
The Armed Forces of the Argentine Republic are the combined armed forces of Argentina. It is controlled by the Commander-in-Chief and a civilian Minister of Defense. In addition to the Army, Navy and Air Force, there are two security forces, controlled by the Ministry of Security, which can be mobilized on occasion of an armed conflict: the National Gendarmerie, a gendarmerie used to guard borders and places of strategic importance; and the Naval Prefecture, a coast guard used to protect internal major rivers and maritime territory.

The Argentine Air Force is the air force of Argentina and one of three branches of the Armed Forces of the Argentine Republic. In 2018, it had 13,837 military and 6,900 civilian personnel. FAA commander in chief is Brigadier Gustavo Valverde.

The AN/APG-79 is a type of active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar that was developed for use on the United States Navy's Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet and Boeing EA-18G Growler aircraft. The radar's AESA technology provides quick updates on multiple targets, and its solid-state antenna construction makes it more reliable and cost-effective than traditional radar systems. The radar has a range of up to 150 km and can track multiple targets simultaneously. It is capable of firing weapons such as the AIM-120 AMRAAM's D model and guiding multiple missiles to targets located at varying distances and directions. As of July 2008, 100 APG-79 sets had been delivered to the United States Navy, and the Navy expects to order around 437 production radars. In January 2013, the Director, Operational Test & Evaluation (DOT&E) disclosed some issues with the APG-79 radar during its initial operational testing, but upgrades have been made over time.

The AN/FPS-117 is an L-band active electronically scanned array (AESA) 3-dimensional air search radar first produced by GE Aerospace in 1980 and now part of Lockheed Martin. The system offers instrumented detection at ranges on the order of 200 to 250 nautical miles and has a wide variety of interference and clutter rejection systems.

The AN/TPS-43 is a transportable air search 3D radar produced in the United States originally by Westinghouse Electric Corporation's Defense and Electronic Division, which was later purchased by Northrop Grumman. It is used primarily for early warning and tactical control, often for control over an associated surface-to-air missile battery or airfield. It is designed to be transported in two M35 cargo trucks and easily air-transportable on two pallets.

The AN/TPS-75 is a transportable passive electronically scanned array air search 3D radar produced in the United States. It was originally designated the TPS-43E2. Although the antenna is a radically new design from the TPS-43, the radar van itself, which houses the transmitter, receiver processors, and displays is very similar to the older TPS-43E2. It is produced in the United States originally by Westinghouse Defense and Electronic Division, which was later purchased by Northrop Grumman.

The Bolivian Air Force is the air force of Bolivia and branch of the Bolivian Armed Forces.

The AN/FPS-4 Radar was a Height-Finder Radar used by the United States Air Force Air Defense Command.

The AN/TPS-1 Radar was an early warning and tactical control radar developed by Bell Labs and the MIT Radiation Laboratory during World War II. Initially used by the US Army, it was later used by the United States Air Force Air Defense Command, and a number of European armed forces. A number of variations were produced by several vendors, including Western Electric, Westinghouse Electric, Bendix Corporation and several European manufacturers in the post-war era. In Royal Air Force service it was known as AMES Type 61.

Canadian Forces Station Ramore is a closed General Surveillance Radar station. It is located 4 miles (6.4 km) east of Ramore, Ontario. It was closed in 1974. It was operated as part of the Pinetree Line network controlled by NORAD. It has since been sold and is now private property.

The AN/FPS-19 was a long-range search radar developed for the NORAD Distant Early Warning Line by Raytheon. It was an L-band system working between 1220 and 1350 MHz produced by a 500 kW magnetron. Two such systems were placed back-to-back, one with an antenna that produced a narrow beam to improve range for long-range detection, and the second with a wider fan-shaped beam to cover higher angles at shorter ranges. The former could detect bomber-sized targets to about 160 miles (260 km) and the latter covered up to 65,000 ft (20,000 m) altitude.

The AN/TPS-80 Ground/Air Task Oriented Radar (G/ATOR) is the United States Marine Corps next-generation Air Surveillance/Air Defense and Air Traffic Control (ATC) Radar. The mobile active electronically scanned array radar system is being developed by Northrop Grumman and was expected to reach initial operating capability in August 2016.

The Ground Master 400 (GM400) is a mobile long range radar system manufactured by Thales. GM400 is a fully digital active electronically scanned array long-range air defense 3D radar, offering detection from very high to very low altitudes. It tracks a wide range of targets from highly maneuverable tactical aircraft flying below several hundred feet to the unconventional small radar cross section devices, such as UAVs or cruise missiles.

TAFLIR is the abbreviation for the "Tactical Flight Radar" of the Swiss Air Force. TAFLIR is used to improve the Recognized Air Picture and to support air traffic control and air surveillance of the Swiss Air Force.

The Target allocation radar TPS-1E is an omnidirectional pulse radar device. It was used from 1958 until 1989 by the Swiss Air Force. It was also used by German army (Heer) air defence reconnaissance platoons up until the early 1990s.

AN/TPS-70 is a mobile rotating S band phased array 3D radar produced by Westinghouse. It can track 500 targets, displaying target range, height, azimuth, identification friend or foe (IFF) information from an altitude of 0 to 100,000 feet to a maximum range of 240 nautical miles. It is the successor of the AN/TPS-43. The TPS-70 tactical radar provides reliability, sensitivity, and accuracy, even in the face of jamming and high-clutter conditions. It is being replaced by newer systems, but is still in service all around the world.

Army/Navy Transportable Pulse-Radar Search-32 (AN/TPS-32) was a three-dimensional, tactical long-range surveillance radar operated by the United States Marine Corps from the early 1970s through the early 1990s. Developed by ITT Gilfillan in Van Nuys, California, the radar was the primary sensor for the Marine Corps' Tactical Air Operations Center (TAOC) and was optimized to work in concert with the MIM-23 Hawk Missile System and the Marine Tactical Data System.
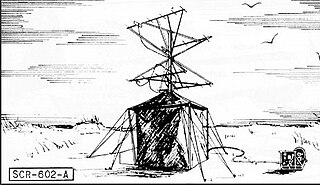
The SCR-602 also known as the AN/TPS-3, was a mobile, lightweight, medium-range, early-warning radar utilized by the United States and its allies during World War II. The radar was originally designed for use during the initial stages of an amphibious assault or military operation where its lightweight relative to other radar systems was a distinct advantage. Once larger radars such as the SCR-270 or AN/TPS-1 came online the SCR-602 could also be used to fill in gaps in radar coverage.

AN/SPS-6 is a two-dimensional radar manufactured by Bendix and Westinghouse Electric. It was used by the US Navy as a first-generation air-search radar after World War II, and was widely exported to allies. In addition, the improved AN/SPS-12 is the derivative types developed in other countries.

The AN/TPS-63 was a medium range, Two-dimensional, L band radar system utilized by the United States Marine Corps from the early 1980s until finally retired in 2018. This mobile radar was developed by Northrop Grumman and complimented the AN/TPS-59 long range radar by providing 360 degree, gap-filling coverage of low altitude areas. Because it was more mobile, the TPS-63 was also employed as the first radar ashore during amphibious operations until the larger and more capable AN/TPS-59 was established. The TPS-63 was used in combat operations during the Gulf War, the 2003 invasion of Iraq and subsequent operations in Iraq and Afghanistan. The TPS-63 was eventually phased out of service in 2018 as it was replaced by the AN/TPS-80 Ground/Air Task Oriented Radar.


















