
A public utility company is an organization that maintains the infrastructure for a public service. Public utilities are subject to forms of public control and regulation ranging from local community-based groups to statewide government monopolies.
SWEB Energy, formerly South Western Electricity Board (SWEB) was a British state-owned regional electricity company operating in South West England which was privatised by the Thatcher government. Although sold many times, the 'SWEB' brand name survived until 2006.
The Central Electricity Generating Board (CEGB) was responsible for electricity generation, transmission and bulk sales in England and Wales from 1958 until privatisation of the electricity industry in the 1990s.

Scottish Power Limited, trading as ScottishPower, is a vertically integrated energy company based in Glasgow, Scotland. It is a subsidiary of Spanish utility firm Iberdrola.
British Energy was the UK's largest electricity generation company by volume, before being taken over by Électricité de France (EDF) in 2009. British Energy operated eight former UK state-owned nuclear power stations and one coal-fired power station.

Électricité de France SA, commonly known as EDF, is a French multinational electric utility company owned by the government of France. Headquartered in Paris, with €139.7 billion in sales in 2023, EDF operates a diverse portfolio of at least 120 gigawatts of generation capacity in Europe, South America, North America, Asia, the Middle East, and Africa. In 2009, EDF was the world's largest producer of electricity. Its 56 active nuclear reactors in France are spread out over 18 sites. They comprise 32 reactors of 900 MWe, 20 reactors of 1,300 MWe, and 4 reactors of 1,450 MWe, all PWRs.
Public electricity suppliers (PES) were the fourteen electricity companies created in Great Britain when the electricity market in the United Kingdom was privatised following the Electricity Act 1989. The Utilities Act 2000 subsequently split these companies between distribution network operators and separate supply companies.

EDF Energy is a British integrated energy company, wholly owned by the French state-owned EDF, with operations spanning electricity generation and the sale of natural gas and electricity to homes and businesses throughout the United Kingdom. It employs 11,717 people, and handles 5.22 million business and residential customer accounts.
The utility infrastructure of London, England comprises a range of services and facilities that support and enable the functioning of London as a world city. Infrastructure includes facilities associated with products and materials that are consumed such as electricity, gas, water, heating and liquid fuels; materials that are produced such as sewage and solid waste; and facilities that enable communication and connectivity – telecommunications.

Eastern Electricity plc was an electricity supply and distribution utility serving Eastern England, including East Anglia and part of Greater London. It was renamed Eastern Group under which name it was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index until it was acquired by Hanson plc in 1995, before being purchased by Texas Utilities in 1998.
Seeboard, formerly South Eastern Electricity Board (SEEB), was a British electricity company. The electrical power industry in the United Kingdom was nationalised by the Electricity Act 1947, when over 600 electric power companies were merged into 12 area boards, one of which was the South Eastern Electricity Board. It acquired the former Princes Hotel on the seafront in Hove, East Sussex, and converted it into its headquarters. The building was refurbished and substantially extended between 1979 and 1981.
The London Electricity Board was the public sector utility company responsible for the supply and distribution of electricity to domestic, commercial and industrial consumers in London prior to 1990. It also sold and made available for hire and hire-purchase domestic electrical appliances through local showrooms where electricity bills could also be paid. It was shortened to LEB in its green and blue logo, consisting of the three letters. As London Electricity plc it was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.
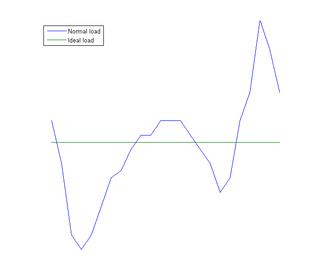
Load management, also known as demand-side management (DSM), is the process of balancing the supply of electricity on the network with the electrical load by adjusting or controlling the load rather than the power station output. This can be achieved by direct intervention of the utility in real time, by the use of frequency sensitive relays triggering the circuit breakers, by time clocks, or by using special tariffs to influence consumer behavior. Load management allows utilities to reduce demand for electricity during peak usage times, which can, in turn, reduce costs by eliminating the need for peaking power plants. In addition, some peaking power plants can take more than an hour to bring on-line which makes load management even more critical should a plant go off-line unexpectedly for example. Load management can also help reduce harmful emissions, since peaking plants or backup generators are often dirtier and less efficient than base load power plants. New load-management technologies are constantly under development — both by private industry and public entities.

Engie SA is a French multinational power company, headquartered in La Défense, Courbevoie, which operates in the fields of electricity generation and distribution, natural gas, nuclear power, renewable energy, and in the petroleum industry. It is involved in both upstream and downstream activities.
Differential tariff is an example of demand side management where the price per unit of energy varies with the consumption. If a power utility uses differential tariff, it may change the rate per kWH of energy used during different times, such as raising the price during times of high energy consumption and lowering the price during times of low energy consumption. This helps balance the rate at which power is used and the rate at which power is created.

Itron, Inc. is an American technology company that offers products and services for energy and water resource management. It is headquartered in Liberty Lake, Washington, United States. The company's products measure and analyze electricity, gas and water consumption. Its products include electricity, gas, water and thermal energy measurement devices and control technology, communications systems, software, as well as managed and consulting services.

UK Power Networks (UKPN) is a distribution network operator for electricity covering South East England, the East of England and London. It manages three licensed distribution networks which together cover an area of 30000 square kilometres and approximately eight million customers.
The Big Six were the United Kingdom's largest retail suppliers of gas and electricity, who dominated the market following liberalisation in the late 1990s. By 2002, six companies – British Gas, EDF Energy, E.ON, RWE npower, Scottish Power and SSE – had emerged from the 15 former incumbent monopoly suppliers.
The Caribbean Electric Utility Services Corporation (CARILEC) is an association of electric energy solution providers operating in the electricity industry in the Caribbean, Central and Southern Americas.








