Service history
The 38th Sustainment Brigade’s origins date to the Mexican Border Crisis when this unit function as a combat arms company. The Indiana National Guard unit was organized and federally recognized on June 3, 1916 as Headquarters Company, 3rd Battalion, 2nd Infantry in Indianapolis. From June 28, through July 9, 1916, the unit was mustered into federal service in support of Mexican Border service. After nearly eight months, it was mustered out of federal service from February 21-26, 1917.
Several weeks later, this unit was called up for World War I duties. Entering federal service on March 25, 1917, its members were sent to Camp Shelby, Mississippi, where the unit was redesignated as Headquarters Company, 3rd Battalion, 152nd Infantry, a company of the 38th Division.
The 38th Infantry Division arrived in Europe in October 1918 and was dispersed into front-line fighting units. After the Armistice of 11 November 1918 was signed, the division was demobilized March 8, 1919, at Camp Taylor, Louisville, Kentucky.
After World War I, Headquarters Company, 3rd Battalion, 152nd Infantry was reorganized and federally recognized September 22, 1921, at Indianapolis. Subsequently, this unit went through two changes prior to World War II:
- Redesignation as Headquarters Company, 1st Battalion, 151st Infantry on January 1, 1922; and
- Reorganization and redesignation as Headquarters Company, 151st Infantry Regiment on March 20, 1934.
Its members were then inducted into World War II federal service in Indianapolis on January 17, 1941. On February 10, 1942, the 38th Division was redesignated as the 38th Infantry Division. When the unit's mission changed from service in the European to Pacific theatres, subsequent to Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor, the 38th Division then underwent three years of training at Camp Shelby, Mississippi. It then departed for Hawaii in January 1944 for additional training and security operations.
The next stop was Oro Bay, New Guinea, for jungle training and several brief encounters with Japanese troops. From there the division headed to Leyte, where it engaged in a fierce battle with the Japanese in December 1944. The next landing, Luzon, was to be the unit's assault landing, but because ground troops in the area had already secured the area, members of the division were met instead by local residents carrying baskets of food. The remainder of the tour resembled the unit's Leyte experience.
The 38th Infantry Division was then assigned the M-7 Operation to assist in eradicating the presence of Japanese troops in the Philippine Peninsula and Islands in Manila Bay as part of a five-phase plan, which included clearing Highway 1 in the north, the Fort Stotsenburg area in the very south (initiated by the landing at Mariveles), the Zambales Mountains between, and the Islands of Caraballo, Carabao, and El Fraille (Fort Drum).
Headquarters Company, 151st Infantry Regiment, was responsible for overseeing the missions of the 151st Infantry Regiment, which consisted of three battalions. The 151st, along with the 152nd and 149th Infantry Regiments, was involved in the clearing of Highway 1. The battle, now called "The Battle of Zig Zag Pass," was a bloody standstill between the Japanese and the 38th Division’s Infantry Regiments, but ultimately, the 38th Infantry Division prevailed. The 151st was also involved in the clearing of the Zambales Mountains, as well as the Island Operations. In February 1945, the Philippine Peninsula was declared clear of the Japanese. Legend has it on this day General Douglas C. MacArthur declared the 38th Infantry Division, "The Avengers of Bataan". The nickname stuck for five decades, and in 2011, the Center of Military History granted the "nickname" as the 38th Infantry Divisions "Distinctive Designation". Following the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki and the unconditional surrender by the Empire of Japan, the Japanese on the Philippine Peninsula surrendered to the 38th Infantry Division.
By June 1945, the 38th Infantry Division had completed operations. By November 1945, its members had returned home to Indiana by way of Camp Anza, California.
After World War II, National Guard units across the nation were required to undergo federal recognition inspections. For Headquarters Company 151st Infantry Regiment, this occurred July 29, 1947, at Indianapolis.
On February 1, 1959, Headquarters Company 151st Infantry Regiment was reorganized into a Combat Support element as Headquarters and Headquarters Detachment, 38th Infantry Division Trains. The unit would undergo two more major reorganizations to become the sustainment element it is today. The first one occurred March 1, 1963, which reorganized and redesignated Headquarters and Headquarters Detachment, 38th Infantry Division Trains as Headquarters, Headquarters Company, 38th Infantry Division Support Command (DISCOM). The maintenance aspect of sustainment was added when HHC 38th Infantry Division Support Command was consolidated with 38th Infantry Division Material Management Center on September 1, 1993.
In May 2006, HHC Division Support Command was ordered into active federal service in support of the Global War on Terrorism, Operation Iraqi Freedom. This was the first time in Indiana National Guard history that a brigade-echelon unit was deployed with a female commander, COL Marjorie Courtney. Under the name "Task Force Indy" – HHC DISCOM served as the Garrison Command for Victory Base Complex in Baghdad. DISCOM was released from active federal service in November 2007 and reverted to state control.
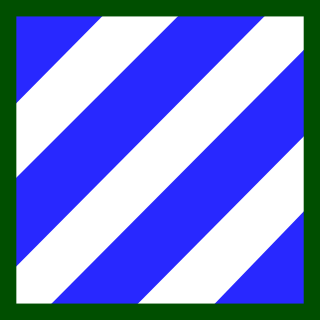
On September 1, 2008, HHC DISCOM went from a "Support" element to a "Sustainment" element when it was expanded, reorganized, and redesignated as Headquarters and Headquarters Company, 38th Sustainment Brigade. This reorganization would also make the 38th Sustainment Brigade a "separate" brigade (not doctrinally aligned to a specific division). This status authorized the Brigade a new Shoulder Sleeve Insignia (SSI), Distinctive Unit Insignia (DUI) and Motto. Drawing from its 38th Infantry Division roots, the brigade included elements of the 38th ID in both the DUI, and SSI, including the red and blue background on both the SSI and DUI, the cloverleaf on the DUI, and the three stripes on the SSI, which signify the three wars that the unit participated in as a part of the 38th ID (World War I, World War II, and GWOT). The brigade also adopted the nickname, "Avengers," which alludes back to the 38th ID’s distinctive designation, "Avengers of Bataan."
The Avengers were activated again for federal service in support of Operation Enduring Freedom on August 26, 2012. Their mission was to perform sustainment operations throughout the Kuwait theatre and facilitate the drawdown of troops from Afghanistan. It would also be the first time in Indiana National Guard history that the commander and the command sergeant major were both female, COL Deedra Thombleson and CSM Karolyn Peeler, both were later relieved of their command.
In June 2013 the brigade was relieved from its deployment to Kuwait, and demobilized through North Fort Hood, Texas, and was slated to be relieved by the 371st Sustainment Brigade (United States), Ohio Army National Guard.