
The Ames Research Center (ARC), also known as NASA Ames, is a major NASA research center at Moffett Federal Airfield in California's Silicon Valley. It was founded in 1939 as the second National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) laboratory. That agency was dissolved and its assets and personnel transferred to the newly created National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) on October 1, 1958. NASA Ames is named in honor of Joseph Sweetman Ames, a physicist and one of the founding members of NACA. At last estimate NASA Ames has over US$3 billion in capital equipment, 2,300 research personnel and a US$860 million annual budget.

A railgun is a device that uses electromagnetic force to launch high velocity projectiles, by means of a sliding armature that is accelerated along a pair of conductive rails. It is typically constructed as a weapon, and the projectile normally does not contain explosives, instead relying on the projectile's high speed to inflict damage. The railgun uses a pair of parallel conductors—rails—along which a sliding armature is accelerated by the electromagnetic effects of a current that flows down one rail, into the armature and then back along the other rail. It is based on principles similar to those of the homopolar motor.

A recoilless rifle, recoilless launcher or recoilless gun, sometimes abbreviated "RR" or "RCL" is a type of lightweight artillery system or man-portable launcher that is designed to eject some form of countermass such as propellant gas from the rear of the weapon at the moment of firing, creating forward thrust that counteracts most of the weapon's recoil. This allows for the elimination of much of the heavy and bulky recoil-counteracting equipment of a conventional cannon as well as a thinner-walled barrel, and thus the launch of a relatively large projectile from a platform that would not be capable of handling the weight or recoil of a conventional gun of the same size. Technically, only devices that use spin-stabilized projectiles fired from a rifled barrel are recoilless rifles, while smoothbore variants are recoilless guns. This distinction is often lost, and both are often called recoilless rifles.
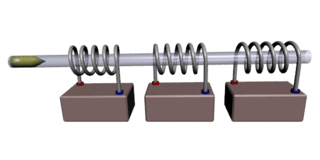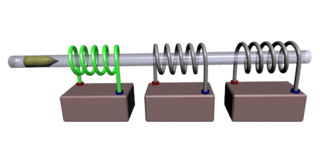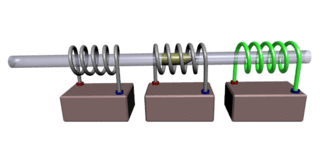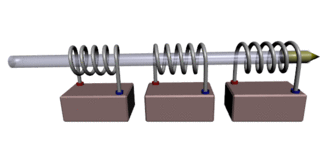
A coilgun or Gauss rifle is a type of projectile accelerator consisting of one or more coils used as electromagnets in the configuration of a linear motor that accelerate a ferromagnetic or conducting projectile to high velocity. In almost all coilgun configurations, the coils and the gun barrel are arranged on a common axis. It is not a rifle as the barrel is not rifled. The name "Gauss" is in reference to Carl Friedrich Gauss, who formulated mathematical descriptions of the magnetic effect used by magnetic accelerator cannons.
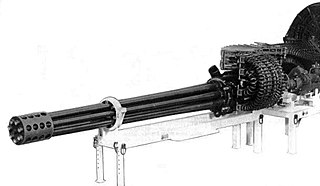
The General Electric GAU-8/A Avenger is a 30 mm hydraulically driven seven-barrel Gatling-style autocannon that is typically mounted in the United States Air Force's Fairchild Republic A-10 Thunderbolt II. Designed specifically for the anti-tank role, the Avenger delivers very powerful rounds at a high rate of fire. The GAU-8/A is also used in the Goalkeeper CIWS ship weapon system, which provides defense against short-range threats such as highly maneuverable missiles, aircraft, and fast maneuvering surface vessels.

Jet fuel, aviation turbine fuel (ATF), or avtur, is a type of aviation fuel designed for use in aircraft powered by gas-turbine engines. It is colorless to straw-colored in appearance. The most commonly used fuels for commercial aviation are Jet A and Jet A-1, which are produced to a standardized international specification. The only other jet fuel commonly used in civilian turbine-engine powered aviation is Jet B, which is used for its enhanced cold-weather performance.

The light-gas gun is an apparatus for physics experiments, a highly specialized gun designed to generate very high velocities. It is usually used to study high-speed impact phenomena, such as the formation of impact craters by meteorites or the erosion of materials by micrometeoroids. Some basic materials research relies on projectile impact to create high pressure: such systems are capable of forcing liquid hydrogen into a metallic state.
The University of Tennessee Space Institute, also known as UTSI, is a satellite campus of the University of Tennessee located near Tullahoma, Tennessee.
Arnold Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located in Coffee and Franklin counties, Tennessee, adjacent to the city of Tullahoma. It is named for General Henry "Hap" Arnold, the father of the U.S. Air Force.
A chicken gun is a large-diameter, compressed-air cannon used to fire dead chickens at aircraft components in order to simulate high-speed bird strikes during the aircraft's flight. Jet engines and aircraft windshields are particularly vulnerable to damage from such strikes, and are the most common target in such tests. Whole, dead, standard-size chickens, as would be used for cooking, are thought to accurately simulate a large, live bird striking a plane in flight.
The Rheinmetall-Borsig MK 103 was a German 30 mm caliber autocannon that was mounted in German combat aircraft during World War II. Intended to be a dual purpose weapon for anti-tank and air-to-air fighting, it was developed from the MK 101. Compared to the MK 101 it was faster firing, and was originally intended to develop a higher muzzle velocity than the MK 101. Unlike the MK 101, the MK 103 used a belt feed, allowing it to potentially carry a larger ammunition load. The MK 103 used electrically-primed rather than percussion-primed ammunition. The operating mechanism differed from the recoil-operated MK 101 in that it used a combination of gas and recoil operation. After firing, gas pressure served to unlock the breech, while barrel recoil was used to cycle the action.

Armour-piercing fin-stabilized discarding sabot (APFSDS) is a type of kinetic energy penetrator ammunition used to attack modern vehicle armour. As an armament for main battle tanks, it succeeds armour-piercing discarding sabot (APDS) ammunition, which is still used in small or medium caliber weapon systems.

25 mm automatic air defense gun M1940 (72-K) was a Soviet 25 mm caliber anti-aircraft gun used during the Great Patriotic War. The gun was developed from the end of 1939 to the beginning of 1940 at 8th Kalinin Artillery Plant under the guidance of its Chief Designer Mikhail Loginov, supervised by Lev Loktev. The cannon was given the factory code 72-K before being accepted into service by the Red Army as the 25 mm automatic air defense gun M1940.

A steam cannon is a cannon that launches a projectile using only heat and water, or using a ready supply of high-pressure steam from a boiler. The first steam cannon was designed by Archimedes during the Siege of Syracuse. Leonardo Da Vinci was also known to have designed one.

A potato cannon is a pipe-based cannon which uses air pressure (pneumatic), or combustion of a flammable gas, to launch projectiles at high speeds. They are built to fire chunks of potato, as a hobby, or to fire other sorts of projectiles, for practical use. Projectiles or failing guns can be dangerous and result in life-threatening injuries, including cranial fractures, enucleation, and blindness if a person is hit.

A gun is a ranged weapon typically designed to pneumatically discharge projectiles that are solid but can also be liquid or even charged particles and may be free-flying or tethered.

AEDC Range G is a two-stage light-gas gun owned by the United States Air Force.
The High-Low system, also referred to as the "High-Low Pressure system", the "High-Low Propulsion System", and the "High-Low projection system", is a design of cannon and antitank launcher using a smaller high-pressure chamber for storing the propellant. It enables a much larger projectile to be launched without the heavy equipment typically required for large caliber weapons. When the propellant is ignited, the higher pressure gases are bled out through vents at reduced pressure to a much larger low pressure chamber to push the projectile forward. With the High-Low System a weapon can be designed with reduced or negligible recoil. The High-Low System also allows the weight of the weapon and its ammunition to be significantly reduced. Manufacturing cost and production time are drastically lower than for standard cannon or other small-arm weapon systems firing a projectile of the same size and weight. It has a far more efficient use of the propellant, unlike earlier recoilless weapons, where most of the propellant is expended to the rear of the weapon to counter the recoil of the projectile being fired.



















