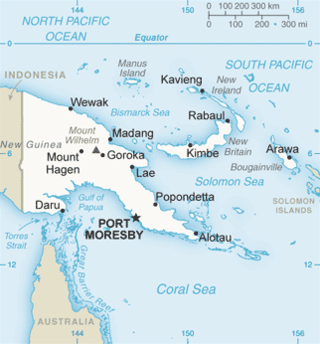
Madang is the capital of Madang Province and is a town with a population of 27,420 on the north coast of Papua New Guinea. It was first settled by the Germans in the 19th century.

Morobe Province is a province on the northern coast of Papua New Guinea. The provincial capital and largest city is Lae. The province covers 33,705 km2, with a population of 674,810, and since the division of Southern Highlands Province in May 2012 it is the most populous province. It includes the Huon Peninsula, the Markham River, and delta, and coastal territories along the Huon Gulf. The province has nine administrative districts. At least 101 languages are spoken, including Kâte and Yabem language. English and Tok Pisin are common languages in the urban areas, and in some areas pidgin forms of German are mixed with the native language.

The culture of Papua New Guinea is many-sided and complex. It is estimated that more than 7000 different cultural groups exist in Papua New Guinea, and most groups have their own language. Because of this diversity, in which they take pride, many different styles of cultural expression have emerged; each group has created its own expressive forms in art, dance, weaponry, costumes, singing, music, architecture and much more. To unify the nation, the language Tok Pisin, once called Neo-Melanesian has evolved as the lingua franca — the medium through which diverse language groups are able to communicate with one another in Parliament, in the news media, and elsewhere. People typically live in villages or dispersed hamlets which rely on the subsistence farming of yams and taro. The principal livestock in traditional Papua New Guinea is the oceanic pig.

The Papua New Guinea Institute of Medical Research (PNG IMR) is the principal institution conducting health research in Papua New Guinea with a focus on health problems affecting the country's population.

Papua New Guinea is divided into four regions, which are its broadest administrative divisions of Papua New Guinea. While the 22 provincial-level divisions are the primary administrative divisions of PNG, the regions are quite significant in daily life, as they are often the basis for organisation of government services, corporate operations, sporting competitions, and even the machinations of politics.

Papua New Guinea, a sovereign state in Oceania, is the most linguistically diverse country in the world. According to Ethnologue, there are 840 living languages spoken in the country. In 2006, Papua New Guinea Prime Minister Sir Michael Somare stated that "Papua New Guinea has 832 living languages ."

The Monumbo or Bogia Bay languages are a pair of closely related languages that constitute a branch of the Torricelli language family. They are spoken in a few coastal villages around Bogia Bay of Bogia District, Madang Province in Papua New Guinea. Unlike all other Torricelli branches except for the Marienberg languages, word order in the Bogia languages is SOV, likely due to contact with Lower Sepik-Ramu and Sepik languages.
The Ottilien or Watam-Awar-Gamay languages languages are a small family of clearly related languages,

The Sepik is the longest river on the island of New Guinea, and the second largest in Oceania by discharge volume after the Fly River. The majority of the river flows through the Papua New Guinea (PNG) provinces of Sandaun and East Sepik, with a small section flowing through the Indonesian province of Papua.
The Arafundi languages are a small family of clearly related languages in East Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea. They are conjectured to be related to the Piawi and Madang languages. They are named after the Arafundi River.
The Lower Ramu or Ottilien–Misegian languages consist of two branches in the Ramu language family. They are all spoken in Yawar Rural LLG, Madang Province, Papua New Guinea.
Marangis a.k.a. Watam is a Ramu language of Papua New Guinea. Like Bosmun, it shares a number of irregular plural markers with the Lower Sepik languages, supporting the proposal of a Ramu – Lower Sepik language family.
As of 24 September 2012, a cholera outbreak in Sierra Leone had caused the deaths of 392 people. It was the country's largest outbreak of cholera since first reported in 1970 and the deadliest since the 1994–1995 cholera outbreak. The outbreak has also affected Guinea, which shares a reservoir near the coast. This was the largest cholera outbreak in Africa in 2012.
Samaritan Aviation is a 501 C-3 non-profit Christian organization that serves the population in the East Sepik Province of Papua New Guinea through emergency evacuation flights, the delivery of medical supplies, and continued community outreach and health programs. The non-profit is funded by the Papua New Guinea government and individual donations.
Sepik virus (SEPV) is an arthropod-borne virus (arbovirus) of the genus Flavivirus and family Flaviviridae. Flaviviridae is one of the most well characterized viral families, as it contains many well-known viruses that cause diseases that have become very prevalent in the world, like Dengue virus. The genus Flavivirus is one of the largest viral genera and encompasses over 50 viral species, including tick and mosquito borne viruses like Yellow fever virus and West Nile virus. Sepik virus is much less well known and has not been as well-classified as other viruses because it has not been known of for very long. Sepik virus was first isolated in 1966 from the mosquito Mansoniaseptempunctata, and it derives its name from the Sepik River area in Papua New Guinea, where it was first found. The geographic range of Sepik virus is limited to Papua New Guinea, due to its isolation.
John Z'graggen was a Swiss Roman Catholic priest, missionary, linguist, and anthropologist known for his extensive work on Papuan and Oceanic languages, especially the Madang languages. He has also documented languages in Sepik, Manus, and Gulf Provinces.
References
- "Cholera hits 2,000 in PNG: officials". The Sydney Morning Herald. February 8, 2010.