This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
Medical psychology is the application of psychological principles to the practice of medicine, and is clearly comprehensive rather than primarily drug-oriented, for both physical and mental disorders. The specialty of Medical Psychology and the National Alliance of Professional Psychology Providers (www.nappp.org) has been instrumental in advocacy and professional publications in increasing the awareness of Governmental Agencies, Scientific Societies, and the World Health Associations about the limited effect of "medication only approaches" to mental disorders and many related chronic physical disorders. A Medical Psychologist is a specialist who holds board certification in Medical Psychology from the American Board of Medical Psychology (www.amphome.org) and approved by the national psychology practitioner association in psychology(www.nappp.org). A specialist in Medical Psychology holds a doctoral degree in one of the clinical specialties in psychology, has done post doctoral graduate or approved didactic training in biomedical and pharmaceutical sciences and physical disease with behavioral and lifestyle components, and has completed a supervised residency providing advanced clinical diagnoses, prescribing or collaborating on medication and psychological treatment interventions in a comprehensive treatment plan, and they have passed one of the acceptable national written examinations, and supplied reviewed work product, and passed an Oral Examination. Medical psychologists are prepared to provide leadership and active roles in primary care and specialty healthcare facilities or consultation services essential for these facilities. A psychopharmacologist is very different than a Medical Psychologist, though one state uses confusing language in its laws.

A physician, medical practitioner, medical doctor, or simply doctor is a professional who practises medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining, or restoring health through the study, diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of disease, injury, and other physical and mental impairments. Physicians may focus their practice on certain disease categories, types of patients and methods of treatment—known as specialities—or they may assume responsibility for the provision of continuing and comprehensive medical care to individuals, families, and communities—known as general practice. Medical practice properly requires both a detailed knowledge of the academic disciplines underlying diseases and their treatment—the science of medicine—and also a decent competence in its applied practice—the art or craft of medicine.
Osteopathy is a type of alternative medicine that emphasizes manual readjustments, myofascial release and other physical manipulation of muscle tissue and bones. Practitioners of osteopathy are referred to as osteopaths. Its name derives from Ancient Greek "bone" (ὀστέον) and "sensitive to" or "responding to" (-πάθεια).

Podiatry or podiatric medicine is a branch of medicine devoted to the study, diagnosis, and medical and surgical treatment of disorders of the foot, ankle and lower extremity. The term podiatry came into use in the early 20th century in the United States and is now used worldwide, including countries such as the United Kingdom and Australia.

The World Medical Association (WMA) is an international and independent confederation of free professional medical associations, therefore representing physicians worldwide. WMA was formally established on September 18, 1947 and has grown in 2018 to 113 national medical associations and more than 10 million physicians.
Apma is the language of central Pentecost island in Vanuatu. Apma is an Oceanic language. Within Vanuatu it sits between North Vanuatu and Central Vanuatu languages, and combines features of both groups.
Sowa was the original language of south-central Pentecost island in Vanuatu. In recent times it has been totally displaced by Apma, a neighbouring language. Sowa was closely related to Ske, another south Pentecost language.

David G. Armstrong is an American podiatric surgeon and researcher most widely known for his work in amputation prevention, the diabetic foot, and wound healing. He and his frequent collaborators, Lawrence A. Lavery and Andrew J.M. Boulton, have together produced many key works in the taxonomy, classification and treatment of the diabetic foot. He is Professor of Surgery director of the Southwestern Academic Limb Salvage Alliance (SALSA) at the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California and has produced more than 475 peer reviewed manuscripts and more than 80 book chapters.

Alpha Gamma Kappa is the oldest and largest professional fraternal organization for students and practitioners of podiatric medicine in the United States and Canada. The fraternity was founded in 1939 at the Dr. William M. Scholl College of Podiatric Medicine in Chicago, Illinois.
Ske is an endangered language of south-western Pentecost island in Vanuatu. Ske is an Oceanic language.

Avoiuli is a writing system used by the Turaga indigenous movement on Pentecost Island in Vanuatu. It was devised by Chief Viraleo Boborenvanua over a 14-year period, based on designs found in traditional sand drawings, and intended as a native alternative to the Latin alphabet. It is used mainly for writing in the area's native Raga language, although it can also be used for other languages including Apma, Bislama and English.

Melsisi is a large settlement and Catholic mission on the west coast of Pentecost Island, Vanuatu.
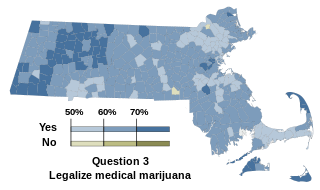
The Massachusetts Medical Marijuana Initiative, appeared as the third question on the state's 2012 ballot as an indirect initiated state statute. The measure allows cannabis to be used for medical purposes in the state. The initiative—backed by the American Civil Liberties Union, the Massachusetts Patient Advocacy Alliance, and the Committee for Compassionate Medicine—was filed with proponents turning in the required signatures to the Massachusetts Attorney General's office by the August 3, 2011 deadline. Those signatures were needed for the required ten qualified voters who submitted the original petition to put forward the full text of the law they want enacted. The initiative passed with support from 63% of state voters.
The Alternative Press Music Awards is an annual music awards show in the United States, founded by the music magazine Alternative Press.
Sindhi Americans are Americans or residents of the United States who are of Sindhi descent. They are a subgroup of Pakistani Americans and Indian Americans.







