Related Research Articles

The Very Large Telescope (VLT) is a facility operated by the European Southern Observatory, located on Cerro Paranal in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile. It consists of four individual telescopes, each equipped with a primary mirror that measures 8.2 meters in diameter. These optical telescopes, named Antu, Kueyen, Melipal, and Yepun, are generally used separately but can be combined to achieve a very high angular resolution. The VLT array is also complemented by four movable Auxiliary Telescopes (ATs) with 1.8-meter apertures.

Subaru Telescope is the 8.2-metre (320 in) telescope of the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, located at the Mauna Kea Observatory on Hawaii. It is named after the open star cluster known in English as the Pleiades. It had the largest monolithic primary mirror in the world from its commissioning until 2005.

The Large Binocular Telescope (LBT) is an optical telescope for astronomy located on 10,700-foot (3,300 m) Mount Graham, in the Pinaleno Mountains of southeastern Arizona, United States. It is a part of the Mount Graham International Observatory.

The W. M. Keck Observatory is an astronomical observatory with two telescopes at an elevation of 4,145 meters (13,600 ft) near the summit of Mauna Kea in the U.S. state of Hawaii. Both telescopes have 10 m (33 ft) aperture primary mirrors, and when completed in 1993 and 1996 were the largest optical reflecting telescopes in the world. They are currently the 3rd and 4th largest.
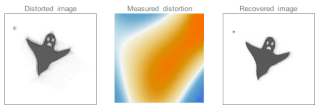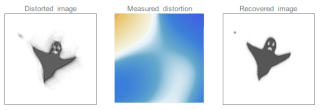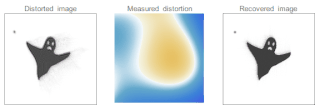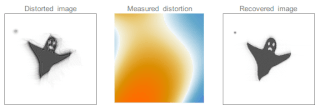
Adaptive optics (AO) is a technique of precisely deforming a mirror in order to compensate for light distortion. It is used in astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of atmospheric distortion, in microscopy, optical fabrication and in retinal imaging systems to reduce optical aberrations. Adaptive optics works by measuring the distortions in a wavefront and compensating for them with a device that corrects those errors such as a deformable mirror or a liquid crystal array.
In astronomy, a guide star is a reference star used to accurately maintain the tracking by a telescope of a celestial body, whose apparent motion through the sky is primarily due to Earth's rotation.

The Gemini Observatory comprises two 8.1-metre (26.6 ft) telescopes, Gemini North and Gemini South, situated in Hawaii and Chile, respectively. These twin telescopes offer extensive coverage of the northern and southern skies and rank among the most advanced optical/infrared telescopes available to astronomers. (See List of largest optical reflecting telescopes).

The New Technology Telescope or NTT is a 3.58-metre Ritchey–Chrétien telescope operated by the European Southern Observatory. It began operations in 1989. It is located in Chile at the La Silla Observatory and was an early pioneer in the use of active optics. The telescope and its enclosure were built to a revolutionary design for optimal image quality.

A laser guide star is an artificial star image created for use in astronomical adaptive optics systems, which are employed in large telescopes in order to correct atmospheric distortion of light. Adaptive optics (AO) systems require a wavefront reference source of light called a guide star. Natural stars can serve as point sources for this purpose, but sufficiently bright stars are not available in all parts of the sky, which greatly limits the usefulness of natural guide star adaptive optics. Instead, one can create an artificial guide star by shining a laser into the atmosphere. Light from the beam is reflected by components in the upper atmosphere back into the telescope. This star can be positioned anywhere the telescope desires to point, opening up much greater amounts of the sky to adaptive optics.

The William Herschel Telescope (WHT) is a 4.20-metre (165 in) optical/near-infrared reflecting telescope located at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on the island of La Palma in the Canary Islands, Spain. The telescope, which is named after William Herschel, the discoverer of the planet Uranus, is part of the Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes. It is funded by research councils from the United Kingdom, the Netherlands and Spain.

The Giant Magellan Telescope is a 25.4-meter, ground-based, extremely large telescope under construction at Las Campanas Observatory in Chile's Atacama Desert. Commissioning is anticipated in the late 2020s. Once complete, the Giant Magellan will be the largest Gregorian telescope ever built observing in optical and mid-infrared light. The telescope uses seven of the world’s largest mirrors to form a light collecting area of 368 square meters.

The Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) is an astronomical observatory under construction. When completed, it will be the world's largest optical/near-infrared extremely large telescope. Part of the European Southern Observatory (ESO) agency, it is located on top of Cerro Armazones in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile.
David L. Fried was an American scientist, best known for his contributions to optics. Fried described what has come to be known as the Fried Parameter, or r0. The Fried Parameter is a measure of the strength of the turbulence in the atmosphere of Earth. The turbulence causes what is known as seeing in astronomy and usually limits the optical resolution of ground-based telescopes and the detail in their images of astronomical objects. The Fried Parameter describes the smallest diameter of a telescope aperture at which the image fidelity starts to suffer significantly from turbulent airflows in the atmosphere of Earth. The Fried Parameter may change quickly on the time scale of minutes, or less. Typical values for the Fried Parameter in the visible spectrum may range from less than one centimeter to some tens of centimeters at good astronomical sites.

The C. Donald Shane telescope is a 120-inch (3.05-meter) reflecting telescope located at the Lick Observatory in San Jose, California. It was named after astronomer C. Donald Shane in 1978, who led the effort to acquire the necessary funds from the California Legislature, and who then oversaw the telescope's construction. It is the largest and most powerful telescope at the Lick Observatory, and was the second-largest optical telescope in the world when it was commissioned in 1959.

Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam (AIP) is a German research institute. It is the successor of the Berlin Observatory founded in 1700 and of the Astrophysical Observatory Potsdam (AOP) founded in 1874. The latter was the world's first observatory to emphasize explicitly the research area of astrophysics. The AIP was founded in 1992, in a re-structuring following the German reunification.

Claire Ellen Max is a Professor of Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC) and is affiliated with the Lick Observatory. She was the Director of the Center for Adaptive Optics at UCSC, 2007-2014. Max received the E.O. Lawrence Award in Physics.
OSIRIS is an integral field spectrograph for the Keck I telescope in Hawaii. As an integral field spectrograph, it can obtain many spectra simultaneously covering a small region of the sky. As such, it combines the capabilities of a traditional spectrograph and a regular imaging camera. The 'OH suppressing' portion of the name refers to the fact that OSIRIS has sufficient spectral resolution that sky glow from OH molecules can be separated and removed from the spectra of the science targets. OSIRIS covers an infrared bandpass from 1 to 2.5 micrometers with a spectral resolution of about 3800. Combined with the Keck laser guide star adaptive optics system, it can obtain diffraction-limited observations on extremely faint targets. OSIRIS was developed by the UCLA Infrared Laboratory under professor James Larkin. OSIRIS achieved first light on February 22, 2005, on the Keck II telescope. OSIRIS was moved to Keck I in January, 2012.
ALPAO is a company which manufactures a range of adaptive optics products for use in research and industry, including deformable mirrors with large strokes, wavefront sensors, and adaptive optics loops. These products are designed for astronomy, vision science, microscopy, wireless optical communications, and laser applications.

The Goode Solar Telescope (GST) is a scientific facility for studies of the Sun named after Philip R. Goode. It was the solar telescope with the world's largest aperture in operation for more than a decade. Located in Big Bear Lake; California, the Goode Solar Telescope is the main telescope of the Big Bear Solar Observatory operated by the New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT). Initially named New Solar Telescope (NST), first engineering light was obtained in December 2008, and scientific observations of the Sun began in January 2009. On July 17, 2017, the NST was renamed in honor of Goode, a former, and founding director of NJIT's Center for Solar-Terrestrial Research and the principal investigator of the facility. Goode conceived, raised the funds, and assembled the team that built and commissioned the telescope, and it was the highest resolution solar telescope in the world (until the end of 2019) and the first facility class solar telescope built in the U.S. in a generation.

Céline d'Orgeville is a Professor and instrument scientist at the Australian National University Research School of Astronomy and Astrophysics. She leads teams designing laser and optical systems for ground based astronomical telescopes. She is a Fellow of SPIE and the Astronomical Society of Australia.
References
- ↑ "ARGOS (Advanced Rayleigh guided Ground layer adaptive Optics System)". Archived from the original on 2 November 2013. Retrieved 16 June 2012.
- ↑ "MPE: Projects (ARGOS)". Archived from the original on 2012-05-27. Retrieved 16 June 2012.
- ↑ "ARGOS-The laser guide star for the LBT" . Retrieved 2 May 2017.
- ↑ "LUCIFER - A Near-Infrared Camera and Spectrograph for the LBT" . Retrieved 2 May 2017.