
The Royal Society of Canada, also known as the Academies of Arts, Humanities, and Sciences of Canada, is the senior national, bilingual council of distinguished Canadian scholars, humanists, scientists, and artists. The primary objective of the RSC is to promote learning and research in the arts, the humanities, and the sciences. The RSC is Canada's national academy and exists to promote Canadian research and scholarly accomplishment in both official languages; to recognize academic and artistic excellence; and to advise governments, non-governmental organizations, and Canadians on matters of public interest.
The Arts and Humanities Citation Index (AHCI), also known as Arts and Humanities Search, is a citation index, with abstracting and indexing for more than 1,700 arts and humanities academic journals, and coverage of disciplines that includes social and natural science journals. Part of this database is derived from Current Contents.
The Arts and Humanities Research Council (AHRC), formerly Arts and Humanities Research Board (AHRB), is a British research council, established in 1998, supporting research and postgraduate study in the arts and humanities.
The Arts and Humanities Data Service (AHDS) was a United Kingdom national service aiding the discovery, creation and preservation of digital resources in and for research, teaching and learning in the arts and humanities. It was established in 1996 and ceased operation in 2008.
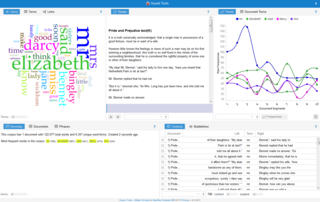
Digital humanities (DH) is an area of scholarly activity at the intersection of computing or digital technologies and the disciplines of the humanities. It includes the systematic use of digital resources in the humanities, as well as the analysis of their application. DH can be defined as new ways of doing scholarship that involve collaborative, transdisciplinary, and computationally engaged research, teaching, and publishing. It brings digital tools and methods to the study of the humanities with the recognition that the printed word is no longer the main medium for knowledge production and distribution.
Oxford Text Archive (OTA) is an archive of electronic texts and other literary and language resources which have been created, collected and distributed for the purpose of research into literary and linguistic topics at the University of Oxford, England.
Stephen Robert Dixon is a British actor and academic.
The Humanities Advanced Technology and Information Institute (HATII) was a research and teaching institute at the University of Glasgow in Scotland. It was established in 1997 with Professor Seamus Ross as Founding Director until 2009. HATII led research in archival and library science and in information/knowledge management. Research strengths were in the areas of humanities computing, digitisation, digital curation and preservation, and archives and records management.

Internet Archaeology is an academic journal and one of the first fully peer-reviewed electronic journals covering archaeology. It was established in 1996. The journal was part of the eLIb project's electronic journals. The journal is produced and hosted at the Department of Archaeology at the University of York and published by the Council for British Archaeology. The journal has won several awards for its creative exemplars of linked e-publications and archives.

The Institute of Museum and Library Services (IMLS) is an independent agency of the United States federal government established in 1996. It is the main source of federal support for libraries and museums within the United States, having the mission to "create strong libraries and museums that connect people with information and ideas." In fiscal year 2015, IMLS had a budget of $228 million. It is a sub-agency of the National Foundation on the Arts and the Humanities, along with the National Endowment for the Arts, the National Endowment for the Humanities, and the Federal Council on the Arts and the Humanities.

The Israel Exploration Journal is a biannual academic journal which has been published by the Israel Exploration Society since 1950. It primarily covers research in archaeology, but also history and geography relating to Israel and the surrounding areas. The editors-in-chief are Shmuel Ahituv, Amihai Mazar, and Z. Weiss. The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Arts & Humanities Citation Index and Current Contents/Arts & Humanities.

The Centre for Research in the Arts, Social Sciences and Humanities (CRASSH) is an interdisciplinary research centre within the University of Cambridge. Founded in 2001, CRASSH came into being as a way to create interdisciplinary dialogue across the University’s many faculties and departments in the arts, social sciences, and humanities, as well as to build bridges with scientific subjects. It has now grown into one of the largest humanities institutes in the world and is a major presence in academic life in the UK. It serves at once to draw together disciplinary perspectives in Cambridge and to disseminate new ideas to audiences across Europe and beyond.

The Department of Digital Humanities (DDH) is an academic department and research centre in the Faculty of Arts & Humanities at King's College London. DDH counts amongst the "most visible" digital humanities centres worldwide. Its research activities cover themes such as digital cultures, past and present; technology, media and participation; data worlds; digital economy and society; and digital epistemology and methods.
The Archaeology Data Service (ADS) is an open access digital archive for archaeological research outputs. It is located in The King's Manor, at the University of York. Originally intended to curate digital outputs from archaeological researchers based in the UK's Higher Education sector, the ADS also holds archive material created under the auspices of national and local government as well as in the commercial archaeology sector. The ADS carries out research, most of which focuses on resource discovery, cross-searching and interoperability with other relevant archives in the UK, Europe and the United States of America.

Music archaeology is an interdisciplinary field of study that combines musicology and archaeology. As it includes the study of music from various cultures, it is often considered to be a subfield of ethnomusicology.
The Oxford Journal of Archaeology is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal published by John Wiley & Sons on behalf of the School of Archaeology, University of Oxford. It was established in 1982 and the editors-in-chief are Nicholas Purcell, Barry Cunliffe, Helena Hamerow, and Chris Gosden.
Australian Archaeology is a peer-reviewed academic journal published by the Australian Archaeological Association. It was established in 1974 and covers all fields of archaeology as well as other subjects that are relevant to archaeological research and practice in Australia and nearby areas. The journal uses a broad definition of archaeology to include prehistoric, historic, and contemporary periods and includes social, biological, and cultural anthropology, history, Aboriginal studies, environmental science, and other related areas. As of December 2021 the editors are Sean Ulm and Annie Ross assisted by associate editor Ariana Lambrides and book review editor Mirani Litster.

Medieval Archaeology is an annual peer-reviewed academic journal covering the archaeology of the medieval period, especially in the United Kingdom and Ireland. It was established in 1957 by the Society for Medieval Archaeology and is published on their behalf by Taylor & Francis. The editor-in-chief is Aleks McClain.
Hella Eckardt is an archaeologist who specialises in Roman archaeology and material culture and a professor at the University of Reading. Since 2018 she has been the Editor of the journal Britannia.