The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol used on Internet Protocol (IP) networks for automatically assigning IP addresses and other communication parameters to devices connected to the network using a client–server architecture.
An Internet Protocol address is a numerical label such as 192.0.2.1 that is connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two main functions: network interface identification and location addressing.

Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol (IP). It is one of the core protocols of standards-based internetworking methods in the Internet and other packet-switched networks. IPv4 was the first version deployed for production on SATNET in 1982 and on the ARPANET in January 1983. It is still used to route most Internet traffic today, even with the ongoing deployment of Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6), its successor.

Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol (IP), the communications protocol that provides an identification and location system for computers on networks and routes traffic across the Internet. IPv6 was developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to deal with the long-anticipated problem of IPv4 address exhaustion, and is intended to replace IPv4. In December 1998, IPv6 became a Draft Standard for the IETF, which subsequently ratified it as an Internet Standard on 14 July 2017.
The Internet Protocol (IP) is the network layer communications protocol in the Internet protocol suite for relaying datagrams across network boundaries. Its routing function enables internetworking, and essentially establishes the Internet.
Classless Inter-Domain Routing is a method for allocating IP addresses and for IP routing. The Internet Engineering Task Force introduced CIDR in 1993 to replace the previous classful network addressing architecture on the Internet. Its goal was to slow the growth of routing tables on routers across the Internet, and to help slow the rapid exhaustion of IPv4 addresses.
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a standardized exterior gateway protocol designed to exchange routing and reachability information among autonomous systems (AS) on the Internet. BGP is classified as a path-vector routing protocol, and it makes routing decisions based on paths, network policies, or rule-sets configured by a network administrator.
A multicast address is a logical identifier for a group of hosts in a computer network that are available to process datagrams or frames intended to be multicast for a designated network service. Multicast addressing can be used in the link layer, such as Ethernet multicast, and at the internet layer for Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4) or Version 6 (IPv6) multicast.

A subnetwork or subnet is a logical subdivision of an IP network. The practice of dividing a network into two or more networks is called subnetting.
In Internet networking, a private network is a computer network that uses a private address space of IP addresses. These addresses are commonly used for local area networks (LANs) in residential, office, and enterprise environments. Both the IPv4 and the IPv6 specifications define private IP address ranges.
The Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP), or simply Neighbor Discovery (ND), is a protocol of the Internet protocol suite used with Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6). It operates at the link layer of the Internet model, and is responsible for gathering various information required for network communication, including the configuration of local connections and the domain name servers and gateways.
In the Internet addressing architecture, the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) have reserved various Internet Protocol (IP) addresses for special purposes.
6LoWPAN was a working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). It was created with the intention of applying the Internet Protocol (IP) even to the smallest devices, enabling low-power devices with limited processing capabilities to participate in the Internet of Things.
An IPv6 transition mechanism is a technology that facilitates the transitioning of the Internet from the Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) infrastructure in use since 1983 to the successor addressing and routing system of Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6). As IPv4 and IPv6 networks are not directly interoperable, transition technologies are designed to permit hosts on either network type to communicate with any other host.
A unique local address (ULA) is an Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) address in the address range fc00::/7. Its purpose in IPv6 is somewhat analogous to IPv4 private network addressing, but with significant differences. Unique local addresses may be used freely, without centralized registration, inside a single site or organization or spanning a limited number of sites or organizations. They are routable only within the scope of such private networks, but not in the global IPv6 Internet.

Locator/ID Separation Protocol (LISP) is a "map-and-encapsulate" protocol which is developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force LISP Working Group. The basic idea behind the separation is that the Internet architecture combines two functions, routing locators and identifiers in one number space: the IP address. LISP supports the separation of the IPv4 and IPv6 address space following a network-based map-and-encapsulate scheme. In LISP, both identifiers and locators can be IP addresses or arbitrary elements like a set of GPS coordinates or a MAC address.

An Internet Protocol Version 6 address is a numeric label that is used to identify and locate a network interface of a computer or a network node participating in a computer network using IPv6. IP addresses are included in the packet header to indicate the source and the destination of each packet. The IP address of the destination is used to make decisions about routing IP packets to other networks.
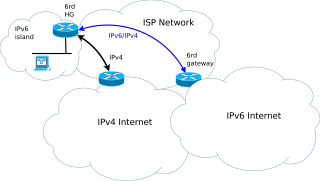
6rd is a mechanism to facilitate IPv6 rapid deployment across IPv4 infrastructures of Internet service providers (ISPs).

Carrier-grade NAT, also known as large-scale NAT (LSN), is a type of network address translation (NAT) for use in IPv4 network design. With CGNAT, end sites, in particular residential networks, are configured with private network addresses that are translated to public IPv4 addresses by middlebox network address translator devices embedded in the network operator's network, permitting the sharing of small pools of public addresses among many end sites. This shifts the NAT function and configuration thereof from the customer premises to the Internet service provider network.
NAT64 is an IPv6 transition mechanism that facilitates communication between IPv6 and IPv4 hosts by using a form of network address translation (NAT). The NAT64 gateway is a translator between IPv4 and IPv6 protocols, for which function it needs at least one IPv4 address and an IPv6 network segment comprising a 32-bit address space. The "well-known prefix" reserved for this service is 64:ff9b::/96.