
Dennis MacAlistair Ritchie was an American computer scientist. He created the C programming language and, with long-time colleague Ken Thompson, the Unix operating system. Ritchie and Thompson were awarded the Turing Award from the ACM in 1983, the Hamming Medal from the IEEE in 1990 and the National Medal of Technology from President Bill Clinton in 1999. Ritchie was the head of Lucent Technologies System Software Research Department when he retired in 2007. He was the "R" in K&R C, and commonly known by his username dmr.
The plumber, in the Plan 9 from Bell Labs and Inferno operating systems, is a mechanism for reliable uni- or multicast inter-process communication of formatted textual messages. It uses the Plan 9 network file protocol, 9P, rather than a special-purpose IPC mechanism.
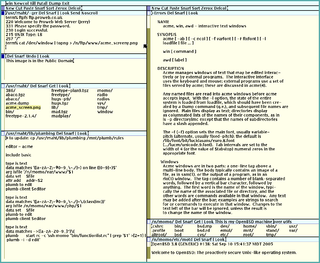
Acme is a text editor and graphical shell from the Plan 9 from Bell Labs operating system, designed and implemented by Rob Pike. It can use the Sam command language. The design of the interface was influenced by Oberon. It is different from other editing environments in that it acts as a 9P server. A distinctive element of the user interface is mouse chording.

The Unix philosophy, originated by Ken Thompson, is a set of cultural norms and philosophical approaches to minimalist, modular software development. It is based on the experience of leading developers of the Unix operating system. Early Unix developers were important in bringing the concepts of modularity and reusability into software engineering practice, spawning a "software tools" movement. Over time, the leading developers of Unix established a set of cultural norms for developing software, norms which became as important and influential as the technology of Unix itself; this has been termed the "Unix philosophy."
Limbo is a programming language for writing distributed systems and is the language used to write applications for the Inferno operating system. It was designed at Bell Labs by Sean Dorward, Phil Winterbottom, and Rob Pike.
This article presents a timeline of events in the history of computer operating systems from 1951 to the current day. For a narrative explaining the overall developments, see the History of operating systems.

Sam is a multi-file text editor based on structural regular expressions. It was originally designed in the early 1980s at Bell Labs by Rob Pike with the help of Ken Thompson and other Unix developers for the Blit windowing terminal running on Unix; it was later ported to other systems. Sam follows a classical modular Unix aesthetic. It is internally simple, its power leveraged by the composability of a small command language and extensibility through shell integration.

rio is Plan 9 from Bell Labs' windowing system. It is well known for making its window management transparent to the application. This allows running rio inside of another window manager.

Inferno is a distributed operating system started at Bell Labs and now developed and maintained by Vita Nuova Holdings as free software. Inferno was based on the experience gained with Plan 9 from Bell Labs, and the further research of Bell Labs into operating systems, languages, on-the-fly compilers, graphics, security, networking and portability. The name of the operating system and many of its associated programs, as well as that of the current company, were inspired by Dante Alighieri's Divine Comedy.
9P is a network protocol developed for the Plan 9 from Bell Labs distributed operating system as the means of connecting the components of a Plan 9 system. Files are key objects in Plan 9. They represent windows, network connections, processes, and almost anything else available in the operating system.
Vismon was the Bell Labs system which displayed authors' faces on one of their internal e-mail systems. The name was a pun on the sysmon program used at Bell to show the load on computer systems. It can also be interpreted as "visual monitor". The system inspired Rich Burridge to develop the similar but more widespread faces system which spread with Unix distributions in the 1980s. This in turn inspired Steve Kinzler to develop the Picons, or personal icons, which have the goal of offering symbols and other images, as well as faces to represent individuals and institutions in email messages. Other systems such as the faces available on the LAN email functions of the NeXTSTEP platform also seem to have been influenced by the original Vismon capabilities. The faces program in Plan 9 is the direct descendant of this system.

In computing, the Blit was a programmable bitmap graphics terminal designed by Rob Pike and Bart Locanthi Jr. of Bell Labs in 1982.
Alef is a discontinued concurrent programming language, designed as part of the Plan 9 operating system by Phil Winterbottom of Bell Labs. It implemented the channel-based concurrency model of Newsqueak in a compiled, C-like language.

The Unix Programming Environment, first published in 1984 by Prentice Hall, is a book written by Brian W. Kernighan and Rob Pike, both of Bell Labs and considered an important and early document of the Unix operating system.
hoc, an acronym for High Order Calculator, is an interpreted programming language that was used in the 1984 book The Unix Programming Environment to demonstrate how to build interpreters using Yacc.

Unix is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, development starting in the 1970s at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others.

Kenneth Lane Thompson, commonly referred to as ken in hacker circles, is an American pioneer of computer science. Having worked at Bell Labs for most of his career, Thompson designed and implemented the original Unix operating system. He also invented the B programming language, the direct predecessor to the C programming language, and was one of the creators and early developers of the Plan 9 operating systems. Since 2006, Thompson has worked at Google, where he co-invented the Go programming language.
Newsqueak is a concurrent programming language for writing application software with interactive graphical user interfaces.












