Related Research Articles

A land mine is an explosive device concealed under or on the ground and designed to destroy or disable enemy targets, ranging from combatants to vehicles and tanks, as they pass over or near it. Such a device is typically detonated automatically by way of pressure when a target steps on it or drives over it, although other detonation mechanisms are also sometimes used. A land mine may cause damage by direct blast effect, by fragments that are thrown by the blast, or by both.

A shaped charge is an explosive charge shaped to focus the effect of the explosive's energy. Different types of shaped charges are used for various purposes such as cutting and forming metal, initiating nuclear weapons, penetrating armor, or perforating wells in the oil and gas industry.

Reactive armour is a type of vehicle armour that reacts in some way to the impact of a weapon to reduce the damage done to the vehicle being protected. It is most effective in protecting against shaped charges and specially hardened kinetic energy penetrators. The most common type is explosive reactive armour (ERA), but variants include self-limiting explosive reactive armour (SLERA), non-energetic reactive armour (NERA), non-explosive reactive armour (NxRA), and electric armour. NERA and NxRA modules can withstand multiple hits, unlike ERA and SLERA, but a second hit in exactly the same location may potentially penetrate any of those, as the armour in that spot is compromised.

Armor-piercing ammunition (AP) is a type of projectile designed to penetrate either body armor or vehicle armor.

High-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) is a type of shaped charge explosive that uses the Munroe effect to penetrate heavy armour. The warhead functions by having an explosive charge collapse a metal liner inside the warhead into a high-velocity superplastic jet; this superplastic jet is capable of penetrating armour steel to a depth of seven or more times the diameter of the charge. The jet's effect is purely kinetic in nature; the round has no explosive or incendiary effect on the target.
A tandem-charge or dual-charge weapon is an explosive device or projectile that has two or more stages of detonation.

USS Bluefish (SSN-675), a Sturgeon-class attack submarine, was the second ship of the United States Navy to be named for the bluefish.

An anti-tank mine is a type of land mine designed to damage or destroy vehicles including tanks and armored fighting vehicles.

Armor with two or more plates spaced a distance apart falls under the category of spaced armour. Spaced armour can be sloped or unsloped. When sloped, it reduces the penetrating power of bullets and solid shot, as after penetrating each plate projectiles tend to tumble, deflect, deform, or disintegrate; spaced armor that is not sloped is generally designed to provide protection from explosive projectiles, which detonate before reaching the primary armor. Spaced armour is used on armoured military vehicles such as tanks and combat bulldozers. In a less common application, it is used in some spacecraft that use Whipple shields.
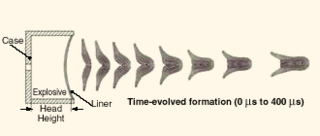
An explosively formed penetrator (EFP), also known as an explosively formed projectile, a self-forging warhead, or a self-forging fragment, is a special type of shaped charge designed to penetrate armor effectively. As the name suggests, the effect of the explosive charge is to deform a metal plate into a slug or rod shape and accelerate it toward a target. They were first developed as oil well perforators by American oil companies in the 1930s, and were deployed as weapons in World War II.

Anti-personnel mines are a form of mine designed for use against humans, as opposed to anti-tank mines, which are designed for use against vehicles. Anti-personnel mines may be classified into blast mines or fragmentation mines; the latter may or may not be a bounding mine.
The RBS 56B BILL 2 Anti-Tank Guided Weapon is a man-portable or vehicle-mounted guided anti-tank missile using the overfly top attack method to attack the weaker parts of an armoured vehicle. BILL is acronym for Bofors Infantry Light & Lethal.
The ATM-6 and ATM-7 are Austrian off-route anti-tank mines that use Misznay Schardin effect warheads to fire self forging fragments into the sides of armoured vehicles. Both mines are mounted on a pedestal base which is used to aim the mine, and have simple sights to aim the mines. The mines originally could be triggered by a variety of means, including contact wire and infra-red fuses, however as a result of Austrian laws, they now only use command detonation.

The FFV 028 is a series of steel cased Swedish anti-tank mines that use electronic fuzes. The mines are circular, with a large Misznay Schardin effect warhead in the center of the mine, with the fuzing and sensor electronics located in the dead space above the main charge. The design of the mine dates from the 1970s and uses a magnetic influence sensor to detonate the mine, making it able to attack the full width of armoured vehicles.
The HAK-1 is a Hungarian plastic encased anti-tank mine. It uses a Misznay Schardin effect warhead combined with an electronic acoustic and magnetic influence fuze. The mine can be programmed for an active life of between three hours and 150 days. Once the acoustic sensor detects a target, the magnetic influence sensor is used to detonate the mine at the optimal point. The warhead is capable of penetrating 45 mm of armour and producing a 130 mm diameter hole.
The VS-HCT series of mines are Italian plastic cased anti-tank mines that use Misznay Schardin effect warheads and have a dual seismic and magnetic fuze. The mines are no longer produced and differ in size and shape.

The HPD-1, HPD-2 and HPD-3 are a series of French electrically fuzed anti-tank landmines that use Misznay Schardin effect warheads. The entire series of mines conform to the United States MIL-STD-331.
The T-93 is an Egyptian scatterable anti-tank mine similar in appearance to the German AT-2 scatterable mine. It can be dispensed from launchers deployed on the ground or mounted on vehicles which can hold as many as 600 mines. The mine is cylindrical with twelve spring-loaded legs folded up against the sides of its body during storage. After the mine is dispensed and strikes the ground, the legs spring open, pointing the mine upright.
Man-portable anti-tank systems are shoulder-launched anti-tank rockets. They are typically unguided weapons and are a threat to armored vehicles, low-flying aircraft, and field fortifications. Generally, MANPATS fall into three distinct categories. The first consist of a small, disposable preloaded launch tube firing a high explosive anti-tank warhead operated by a single soldier. The second is a firing system onto/into which a rocket is loaded, operated by a single soldier. The third are manufactured prepacked and issued as a single unit of ammunition with the launcher discarded after a single use.
The FT5 is a shoulder-launched, unguided and portable anti-tank rocket weapon. The weapon was built in South Africa by Somchem, a division of Denel based in Somerset West, now Rheinmetall Denel Munition. The weapon was designed with the primary function to provide soldiers with a weapon capable of destroying armoured fighting vehicles and modern main battle tanks. The weapon also had a secondary function of destroying bunkers and other fortifications.
References
- Jane's Mines and Mine Clearance 2005-2006.